6.1 Type of Adjustments and Basic Adjustment Procedure
6-3
6.1 Type of Adjustments and Basic Adjustment Procedure
This section describes type of adjustments and the basic adjustment procedure.
6.1.1 Adjustments
Adjustments (tuning) are performed to optimize the responsiveness of the multi-winding drive unit.
The responsiveness is determined by the servo gain that is set in the multi-winding drive unit.
The servo gain is set using a combination of parameters, such as speed loop gain, position loop gain, filters,
friction compensation, and moment of inertia ratio. These parameters influence each other. Therefore, the
servo gain must be set considering the balance between the set values.
Generally, the responsiveness of a machine with high rigidity can be improved by increasing the servo gain. If
the servo gain of a machine with low rigidity is increased, however, the machine will vibrate and the respon-
siveness may not be improved. In such cases, it is possible to suppress the vibration with a variety of vibration
suppression functions in the multi-winding drive unit.
The servo gains are factory-set to appropriate values for stable operation. The following utility function can be
used to adjust the servo gain to increase the responsiveness of the machine in accordance with the actual con-
ditions. With this function, parameters related to adjustment above will be adjusted automatically and the need
to adjust them individually will be eliminated.
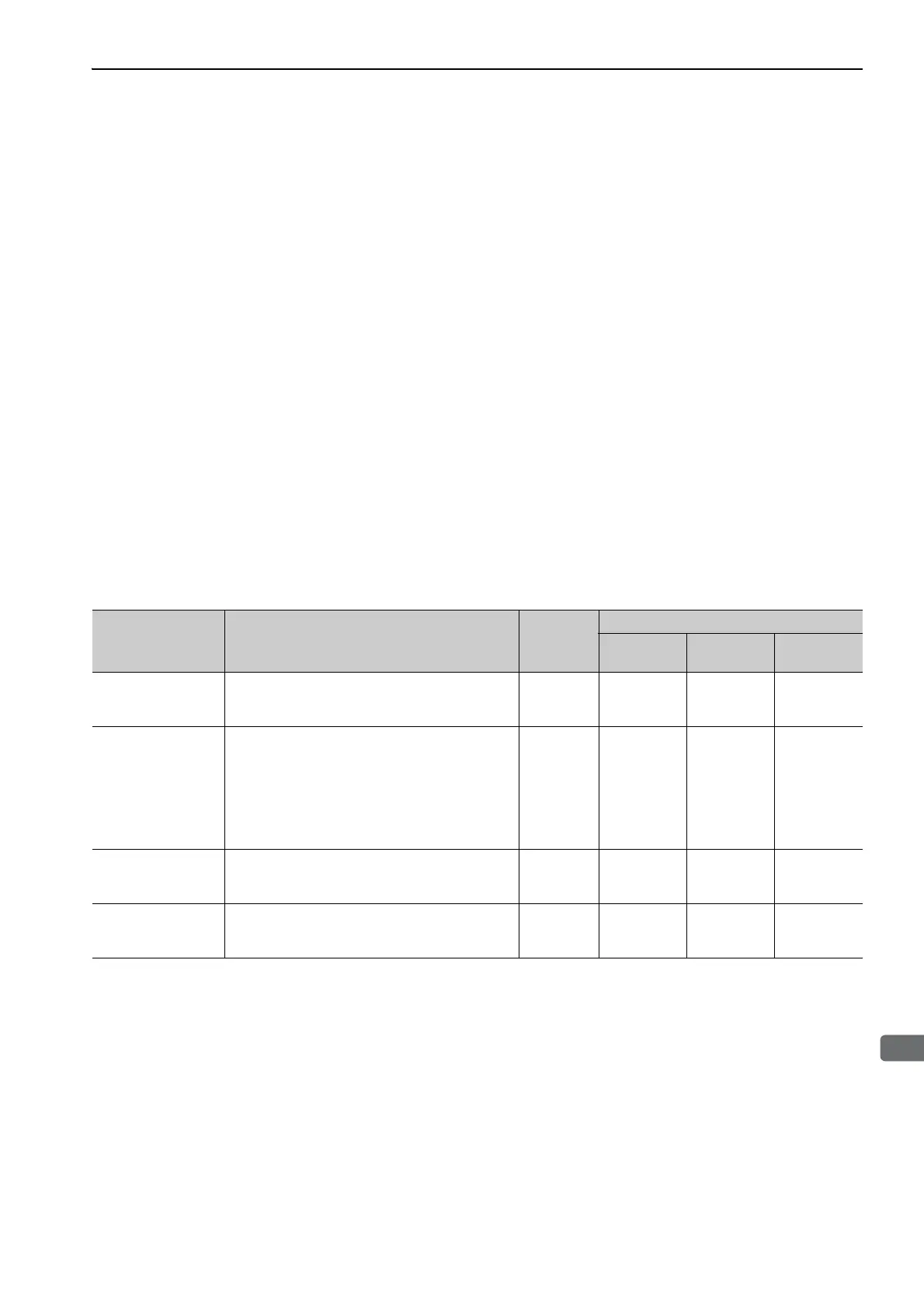
This section describes the following utility adjustment functions.
∗
: Available
Δ
: Can be used but functions are limited.
×
: Not available
Utility Function for
Adjustment
Outline
Applicable
Control
Method
Tool*
Digital
Operator
Panel
Operator
SigmaWin+
Advanced Autotun-
ing (Fn201)
Automatic operation is performed with internal ref-
erences in the multi-winding drive unit to automat-
ically adjust the moment of inertia ratio.
Speed and
Position
×
One-parameter
Tuning (Fn203)
The following parameters are manually adjusted
with the position or speed reference input from the
host controller while the machine is in operation.
• Gains (position loop gain, speed loop gain, etc.)
• Filters (torque reference filter, notch filter)
• Friction compensation
• Anti-resonance control adjustment function
Speed and
Position
Δ
Anti-Resonance
Control Adjustment
Function (Fn204)
This function effectively suppresses continuous
vibration.
Speed and
Position
×
Vibration Suppres-
sion Function
(Fn205)
This function effectively suppresses residual vibra-
tion if it occurs when positioning.
Position
×
 Loading...
Loading...