The voltage drop depends on the cable length and the conductor's
cross section.
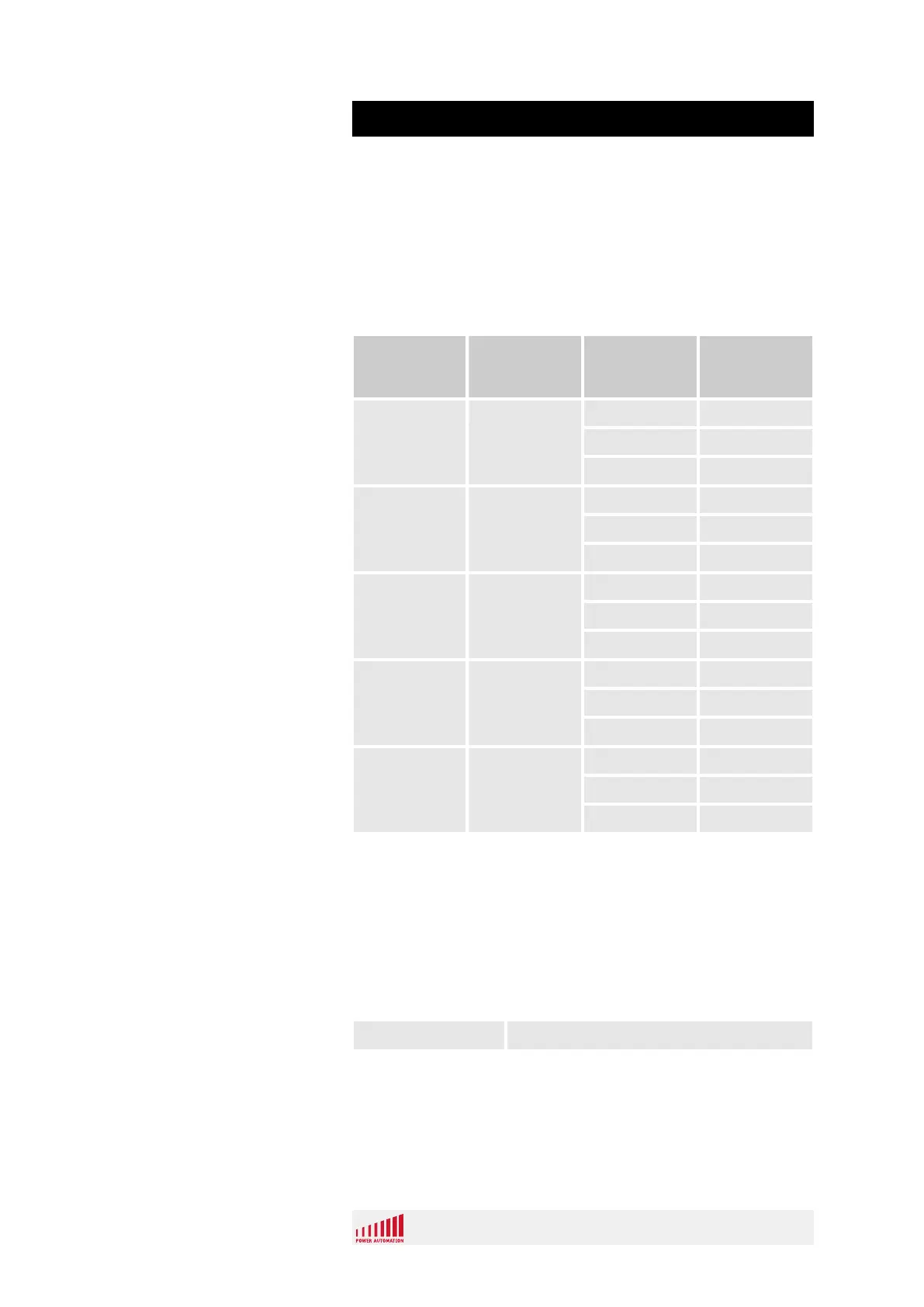
The following table shows some cable examples. The values are
typical and only offered as guidelines.
n For proper compensation, calculate the actual values as shown
in the following section.
Conductor
cross section
[mm
2
]/[AWG]
Specific
resistance
[Ω/m]
Cable length
[m]
Voltage drop
at 100 mA [V]
0.08 / AWG 28 0.235 10 0.47
20 0.94
35 1.65
0.14 / AWG 25 0.131 10 0.26
20 0.52
35 0.92
0.25 / AWG 23 0.075 10 0.15
20 0.30
35 0.53
0.5 / AWG 20 0.040 10 0.08
20 0.16
35 0.28
0.75 / AWG 18 0.025 10 0.05
20 0.10
35 0.18
n Use the actual data obtained from the cable's technical
specifications.
n Double the cable's physical length.
This is necessary as there are two lines: one line to the
RMS (+5 V) and one line from the RMS (grounding).
n Calculate the voltage drop as follows:
Voltage drop [V] = 2 x L x C
R
x P
C
L - Cable length [m]
C - C
R
Specific resistance per meter [Ω/m]
P - P
C
Power consumption [A]
Examples
Calculation
PA 8000 PAMIO
PAMIO Components
12.01.2017 | 104

 Loading...
Loading...