SW Version 2.04 30-January-2009 Page 99 of 128
Note:
The filter also applies for the SNMP trap system.
Note that the alarms shown in the alarm drop down list are all the alarms that are
registered by each module in the system. A module is most often represented by a
card. From the above list the SCR module equals a scrambler card. When an alarm is
raised by the respective module detecting an error condition it is possible for the
module reporting the alarm to override the alarm description, in order to add some
extra info. This may in some cases cause the alarm text displayed in the alarm filter
list not to match the actual alarm text, but it should be obvious which alarm it is.
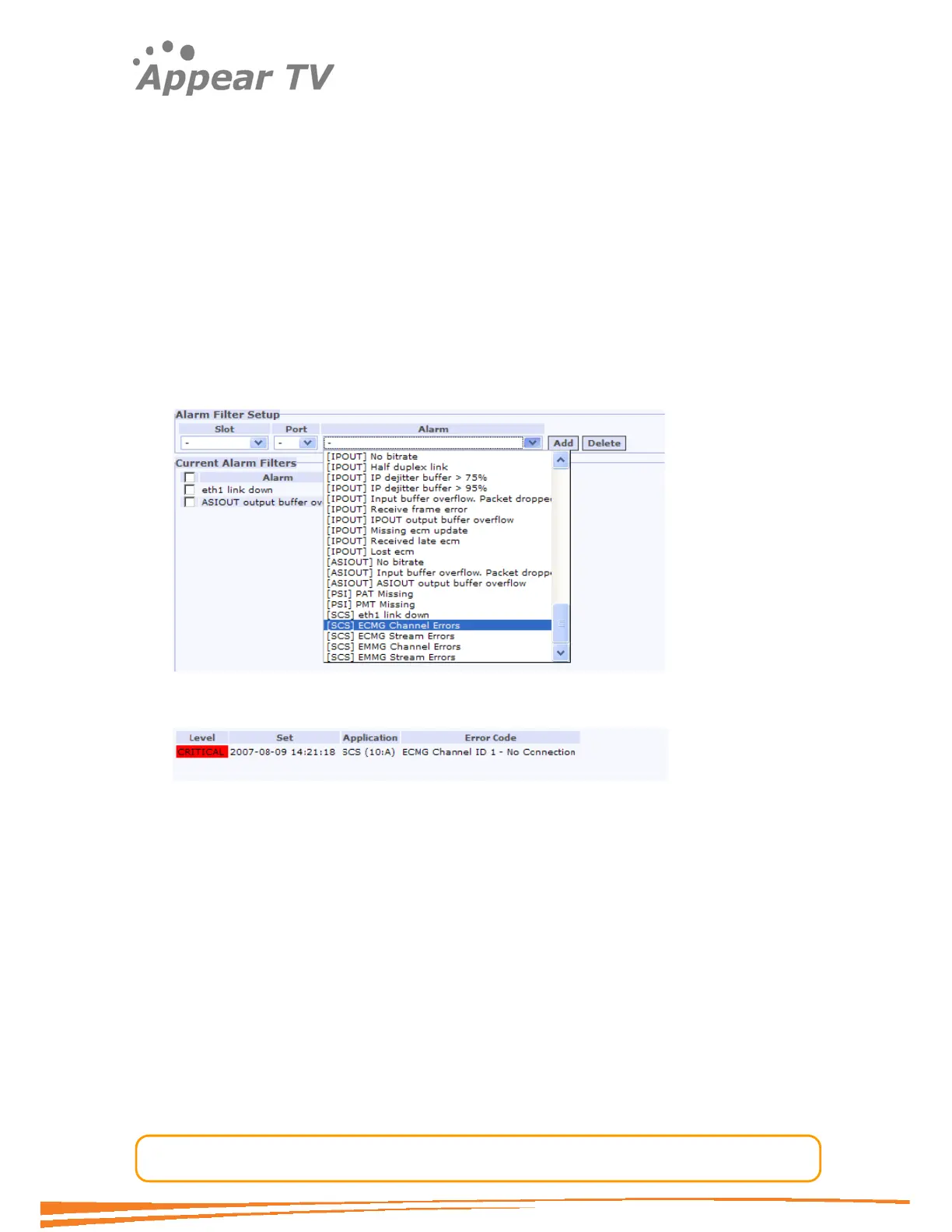
Figure 52 and Figure 53 list the alarms for the SCS cards Channel Errors alarm.
During boot the SCS card registers a general ECMG Channel Error alarm. This alarm is
visible in the filter list as shown below. Then when the card detects a problem with
the channel the alarm is triggered, with some additional information conveyed in the
alarm description, in this case the channel error is no connection with the CA system.
Figure 71 - Registered alarms
Figure 72 - Actual alarm with specialized alarm description
5.2 SNMP
5.2.1 Overview:
The SNMP agent is located on the MMI module, and uses the same IP address. A
number of variables can be configured, including the SNMP configuration file
(containing the public and private community strings, for user access and alarms);
and the trap destination table. This is explained below.
5.2.2 Configuring Public and Private Community Strings:
The SNMP agent supports changing the read and write community strings for
incoming requests and outgoing traps. The incoming community strings are defined in
the configuration file for the SNMP system located on the MMI card.
SNMP configuration file: /etc/snmp/snmp.conf
 Loading...
Loading...