Manual VIPA CPU 21x Chapter 4 Deployment of the CPU 21x-2BT10 with TCP/IP
HB103E - Rev. 05/45 4-11
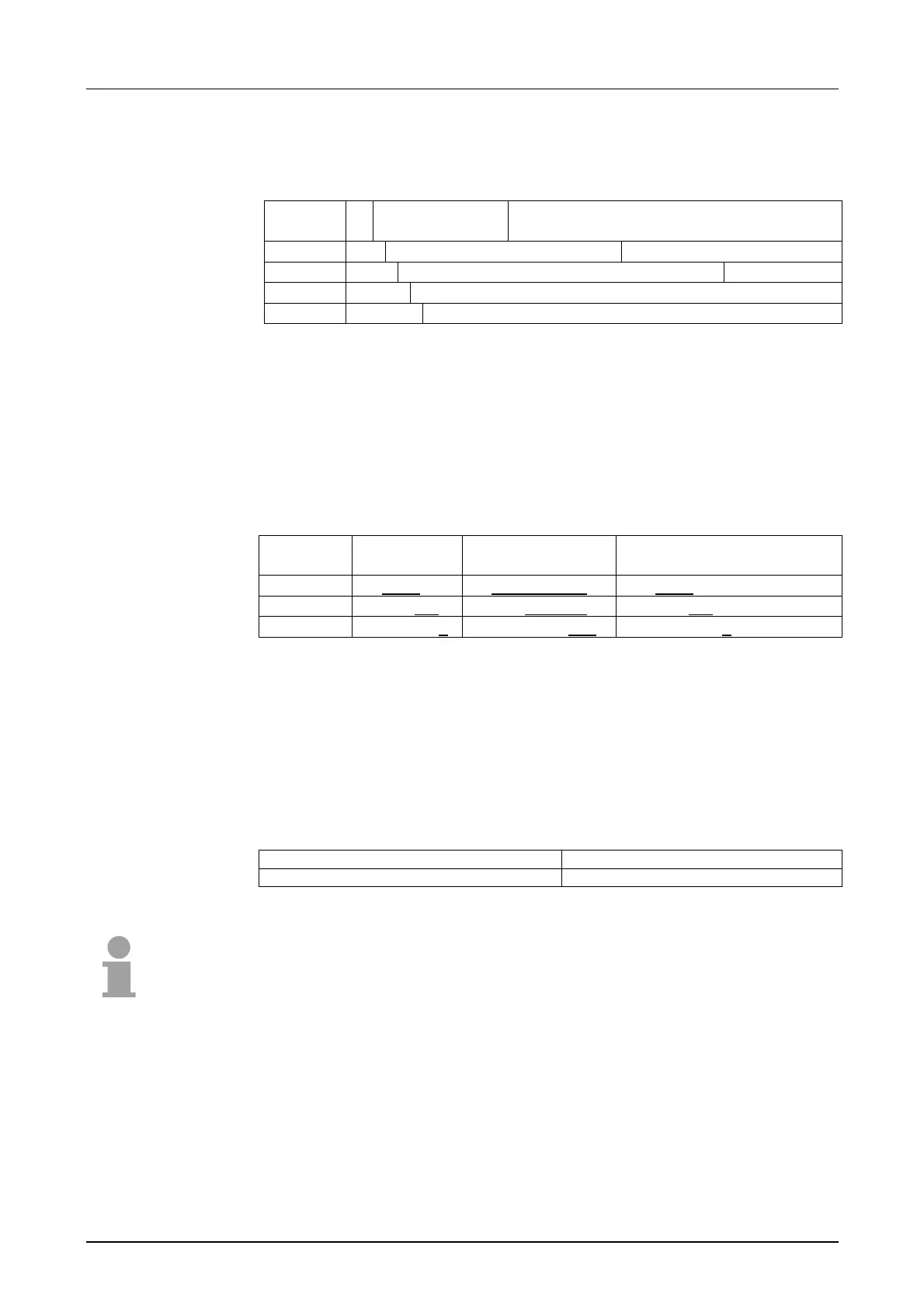
For IPv4 addresses there are five address formats (class A to class E) that
are all of a length of 4 Byte = 32 Bit.
Class A 0 Network-ID
(1+7 bit)
Host-ID (24 bit)
Class B 10 Network-ID (2+14 bit) Host-ID (16 bit)
Class C 110 Network-ID (3+21 bit) Host-ID (8 bit)
Class D 1110 Multicast group
Class E 11110 Reserved
The classes A, B and C are used for individual addresses, class D for
multicast addresses and class E is reserved for special purposes.
The address formats of the 3 classes A, B, C are only differing in the length
of Network-ID and Host-ID.
To build up private IP-Networks within the internet, RFC1597/1918
reserves the following address areas:
Network
class
Start IP End IP Standard subnet mask
A 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255 255.0.0.0
B 172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255 255.255.0.0
C 192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255 255.255.255.0
(The Host-ID is underlined.)
These addresses can be used as net-ID by several organizations without
causing conflicts, for these IP addresses are neither assigned in the
internet nor are routed in the internet.
Some Host-IDs are reserved for special purposes.
Host-ID = 0 Identifier of this network, reserved!
Host-ID = maximum (binary complete 1) Broadcast address of this network
Note!
Never choose an IP address with Host-ID=0 or Host-ID=maximum!
(e.g. for class B with subnet mask = 255.255.0.0, the "172.16.0.0" is
reserved and the "172.16.255.255" is occupied as local broadcast address
for this network.)
Address classes
Private IP networks
Reserved
Host-Ids

 Loading...
Loading...