276
7647H–AVR–03/12
Atmel ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1
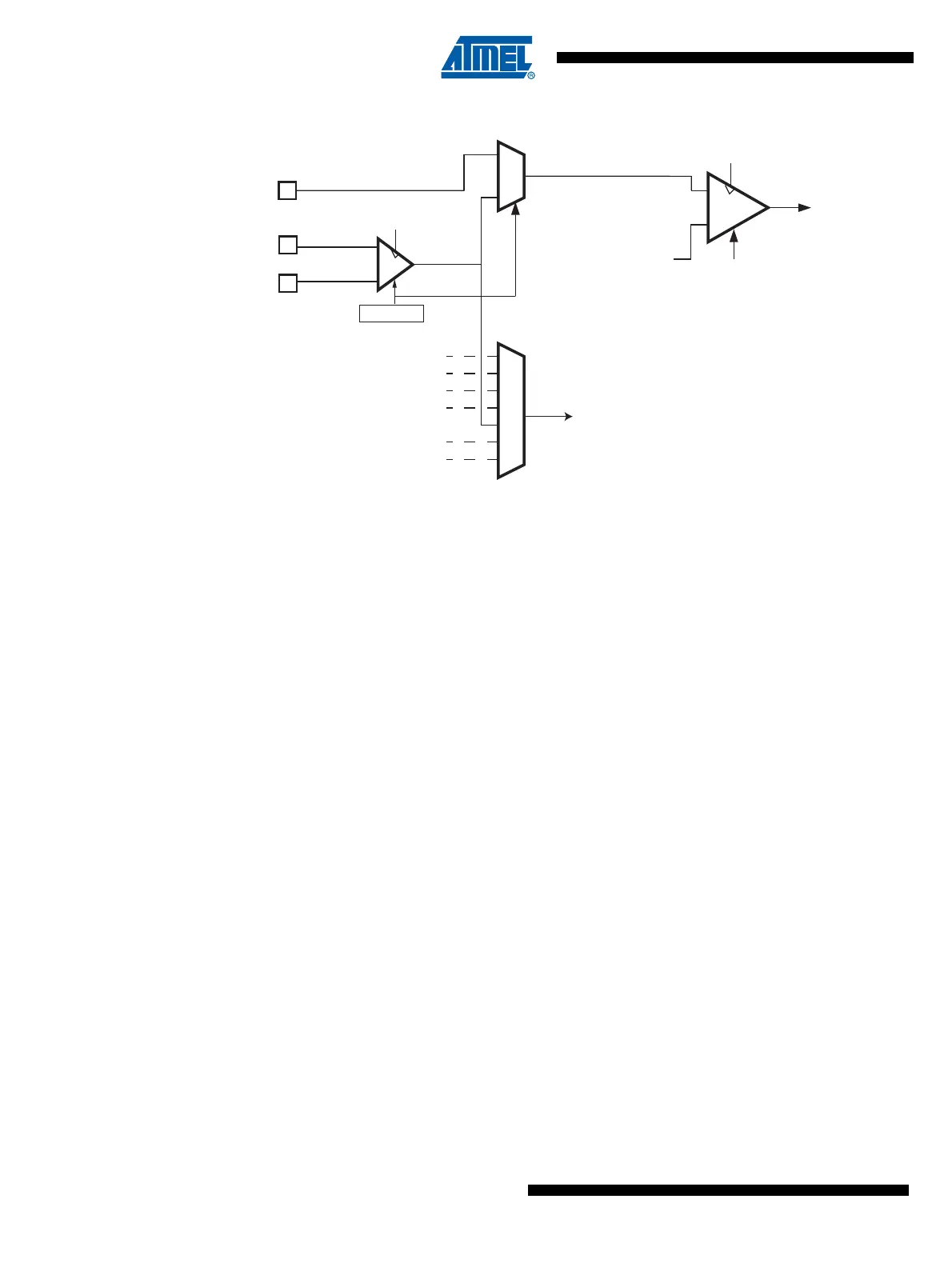
Figure 22-2. Amplifier, Comparator and ADC
22.4 Analog Peripheral Clock Sources
22.4.1 ADC Clock
The ADC clock comes from the clock system (CLKio) and it is divided by the ADC Prescaler.
See “ADC Prescaler Selection” on page 247. The bits described in the ADC Prescaler Selection
determine the division factor between the system clock frequency and input clock of the ADC.
See “Prescaling and Conversion Timing” on page 233. for a complete description of the ADC
clock system.
22.4.2 Comparator Clock
While it is not connected to an amplifier, a comparator is clocked by the comparator clock which
is configured thanks to the ACCKSEL bit in AC0CON register See “Analog Comparator 0 Con-
trol Register – AC0CON” on page 264. One can select between the 16MHz PLL output and the
CLKio.
When it is connected to an amplifier, a comparator is clock by twice the amplifier clock.
22.4.3 Amplifier Clock
When the Amplifier uses the ADC clock, this clock is divided by 8. This insures a maximum fre-
quency of 250kHz for the amplifier when the ADC clock is 2MHz. When the ADC is clocked with
a frequency higher than 2MHz the amplifier cannot be clocked by the ADC clock.
See “Amplifier” on page 250. for a complete description of the Amplifier clock system.
+
-
ACMPx
ACxEN
AMPx
+
-
AMPCMPx
Analog Comparator
Negative Input
Analog Comparator
Output
AMPx+
AMPx-
Comparator
Clock
Amplifier
Clock
ADC
Sampling
& Hold
ADC Multiplexer
 Loading...
Loading...