E-TRA3000 F-S-D-V-C_E-Manual 9/162
1 Description
1.1 The interference sources of the transients
1.1.1 Electrostatic discharge ESD
Electro Static Discharge IEC 61000-4-2 Ed.2
What causes electrostatic discharges?
A person becomes electrostatically charged by walking over an insulating floor surface. The capacity of the
body can be charged to several kilovolts (1000 V). This capacity is discharged when contact is made with
an electronic unit or system. The discharge is visible as a spark in many cases and can be felt by person
concerned, who gets a „shock“. The discharges are harmless to humans, but not to sensitive, modern
electronic equipment. The resulting current causes interference in the units or can make entire systems
„crash“.
For over 25 years it has been known to the electrical industry that electrostatic discharges as encountered
every day can have a disastrous effect on electronic equipment.
The cost of damage caused by ESD is difficult to assess, but amounts to billions of dollars worldwide.
The areas most affected are:
• manufacturing of integrated circuits (chips).
• the chemical industry, e.g. by explosion, fires caused by the sparks from electrostatic discharges.
• malfunctioning of process control with the secondary damage costs.
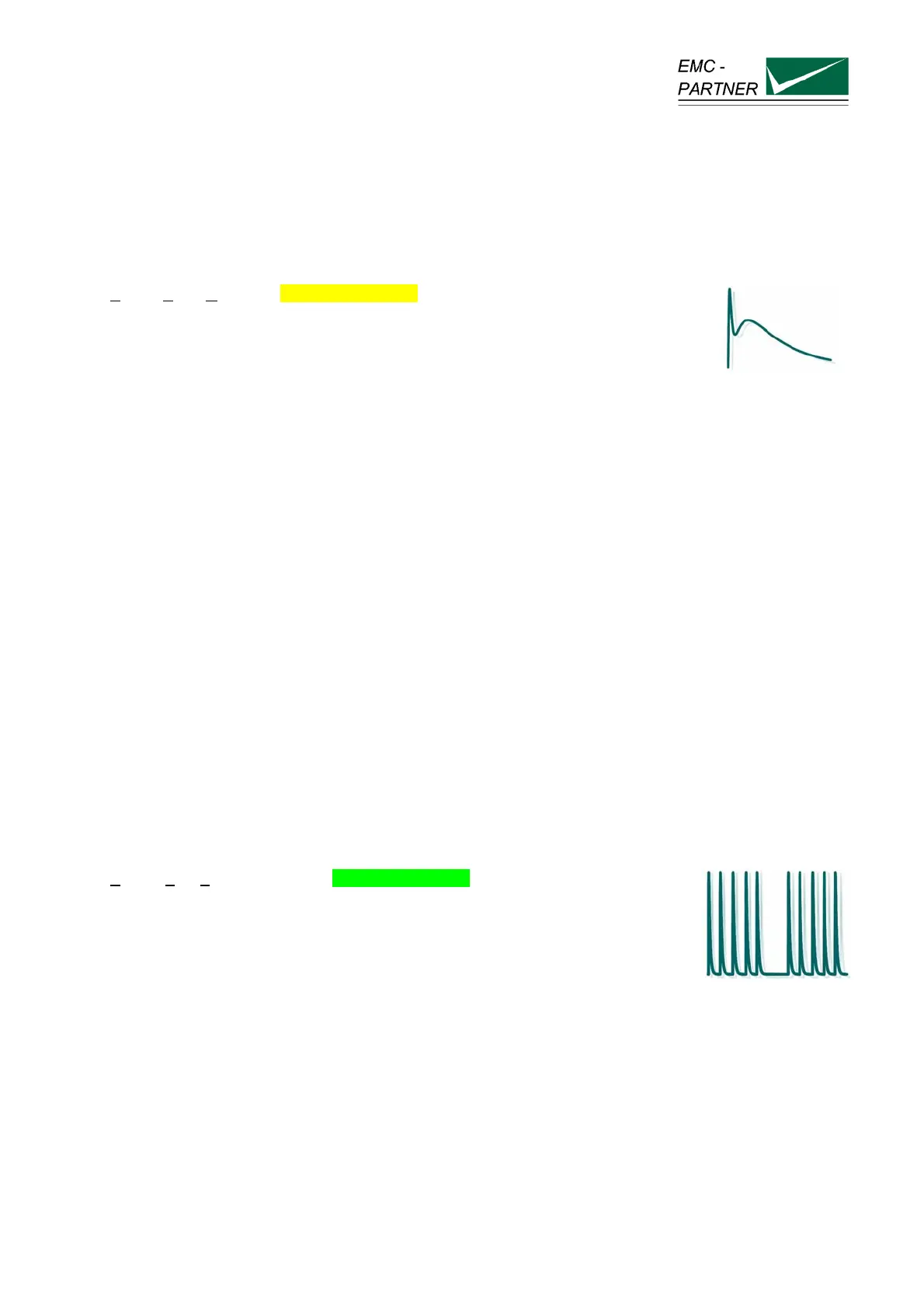
1.1.2 Switched inductance EFT (Burst)
Electric Fast Transient or Burst. IEC 61000-4-4 Ed.2
Industrial measurement and control equipment practically always operates in conjunction with conventional
control units (relays, contactors). Fluorescent lamp ballast units, insufficiently suppressed coffee grinders,
vacuum cleaners, drilling machines, hair dryers, universal motors, etc. can be found everywhere in the
power supply system. All these, primarily inductive loads, produce interference when switched on and off. A
wide range of switching transients, also called bursts, are produced with the following waveform.

 Loading...
Loading...