463
Computing the Cycle Time Section 10-4
Peripheral Servicing Cycle
Time
The peripheral servicing cycle time depends on the same conditions as Paral-
lel Processing with Asynchronous Memory Access.
The peripheral servicing cycle time is the total time required for the PLC to
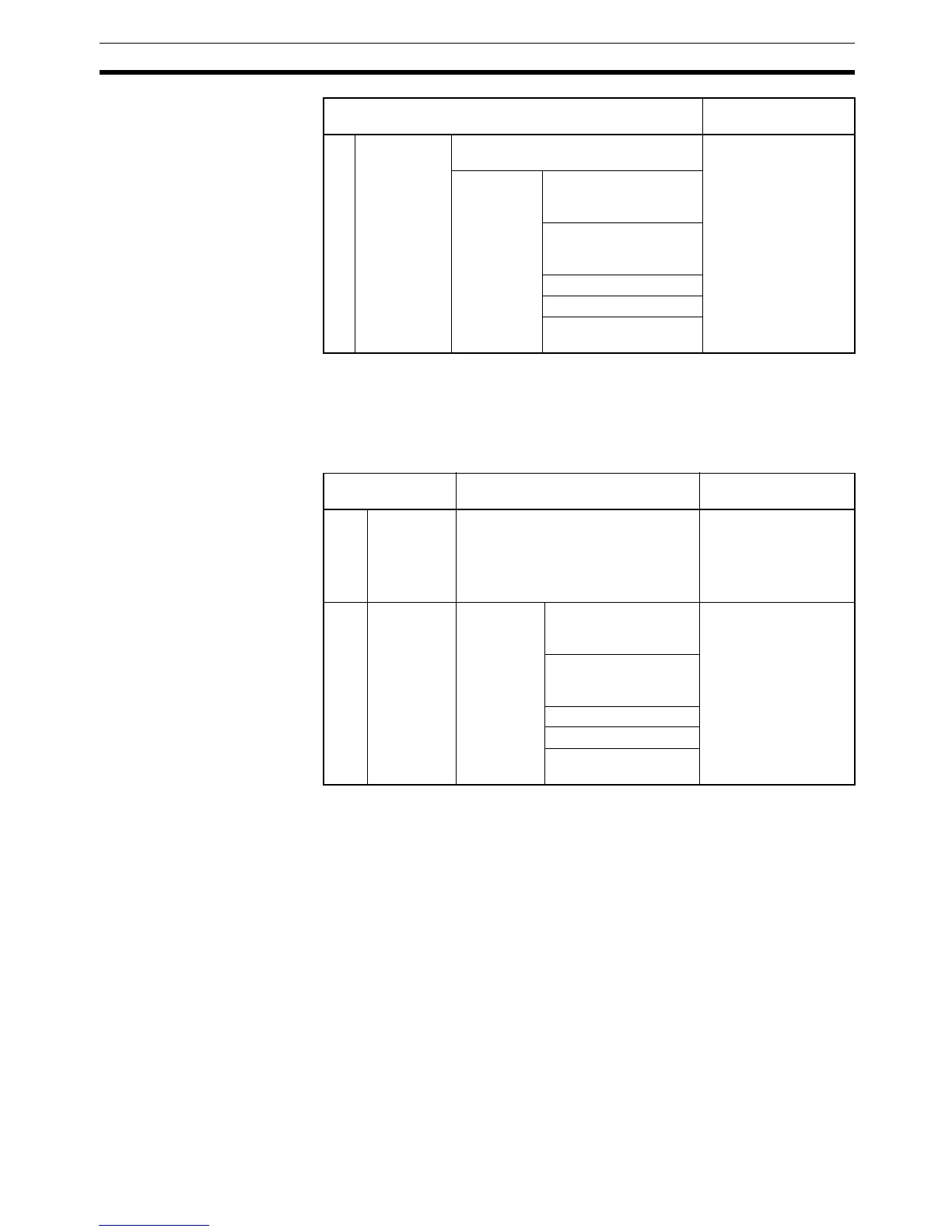
perform the five operations shown in the following tables.
Cycle time = (1) + (2)
Note 1. The cycle time display on a Programming Device is the Program Execution
Cycle Time.
2. The peripheral service cycle time varies with the event load and number of
Units that are mounted. In a Parallel Processing Mode, however, this vari-
ation will not affect the program execution cycle time.
(5) Partial
peripheral
servicing
Servicing file access (Memory Card or
EM file memory)
Same as for Normal
Mode.
Performs
services for
the events
give at the
right that
requires I/O
memory
access
Events with Special I/O
Units (does not include
I/O refreshing)
Events with CPU Bus
Units (does not include
I/O refreshing)
Peripheral port events
RS-232C port events
Events using communi-
cations ports
Details Processing time and
fluctuation cause
Name Processing Processing time and
fluctuation cause
(1) Overseeing
processing
Checks user program memory,
checks for battery errors, etc.
• CJ1H-CPU
@@H-R:
0.18 ms
• CJ1@-CPU
@@H/
CJ1G-CPU
@@P:
0.2 ms
(2) Peripheral
servicing
Performs
services for
the events
give at the
right,
excluding
those that
require I/O
memory
access.
Events with Special I/O
Units (does not include
I/O refreshing)
1.0 ms for each type of
service
If servicing ends before
1 ms has expired, the
next type of servicing
will be started immedi-
ately without waiting.
Events with CPU Bus
Units (does not include
I/O refreshing)
Peripheral port events
RS-232C port events
Events using communi-
cations ports

 Loading...
Loading...