The articulated joint positions required for machining are selected by programming bit 0 ... 2 of
the adjustable STAT address:
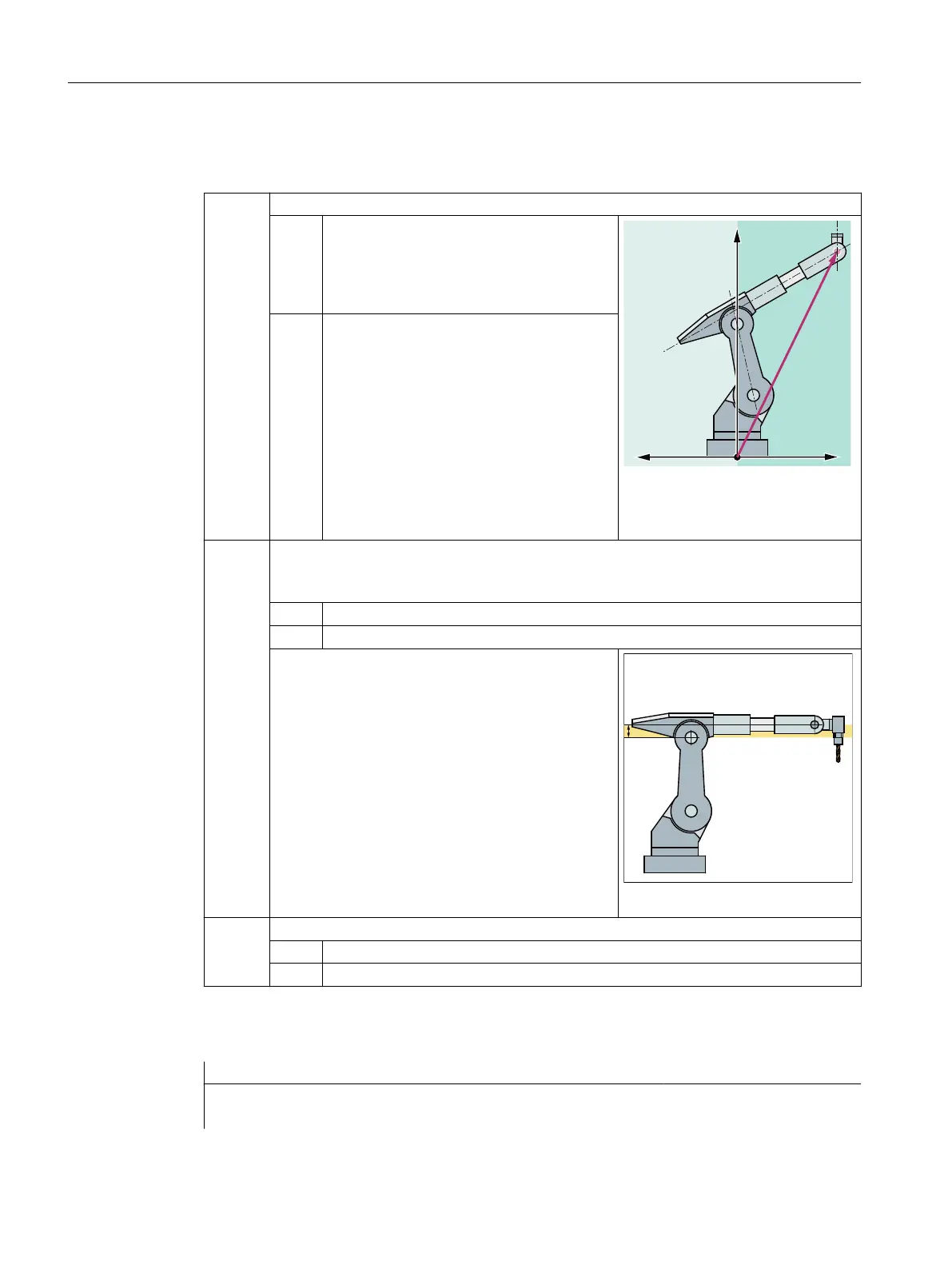
Bit 0 Position of the intersection points of the hand/wrist axes (A4, A5, A6)
= 0 Basic range (shoulder right)
The robot is in the basic range if the X value
of the intersection point of the hand/wrist ax‐
es is positive in relation to to the A1 coordi‐
nate system.
Example: The intersection point of
the hand/wrist axes lies in the basic
range
= 1 Overhead range (shoulder left)
The robot is in the overhead range if the X
value of the intersection point of the hand/
wrist axes is negative in relation to the A1
coordinate system.
Bit 1 Position of axis 3
The angle at which the value of bit 1 changes depends on the particular robot type. The
following applies to robots whose axes 3 and 4 intersect:
= 0 A3 <0° (elbow down)
= 1 A3 ≥0° (elbow up)
Note:
For robots with an offset between axes 3 and 4, the
angle at which the value of bit 1 changes depends on
the magnitude of this offset.
Offset between A3 and A4
Bit 2 Position of axis 5
= 0 A5 ≥0° (no handflip)
= 1 A5 <0° (handflip)
Program example:
Program code Comment
...
N14 T="T8MILLD20" D1 ; $TC_DP3[1,1]=132.95
Work preparation
3.9 Transformations
NC programming
710 Programming Manual, 12/2019, 6FC5398-2EP40-0BA0

 Loading...
Loading...



















