20
7647H–AVR–03/12
Atmel ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1
4. Memories
This section describes the different memories in the ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1. The AVR archi-
tecture has two main memory spaces, the Data Memory and the Program Memory space. In
addition, the ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1 features an EEPROM Memory for data storage. All three
memory spaces are linear and regular.
4.1 In-System Reprogrammable Flash Program Memory
The ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1 contains 16K/32K/64K bytes On-chip In-System Reprogrammable
Flash memory for program storage. Since all AVR instructions are 16 or 32 bits wide, the Flash
is organized as 8K x 16, 16K x 16 , 32K x 16. For software security, the Flash Program memory
space is divided into two sections, Boot Program section and Application Program section.
The Flash memory has an endurance of at least 10,000 write/erase cycles. The
ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1 Program Counter (PC) is 14/15 bits wide, thus addressing the
8K/16K/32K program memory locations. The operation of Boot Program section and associated
Boot Lock bits for software protection are described in detail in “Boot Loader Support –
Read-While-Write Self-Programming ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1” on page 279. “Memory Program-
ming” on page 296 contains a detailed description on Flash programming in SPI or Parallel
programming mode.
Constant tables can be allocated within the entire program memory address space (see the LPM
– Load Program Memory.
Timing diagrams for instruction fetch and execution are presented in “Instruction Execution Tim-
ing” on page 17.
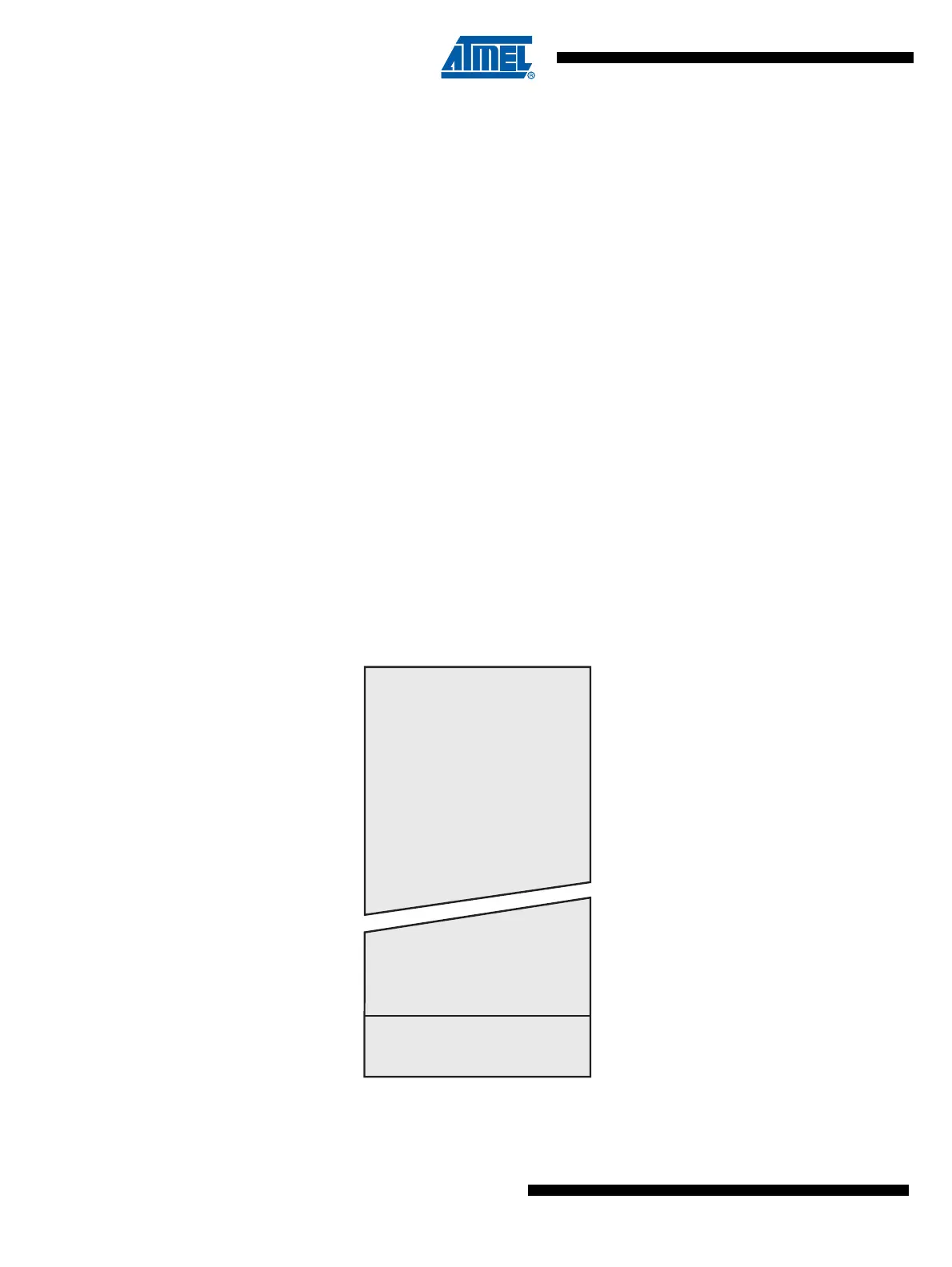
Figure 4-1. Program Memory Map
0x0000
0x1FFF/0x3FFF/0x7
Program Memory
Application Flash Section
Boot Flash Section
 Loading...
Loading...