User Manual NTU Orion 2
18
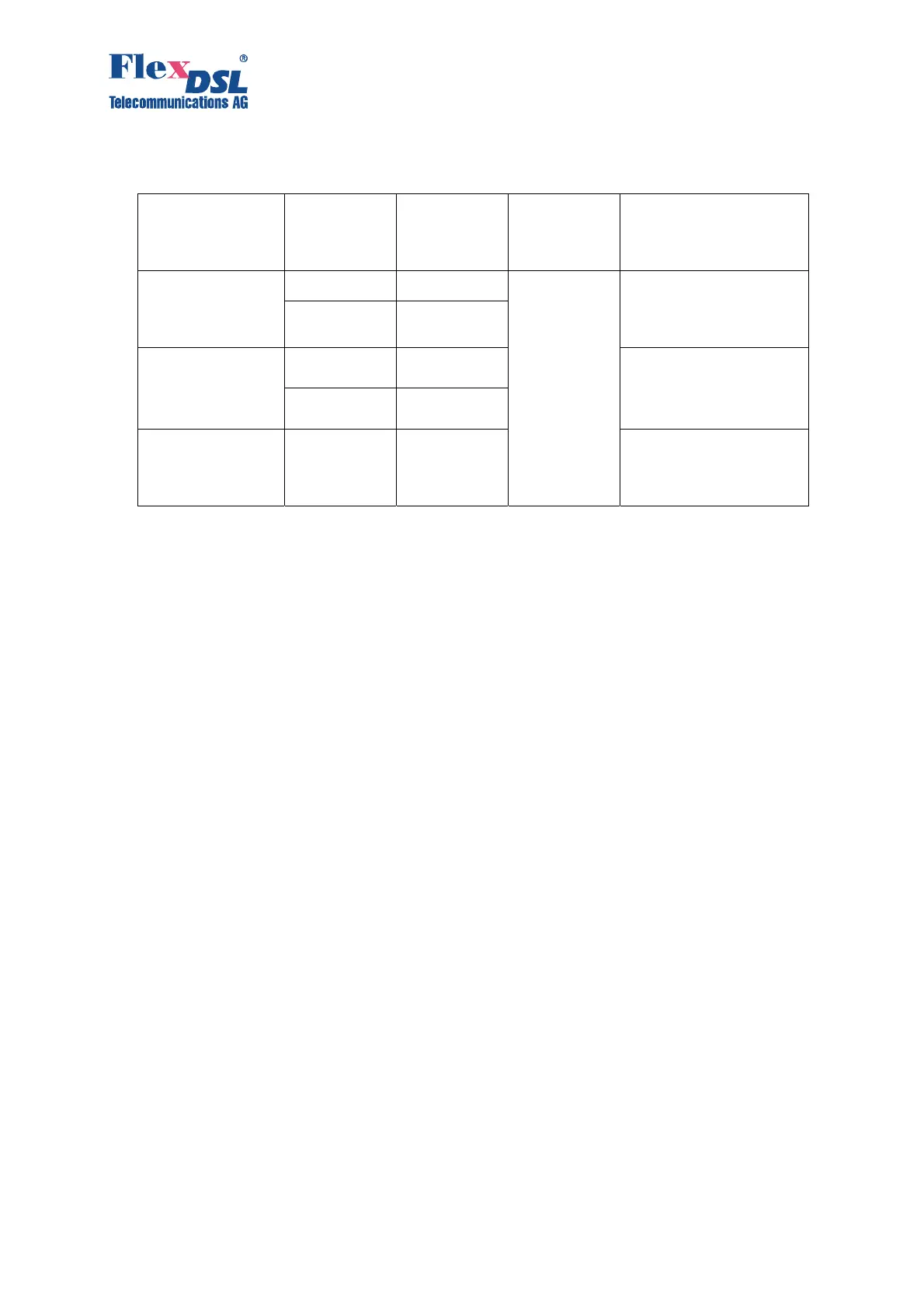
Table 3.3 represents line settings in the independent mode.
Table 3.3 Line settings in the independent mode.
Mode Coding type Baserate Data
transmissio
n rate
Standard
Manual
configuration,
Master, Slave
PAM16 3..60 Baserate* 64
kbit/s
Annex A, Annex B,
Annex AB
(autodetection)
PAM32 12..89
Autodetection,
Master
PAM16 Auto (3..60) Annex AB
(autodetection)
PAM32 Auto (12..89)
Autodetection,
Slave
Auto
(PAM16,
PAM32)
Auto (3..89) Annex AB
(autodetection)
3.3.2.1.1 Master/Slave/Auto
To establish a connection, it is necessary that one transceiver has to be a Master and the other
– a Slave. In this case, the connection is controlled by the Master device. The regenerator can
also automatically detect the “Master/Slave operation modes. In this mode, the regenerator
automatically detects from the side of which of line interface the Master device and the Slave
modem are located.
The MASTER ON/OFF command (the Configuration management menu) is used to configure
the Master/Slave operation modes.
3.3.2.1.2 Multipair modes
FlexDSL Orion2 modems and regenerators support the multipair mode.
If 2, 3 or 4 DSL channels are configured to operate in the multipair mode, they function at the
same clock frequency and line rate as one DSL channel with doubled, tripled or quadrupled
transmission capacity. Similarly to the independent channel, such a combined channel can
simultaneously transmit one or several E1 streams and one WAN stream. This transmission is
plesiochronous. All E1 streams received by one DSL interface should use the same clock
frequency in one direction.
In the multipair mode, one xDSL channel serves as a Master channel, while the other xDSL
channels serve as Slave channels. If the link in one channel fails, links in all other channels
break too and the procedure of connection activation starts again.
The four-channel modems provide a possibility to organize pair-wise channels, i.e., these two
two-pair links will operate independently from each other.
The main application of the multipair modes is the increase in the transmission range. In this
case, some channels operate at low transmission rates. Limitations are imposed on the
Baserate parameter in the multipair mode. These limitations are listed in Table 3.4
 Loading...
Loading...