Enhanced Level Commands
4.10 Macroprograms
04.07
4-155
© Siemens AG 2007 All rights reserved
SINUMERIK 802D sl/840D/840D sl/840Di/840Di sl/810D ISO Milling (PGM) -- 04.07 Edition
Simple call up (G65)
Format
G65P_L_;
Byspecifying“G65P ···L··· <argumentspecification>;”,themacroprogram
which is assigned the program number specified with P is called up and executed L
times.
If it is necessary to pass arguments to the called up macroprogram, these argu-
ments can be specified in this block.
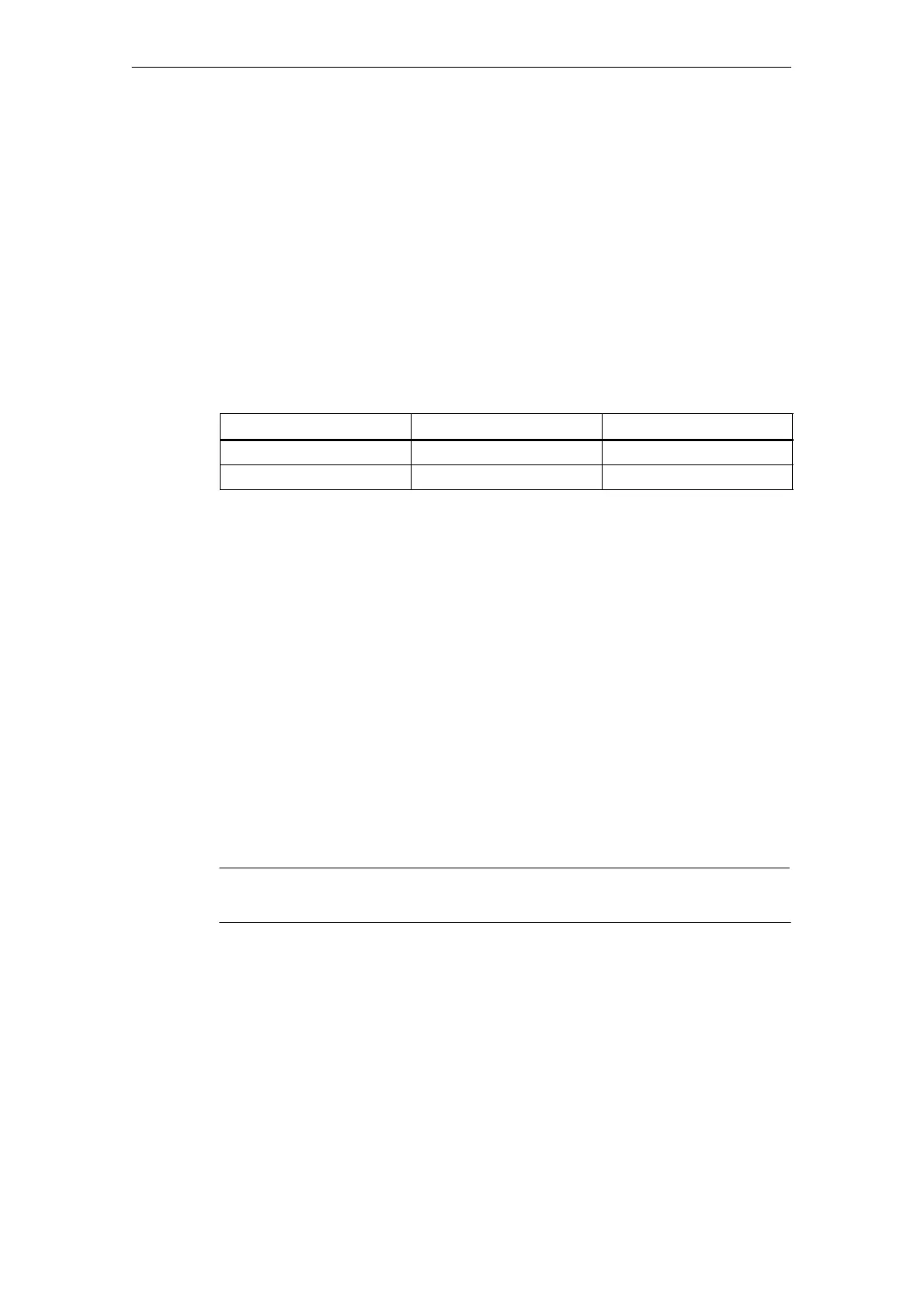
Table 4-8 P and L commands
Address
Description Number of digits
P Program number 5 digits
L Number of repetitions 9 digits
System variables for the addresses I, J, K
Because addresses I, J, and K can be programmed up to ten times in a block by
macro call, an array index must be used to access the system variables for these
addresses. The syntax for these three system variables is then $C_I[..], $C_J[..],
$C_K[..]. The values are stored in the array in the order programmed. The number
of addresses I, J, K programmed in the block is stored in variables $C_I_NUM,
$C_J_NUM, $C_K_NUM.
The passed parameters I, J, K for macro calls are treated as one block, even if
individual addresses a re not programmed. If a parameter is programmed again or a
following parameter has been programmed with reference to the sequence I, J, K,
it belongs to the next block.
To recognize the programming sequence in ISO mode, system variables
$C_I_ORDER, $C_J_ORDER, $C_K_ORDER are set. These are identical arrays
to $C_I, $C_K and contain the associated number of parameters.
Note
The transfer parameters can only be read in the subroutine.
Example:
N5 I10 J10 K30 J22 K55 I44 K33
set1 set2 set3
$C_I_NUM=2
$C_I[0]=10
$C_I[1]=44
$C_I_ORDER[0]=1

 Loading...
Loading...

















