111
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
8.2 Communication
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Information on standard event resister
Information on output queue
bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Not used
MSS ESB MAV
Not used Not used Not used
ESB0
Status b
te re
isters
STB
bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Not used
×
ESB MAV
Not used Not used Not used
ESB0
Service re
uest enable re
isters
SRER
&
Logical
sum
bit6
RQS
MSS
&
Generation of service
re
uest RQS
&
bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Not used
MSS ESB MAV
Not used Not used Not used
ESB0
&
&
Logical
sum
Status b
te re
isters
STB
bit7 bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Not used
×
ESB MAV
Not used Not used Not used
ESB0
Service re
uest enable re
isters
SRER
&
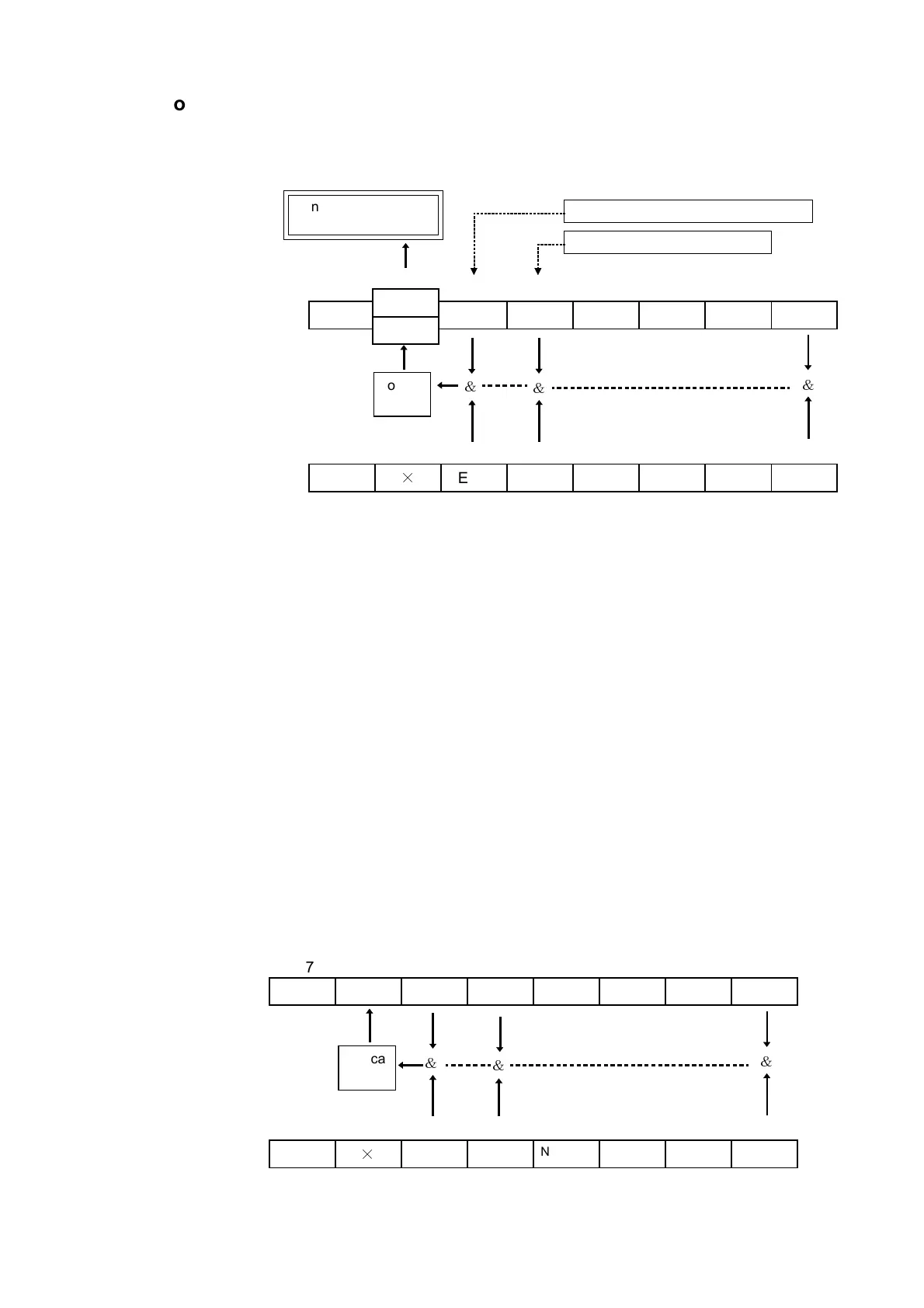
Status Model
The term "event" refers to any phenomenon which generates a service
request.
The status byte register holds information relating to the event registers and
the output queue. It is further possible to use the service request enable
register as a mask to select the items required. If any of the bits selected by
the mask becomes 1, bit 6 (the master summary status or MSS bit) is also
set to 1, an SRQ message is generated, and this generates a service request.
Status Byte Registers
(1) Status byte register (STB)
The status byte register is an 8-bit register whose contents are output from
the 3237/38/39 to the controller, when serial polling is being performed.
If even only one bit in the status byte register has changed from 0 to 1
(provided that it is a bit which has been set in the service request enable
register as a bit which can be used), then the MSS bit is set to 1.
Simultaneously with this the SRQ bit is set to 1, and service request is
generated.
 Loading...
Loading...