78
messages, all PIM routers on the subnet discover their PIM neighbors, maintain PIM neighboring
relationship with other routers, and build and maintain SPTs.
SPT building
The process of building an SPT is the flood-and-prune process:
1. In a PIM-DM domain, when the multicast source S sends multicast data to the multicast group G,
the multicast data is flooded throughout the domain. A router performs an RPF check for the
multicast data. If the RPF check succeeds, the router creates an (S, G) entry and forwards the data
to all downstream nodes in the network. In the flooding process, all the routers in the PIM-DM
domain create the (S, G) entry.
2. The nodes without downstream receivers are pruned. A router that has no downstream receivers
multicasts a prune message to all PIM routers on the subnet. When an upstream node receives the
prune message, it removes the receiving interface from the (S, G) entry. In this way, the upstream
stream node stops forwarding subsequent packets addressed to that multicast group down to this
node.
NOTE:
n (S, G) entry contains a multicast source address S, a multicast
roup address G, an out
oin
interface list, and an incoming interface.
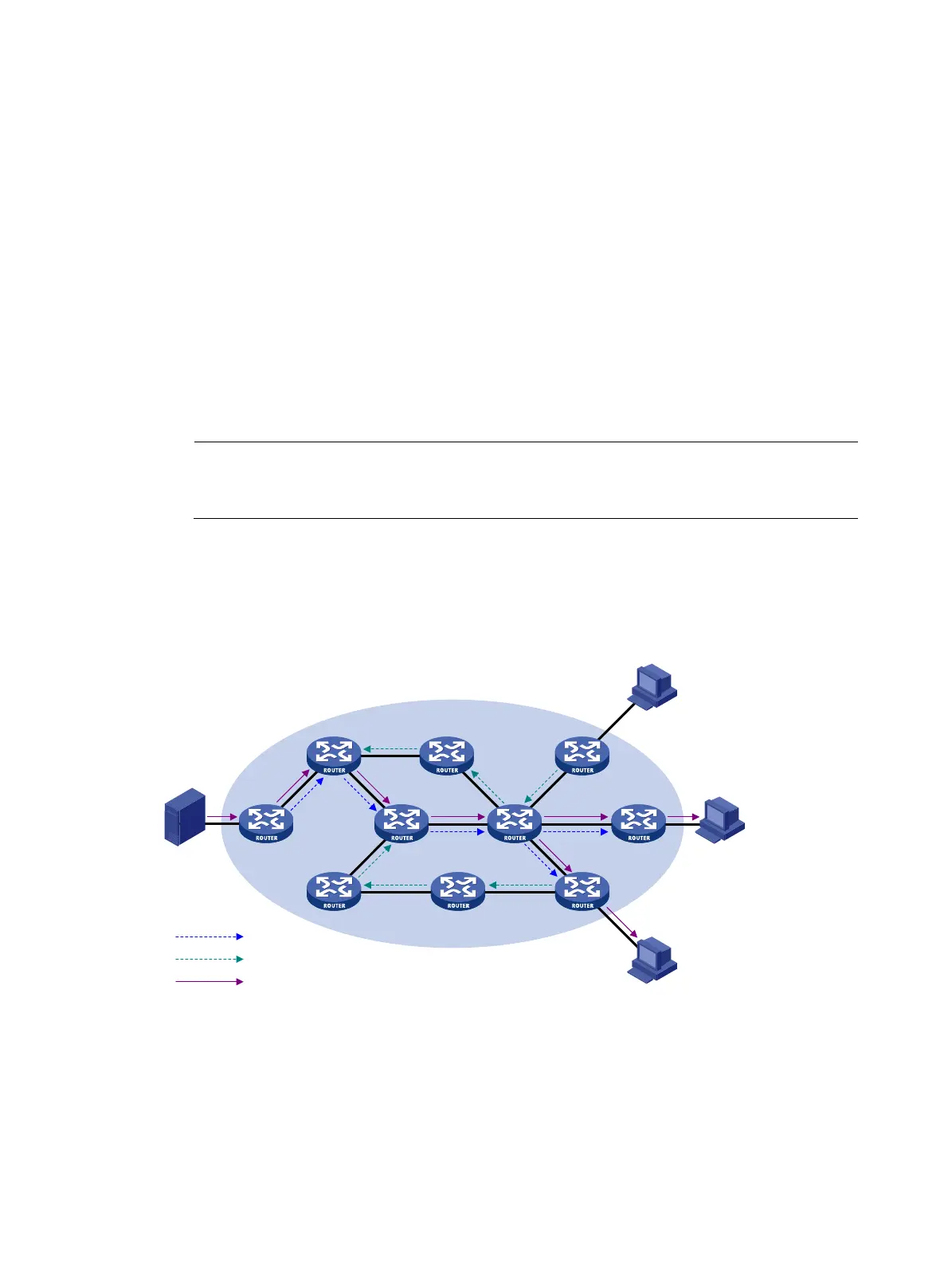
A prune process is initiated by a leaf router. As shown in Figure 29, the router interface that does not have
any downstream receivers initiates a prune process by sending a prune message toward the multicast
source. This prune process goes on until only necessary branches are left in the PIM-DM domain, and
these necessary branches constitute an SPT.
Figure 29 SPT building
The pruned state of a branch has a finite holdtime timer. When the timer expires, multicast data is again
forwarded to the pruned branch. The flood-and-prune cycle takes place periodically to maintain the
forwarding branches.
Graft
A previously pruned branch might have new downstream receivers. To reduce the latency for resuming
the forwarding capability of this branch, a graft mechanism is used as follows:
Source
Server
Host A
Host B
Host C
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast packets
SPT
Prune message
 Loading...
Loading...