178
Controlling Bit Status Section 4-4
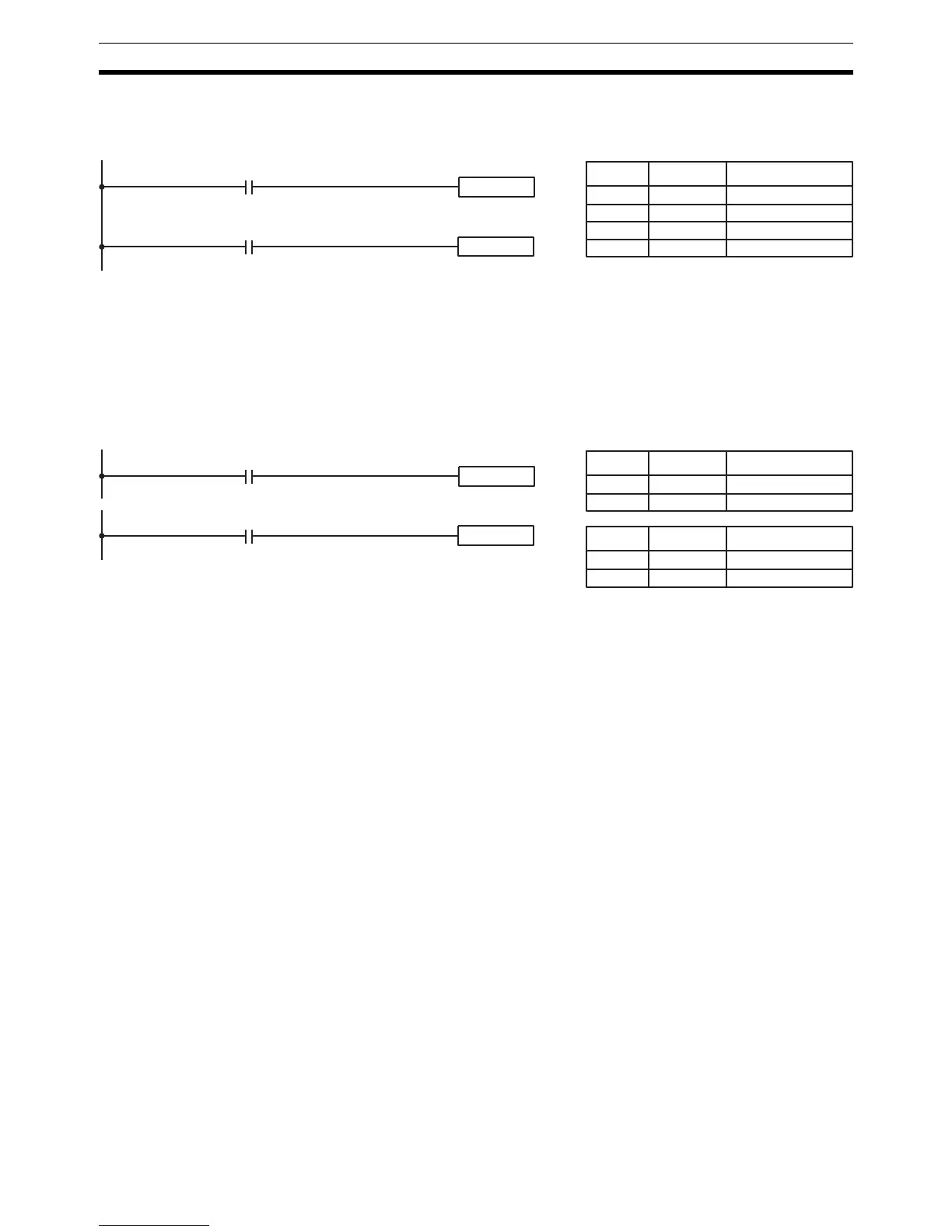
In the following example, IR 10000 will be turned ON when IR 00100 goes ON
and will remain ON until IR 00101 goes ON, regardless of the status of IR
00100. When IR 00101 goes ON, RESET will turn IR 10000 OFF.
4-4-2 DIFFERENTIATE UP and DIFFERENTIATE DOWN
DIFFERENTIATE UP and DIFFERENTIATE DOWN instructions are used to
turn the operand bit ON for one cycle at a time. The DIFFERENTIATE UP
instruction turns ON the operand bit for one cycle after the execution condition
for it goes from OFF to ON; the DIFFERENTIATE DOWN instruction turns ON
the operand bit for one cycle after the execution condition for it goes from ON
to OFF. Both of these instructions require only one line of mnemonic code.
Here, IR 01000 will be turned ON for one cycle after IR 00000 goes ON. The
next time DIFU(13) 01000 is executed, IR 01000 will be turned OFF, regard-
less of the status of IR 00000. With the DIFFERENTIATE DOWN instruction,
IR 01001 will be turned ON for one cycle after IR 00001 goes OFF (IR 01001
will be kept OFF until then), and will be turned OFF the next time DIFD(14)
01001 is executed.
4-4-3 KEEP
The KEEP instruction is used to maintain the status of the operand bit based
on two execution conditions. To do this, the KEEP instruction is connected to
two instruction lines. When the execution condition at the end of the first
instruction line is ON, the operand bit of the KEEP instruction is turned ON.
When the execution condition at the end of the second instruction line is ON,
the operand bit of the KEEP instruction is turned OFF. The operand bit for the
KEEP instruction will maintain its ON or OFF status even if it is located in an
interlocked section of the diagram.
00100
00101
SET 10000
RSET 10000
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00100
00001 SET 10000
00002 LD 00101
00003 RSET 10000
00000
00001
DIFU(13) 01000
DIFD(14) 01001
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 DIFU(13) 01000
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00001
00001 DIFD(14) 01001

 Loading...
Loading...