MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide 51
UG984 (v2018.2) June 21, 2018 www.xilinx.com
Chapter 2: MicroBlaze Architecture
Eight Stage Pipeline
With C_AREA_OPTIMIZED set to 2 (Frequency), the pipeline is divided into eight stages to
maximize possible frequency: Fetch (IF), Decode (OF), Execute (EX), Access Memory 0 (M0),
Access Memory 1 (M1), Access Memory 2 (M2), Access Memory 3 (M3) and Writeback (WB).
The eight stage pipeline has four kinds of data hazard:
• An instruction in OF needs the result from an instruction in EX as a source operand. In
this case, the EX instruction categories are load, store, barrel shift, multiply, divide, and
floating-point instructions. This results in a 1-5 cycle stall.
• An instruction in OF uses the result from an instruction in M0 as a source operand. In
this case, the M0 instruction categories are load, multiply, divide, and floating-point
instructions. This results in a 1-4 cycle stall.
• An instruction in OF uses the result from an instruction in M1 or M2 as a source
operand. In this case, the M1 or M2 instruction categories are load, divide, and
floating-point instructions. This results in a 1-3 or 1-2 cycle stall respectively.
• An instruction in OF uses the result from an instruction in M3 as a source operand. In
this case, M3 instruction categories are load and floating-point instructions. This results
in a 1 cycle stall.
In addition to multi-cycle instructions, there are three other kinds of structural hazards:
• An instruction in OF is a stream instruction, and the instruction in EX is a stream, load,
store, divide, or floating-point instruction with corresponding exception implemented.
This results in a 1 cycle stall.
• An instruction in OF is a stream instruction, and the instruction in M0, M1, M2 or M3 is
a load, store, divide, or floating-point instruction with corresponding exception
implemented. This results in a 1 cycle stall.
• An instruction in M0 is a load or store instruction, and the instruction in M1, M2 or M3
is a load, store, divide, or floating-point instruction with corresponding exception
implemented. This results in a 1 cycle stall.
Pipeline stalls are caused by data hazards, control hazards, structural hazards, memory
accesses using slower memory, instruction fetch from slower memory, or stream accesses.
The multi-cycle instruction categories are divide instructions and floating-point instructions
FDIV, FINT, and FSQRT.
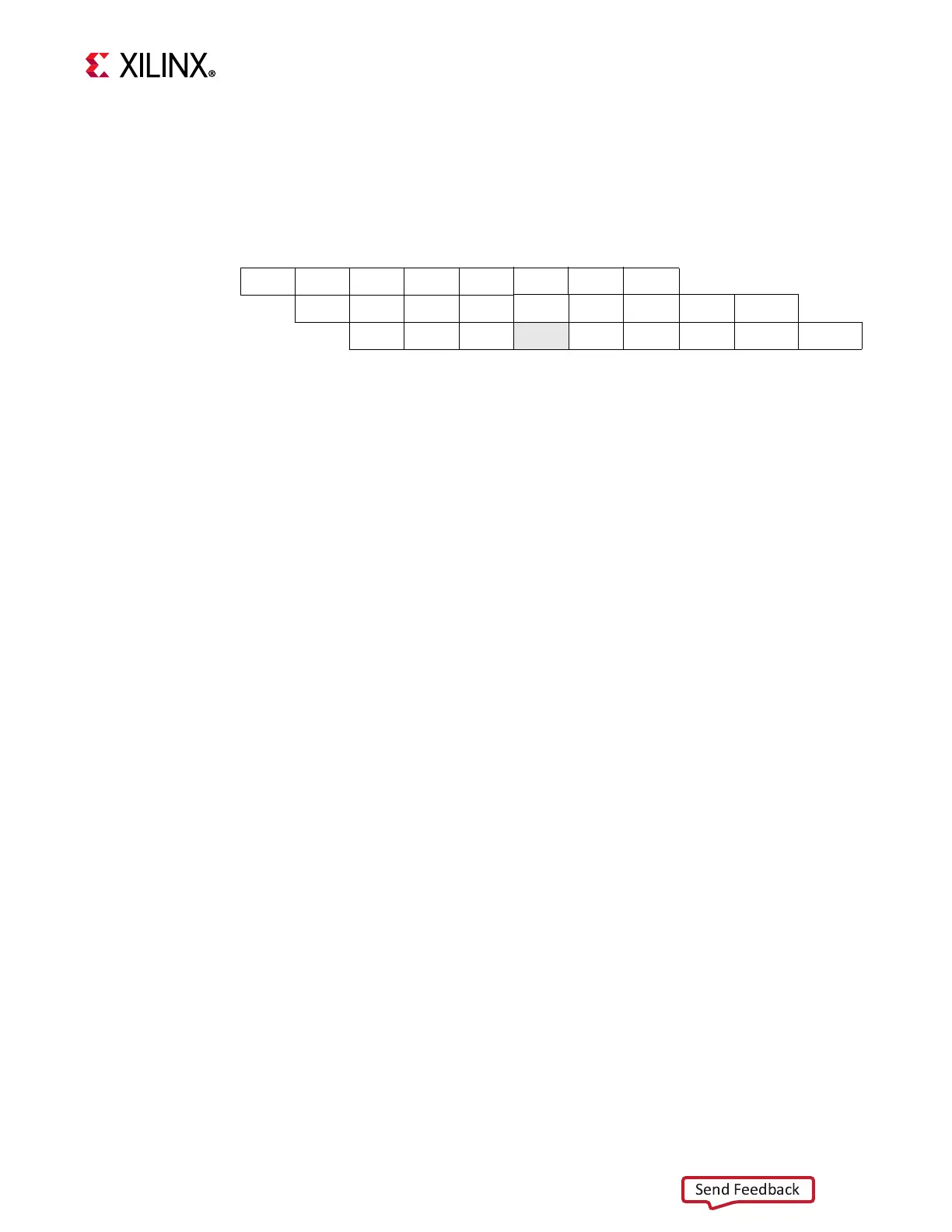
cycle1 cycle2 cycle3 cycle4 cycle5 cycle6 cycle7 cycle8 cycle9 cycle10 cycle11
instruction 1
IF OF EX M0 M1 M2 M3 WB
instruction 2
IF OF EX M0 M0 M1 M2 M3 WB
instruction 3
IF OF EX Stall M0 M1 M2 M3 WB
 Loading...
Loading...









