259
7647H–AVR–03/12
Atmel ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1
19.2 Typical applications
19.2.1 LIN Current Source
During the configuration of a LIN node in a cluster, it may be necessary to attribute dynamically
an unique physical address to every cluster node. The way to do it is not described in the LIN
protocol.
The Current Source offers an excellent solution to associate a physical address to the applica-
tion supported by the LIN node. A full dynamic node configuration can be used to set-up the LIN
nodes in a cluster.
ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1 proposes to have an external resistor used in conjunction with the Cur-
rent Source. The device measures the voltage to the boundaries of the resistance via the Analog
to Digital converter. The resulting voltage defines the physical address that the communication
handler will use when the node will participate in LIN communication.
In automotive applications, distributed voltages are very disturbed. The internal Current Source
solution of ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1 immunizes the address detection against any kind of volt-
age variations.
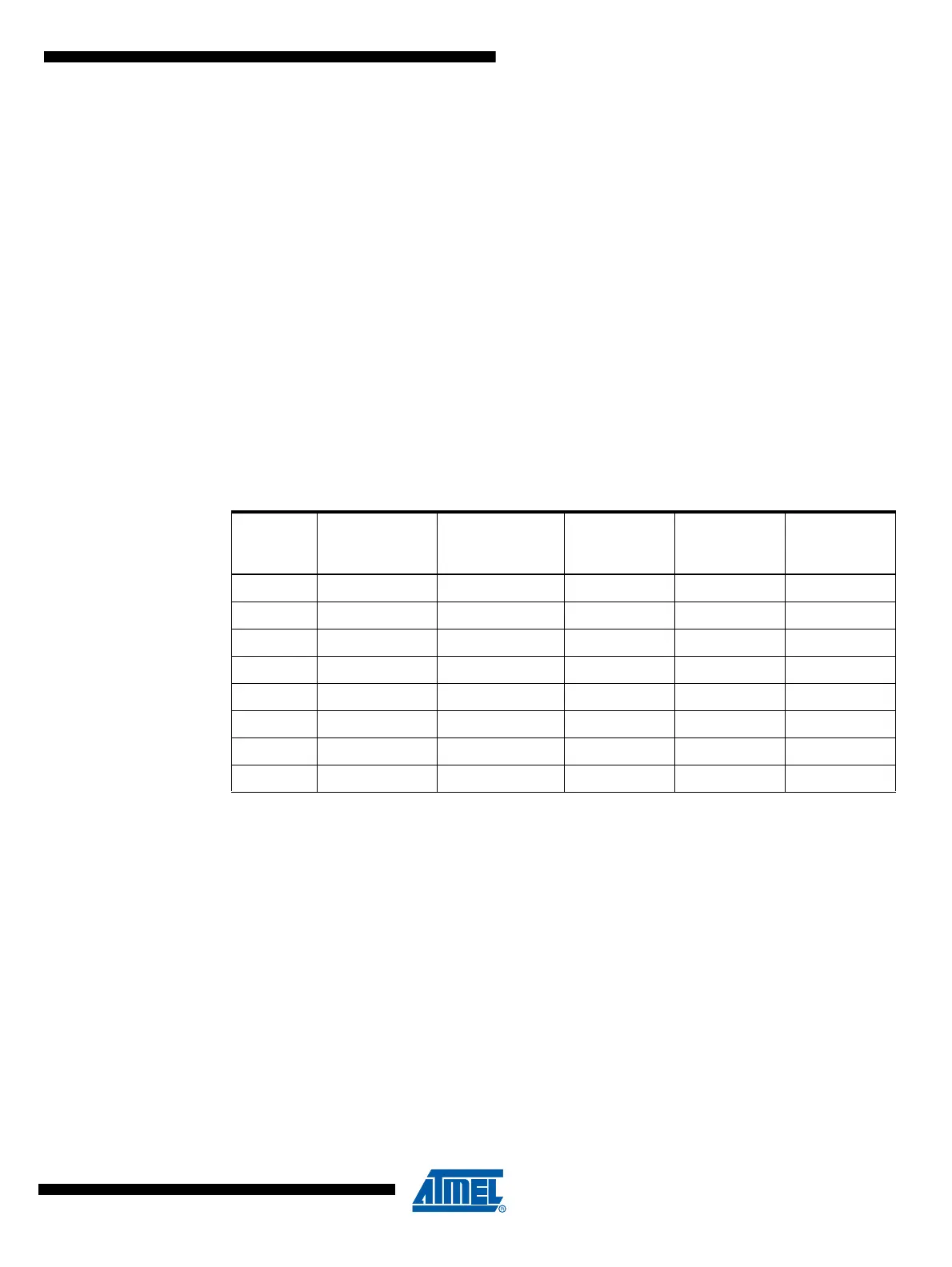
Table 19-1. Example of Resistor Values(±5%) for a 8-address System (AV
CC
= 5V
(1)
)
Physical
Address
Resistor Value
R
load
(Ohm)
Typical
Measured
Voltage (V)
Minimum
Reading with
a 2.56V ref
Typical
Reading with
a 2.56V ref
Maximum
Reading with
a 2.56V ref
0 1 000 0.1 40
1 2 200 0.22 88
2 3 300 0.33 132
3 4 700 0.47 188
4 6 800 0.68 272
5 10 000 1 400
6 15 000 1.5 600
7 22 000 2.2 880
 Loading...
Loading...