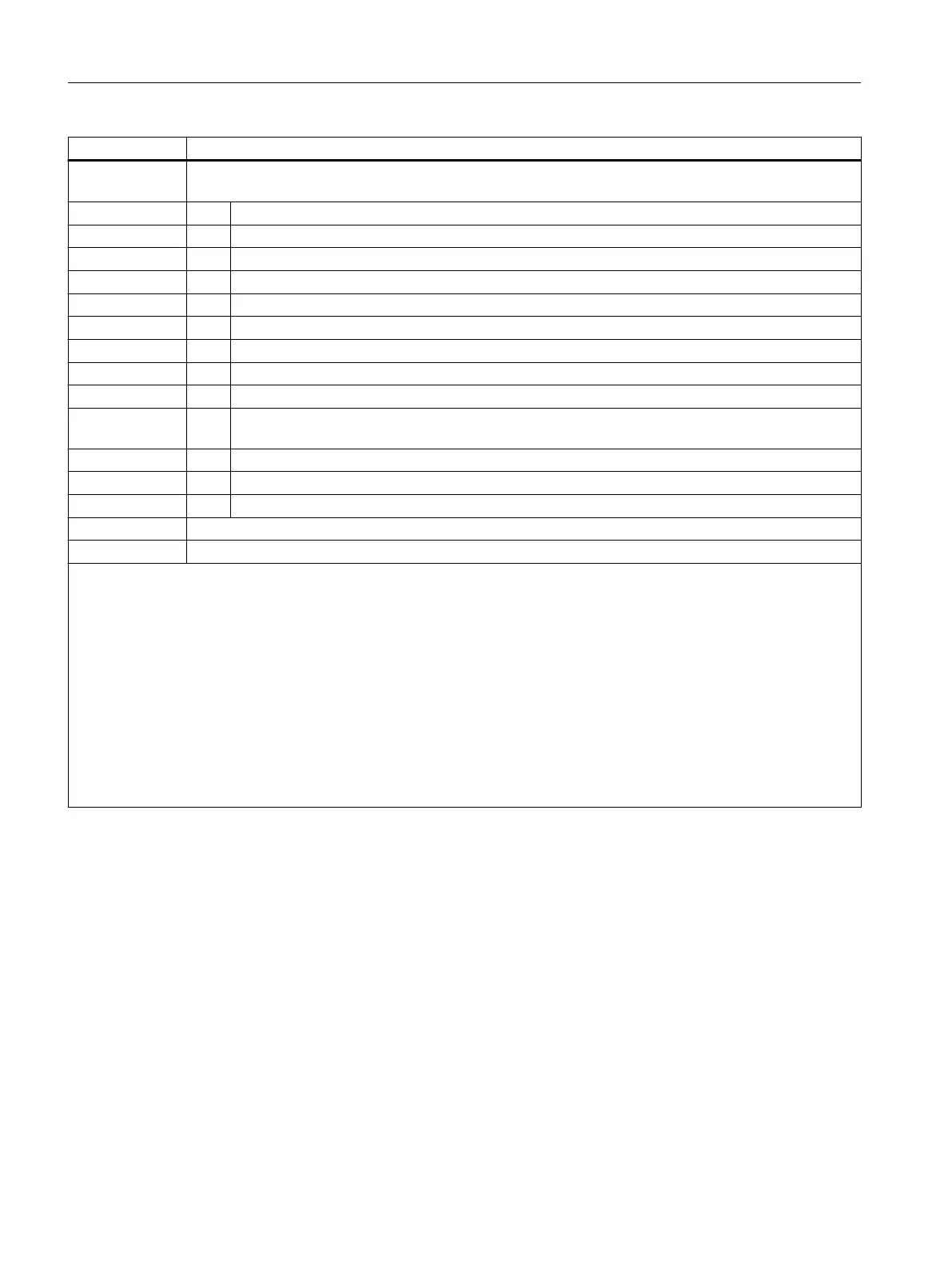
Return value Meaning
2xx The 'name' string is a programmable element of the NC programming language (option/function is active).
The detailed information xx contains additional information about the element type:
xx Meaning
01 DIN address or NC address
2)
02 G command (e.g. G04, INVCW)
03 Function with return value
04 Function without return value
05 Keyword, e.g. DEFINE
06 Machine ($M...), setting ($S...) or option data ($O...)
07 System parameters, e.g. system variable ($...) or arithmetic parameter (R...)
08 Cycle (the cycle must be loaded into the NC and the cycle program must be active
3)
)
09 GUD variable (the GUD variable must be defined in the GUD definition files and the GUD variables
activated)
10 Macro name (the macro must be defined in the macro definition files and macros activated)
4)
11 LUD variable of the actual part program
12 ISO G command (ISO language mode must be active)
400 The 'name' string is an NC address, that was not identified as xx == 01 or xx == 10 and is not G or R
2)
y00 No specific assignment possible
1) Depending on the control, under certain circumstances, only a subset of the Siemens NC language commands are known,
e.g. SINUMERIK 802D sl. For these controls, for strings that are principally Siemens NC language commands, a value of 0
is returned. This behavior can be changed using MD10711 $MN_NC_LANGUAGE_CONFIGURATION. For MD10711 = 1,
then a value of 100 is always returned for Siemens NC language commands.
2) NC addresses are the following letters: A, B, C, E, I, J, K, Q, U, V, W, X, Y, Z. These NC addresses can also be programmed
with an address extension. The address extension can be specified when checking with STRINGIS. Example: 201 ==
STRINGIS("A1").
The letters: D, F, H, L, M, N, O, P, S, T are NC addresses or auxiliary functions that are defined by the user. A value of 400
is always returned for these. Example: 400 == STRINGIS( "D" ). These NC addresses cannot be specified with address
extension when checking with STRINGIS.
Example: 000 == STRINGIS("M02"), but 400 == STRINGIS("M").
3) Names of cycle parameters cannot be checked with STRINGIS.
4) Address, defined as macro, e.g. G, H, M, L are identified as macro.
Examples
In the following examples it is assumed that the NC language elements specified as string - as
long as nothing else is noted - can in principle be programmed in the control.
1. String "T" is defined as auxiliary function:
400 == STRINGIS("T")
000 == STRINGIS ("T3")
2. String "X" is defined as axis:
201 == STRINGIS("X")
201 == STRINGIS("X1")
3. String "A2" is defined as address with extension:
201 == STRINGIS("A")
201 == STRINGIS("A2")
4. String "INVCW" is defined as named G command:
202 == STRINGIS("INVCW")
Work preparation
3.23 Additional functions
NC programming
990 Programming Manual, 12/2019, 6FC5398-2EP40-0BA0

 Loading...
Loading...



















