243
Data Movement Instructions Section 5-17
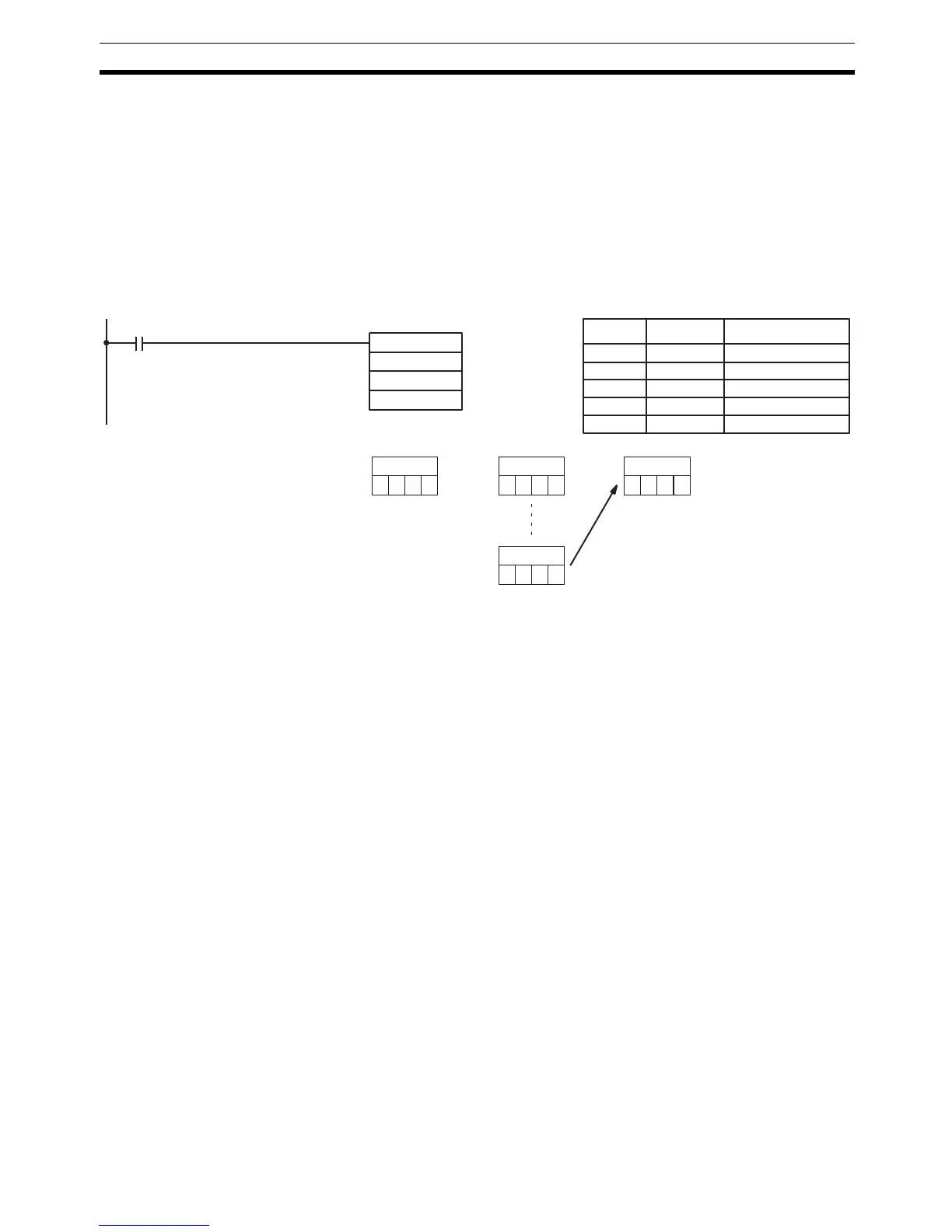
Data Collection When bits 12 to 15 of C=0 to 7, COLL(81) is used for data collection. The
entire contents of C specifies an offset, Of.
When the execution condition is OFF, COLL(81) is not executed. When the
execution condition is ON, COLL(81) copies the content of SBs + Of to D, i.e.,
Of is added to SBs to determine the source word.
Note SBs and SBs+Of must be in the same data area.
Example
The following example shows how to use COLL(81) to copy the content of
DM 0000+Of to IR 001. The content of 010 is #0005, so the content of
DM 0005 (DM 0000 + 5) is copied to IR 001 when IR 00001 is ON.
FIFO Stack Operation When bits 12 to 15 of C=9, COLL(81) can be used for an FIFO stack opera-
tion. The other 3 digits of C specify the number of words in the stack (000 to
999). The content of SBs is the stack pointer.
When the execution condition is ON, COLL(81) shifts the contents of each
word within the stack down by one address, finally shifting the data from
SBs+1 (the first value written to the stack) to the destination word (D). The
content of the stack pointer (SBs) is then decremented by one.
Note COLL(81) will be executed every cycle unless the differentiated form
(@COLL(81)) is used or COLL(81) is used with DIFU(13) or DIFD(14).
Example
The following example shows how to use COLL(81) to create a stack between
DM 0001 and DM 0005. DM 0000 acts as the stack pointer.
When IR 00000 goes from OFF to ON, COLL(81) shifts the contents of DM
0002 to DM 0005 down by one address, and shifts the data from DM 0001 to
@COLL(81)
DM 0000
010
001
00001
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00001
00001 @DIST(80)
DM 0000
010
001
F
001
0 0 F0
DM 0000
0 0 0
F
DM 0005
0 0 F
5
010
0 0 0

 Loading...
Loading...