IM 04L20A01-01E
1-8
1.3 Alarm Function
This function generates an alarm when the measured/computed data meets a certain
condition. When an alarm occurs, information notifying the alarm occurrence is
displayed on the screen. In addition, a signal can be output from the relay output
terminals (/A1, /A2, or /A3 option) on the rear panel of the FX100.
Alarm Type
Number of Alarms
You can set up to four alarms for each channel.
Alarm Conditions
The following eight conditions are available. Letters in the parentheses are the
symbols used for each alarm.
• Upper limit alarm (H)
An alarm occurs when the measured value exceeds the alarm value.
• Lower limit alarm (L)
An alarm occurs when the measured value falls below the alarm value.
alarm value
Alarm release
Measured/computed data
Alarm occurrence
Upper limit alarm
Lower limit alarm
Measured
/computed data
Alarm release
alarm value
Alarm occurrence
• Difference upper limit alarm (h)
*1
An alarm occurs when the difference between the measured values of two channels
becomes greater than or equal to the alarm value.
• Difference lower limit alarm (l)
*1
An alarm occurs when the difference between the measured values of two channels
becomes smaller than or equal to the alarm value.
*1 Can be specified only on difference computation channels.
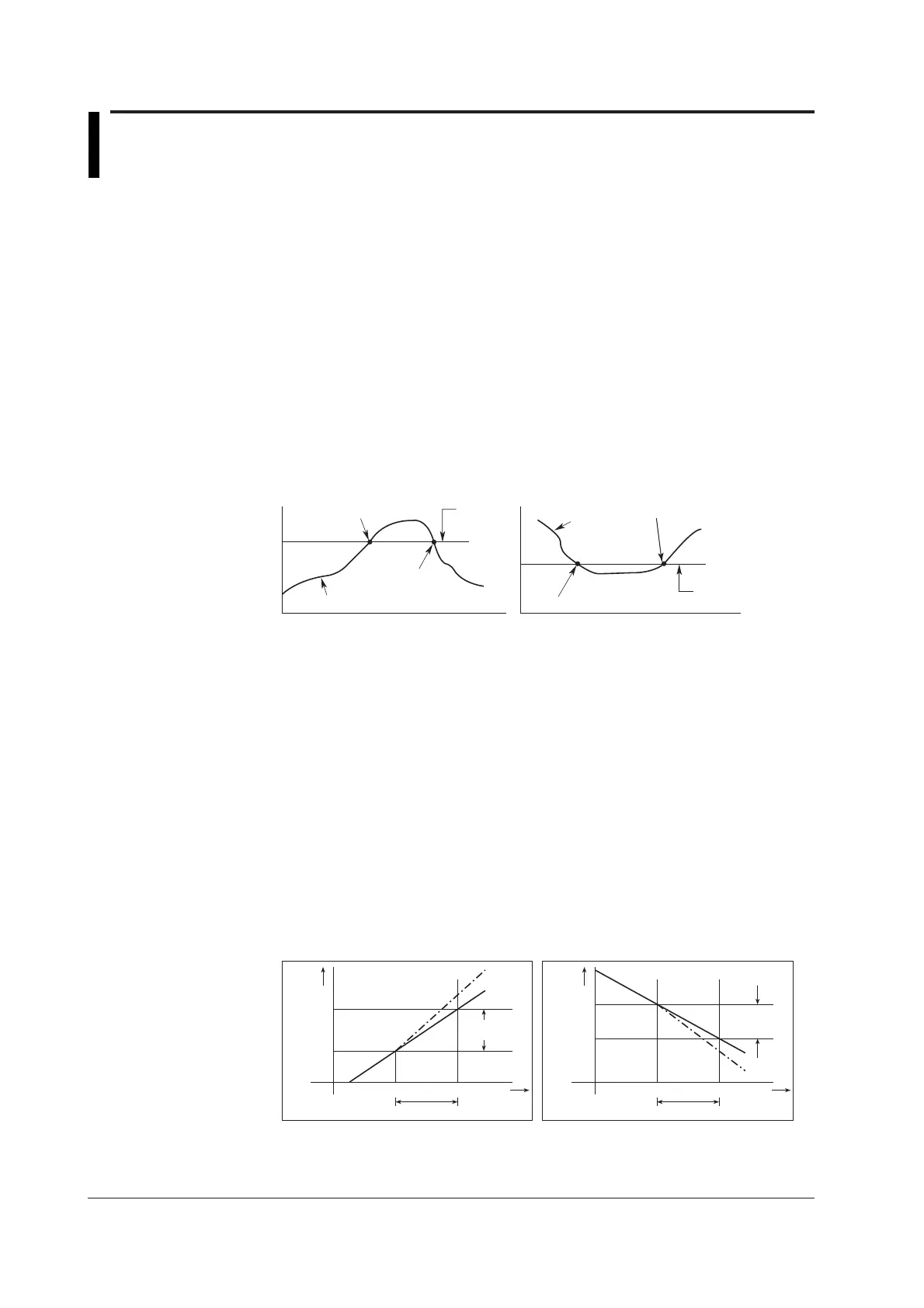
• Upper limit on rate-of-change alarm (R)
*2
The amount of change of the measured values over a certain time interval is checked.
An alarm occurs when the amount of increase becomes greater than or equal to the
specified value.
• Lower limit on rate-of-change alarm (r)
*2
The amount of change of the measured values over a certain time interval is checked.
An alarm occurs when the amount of decrease becomes greater than or equal to the
specified value.
*2 Can be specified only on measurement channels.
Measured
value
Measured
value
R alarm
T1
Time
Interval t
2-t1 Interval t2-t1
T2
T2
T1
t1 t2 t1 t2
Variation
|T
2-T1|
Variation
|T
2-T1|
Time
r alarm
Upper limit on rate-of-change alarm
Lower limit on rate-of-change alarm
The interval is defined by the following equation and is set in terms of the number of
measured data points.
Interval = scan interval × number of measurements

 Loading...
Loading...











