Chapter 4 Deployment of the CPU 21x-2BT10 with TCP/IP Manual VIPA CPU 21x
4-2 HB103E - Rev. 05/45
Industrial Ethernet in automation
The flow of information in a company presents a vast spectrum of
requirements that must be met by the communication systems. Depending
on the area of business the bus system or LAN must support a different
number of users, different volumes of data must be transferred and the
intervals between transfers may vary, etc.
It is for this reason that different bus systems are employed depending on
the respective task. These may be subdivided into different classes. The
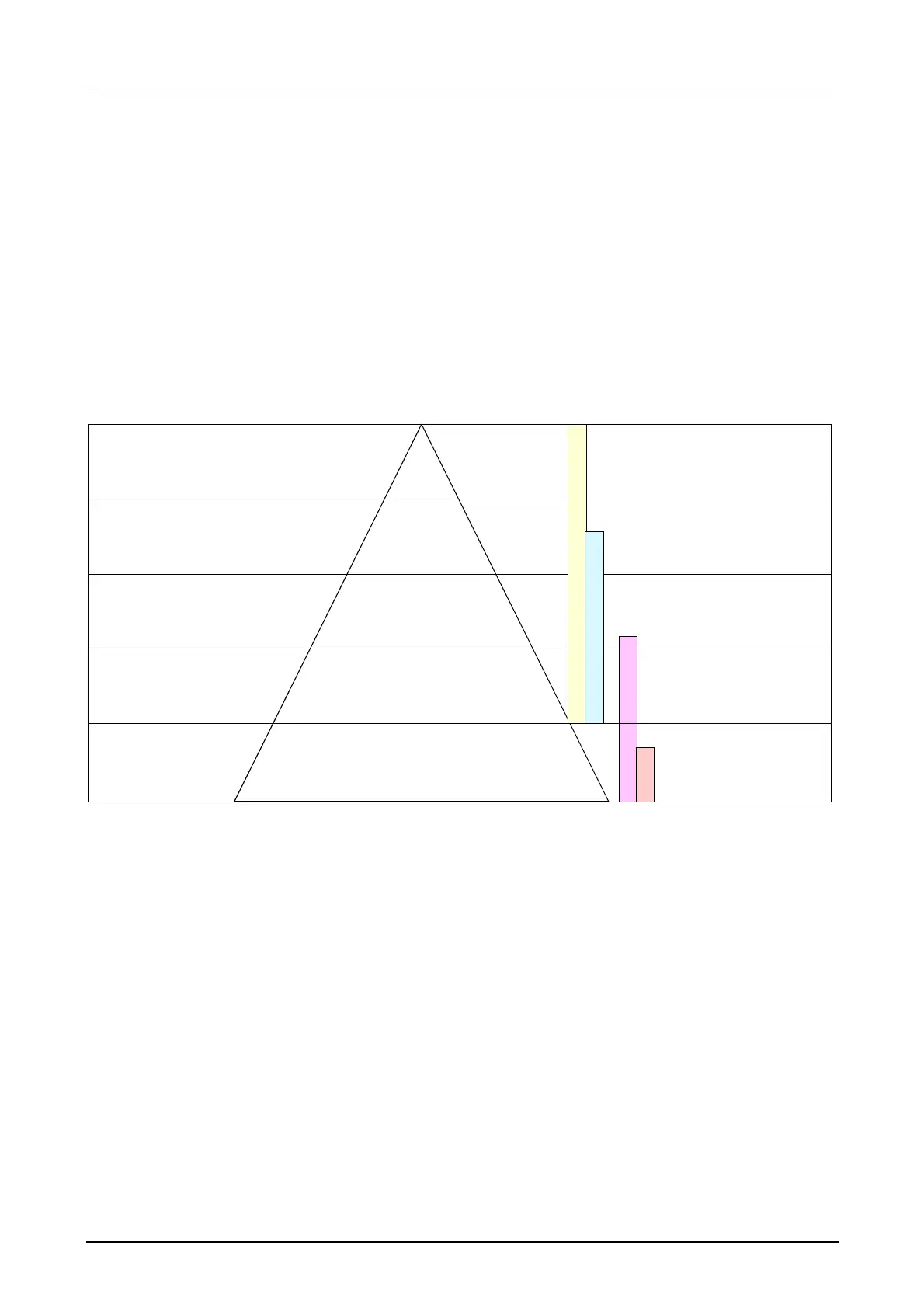
following model depicts the relationship between the different bus systems
and the hierarchical structures of a company:
Operational layer
Management layer
System layer
Prozess layer
Sensor / actuator
layer
Field bus
Sensor / actuator
Bus
H1
Industrial
Ethernet
Plant
computer
PPS CAD
Plant-oriented
control computer
manufacturing, stock,
production data
PPS CAD
Machine and control
computer
Peripheral systems. machines, CNC, NC,
controllers (PLC), measuring systems
Peripheral components
sensor, actuator, regulator, multiplexer, operating consoles
Industrial Ethernet is an electrical net based on shielded twisted pair
cabeling or optical net based on optical fibre.
Industrial Ethernet is defined by the international standard IEEE 802.3. The
net access of Industrial Ethernet corresponds to IEEE 802.3 - CSMA/CD
(Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) scheme: every station
“listens” on the bus cable and receives communication messages that are
addressed to it.
Stations will only initiate a transmission when the line is unoccupied. In the
event that two participants should start transmitting simultaneously, they
will detect this and stop transmitting to restart after a random delay time
has expired.
Using switches there is the possibility for communication without collisions.
Overview
Industrial Ethernet

 Loading...
Loading...