86
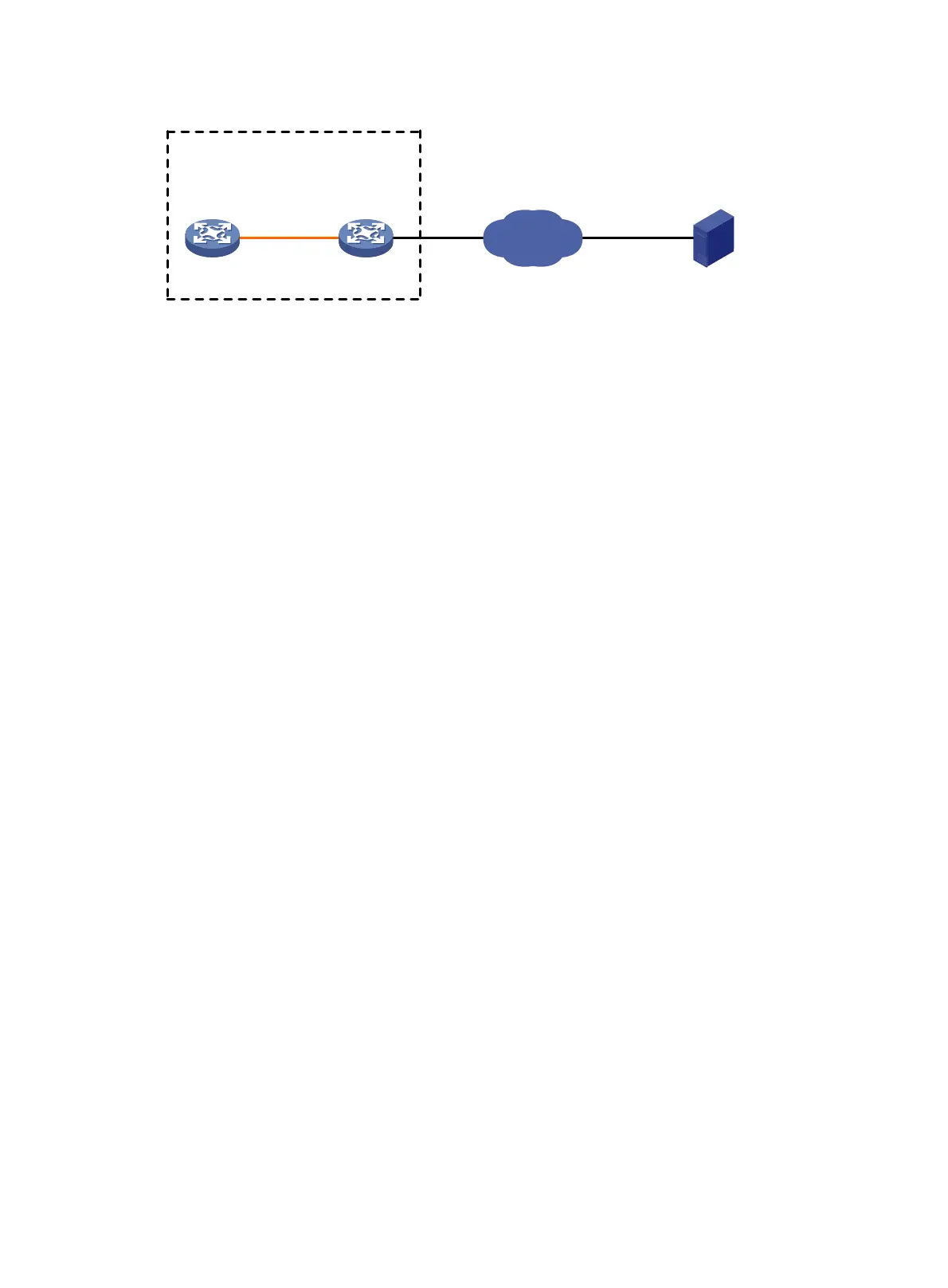
Figure 30 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Configure IP addresses as shown in Figure 30. Make sure the IRF fabric and PC can reach each
other. (Details not shown.)
# Examine the storage space on the member devices. If the free space is insufficient, use the
delete/unreserved file-url command to delete unused files. (Details not shown.)
# Log in to the FTP server at 10.1.1.1 using the username abc and password 123456.
<Sysname> ftp 10.1.1.1
Press CTRL+C to abort.
Connected to 10.1.1.1 (10.1.1.1).
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User (10.1.1.1:(none)): abc
331 Give me your password, please
Password:
230 Logged in successfully
Remote system type is MSDOS.
200 Type is Image (Binary)
ftp>
# Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the Flash root directory of the master device.
ftp> get temp.bin
local: temp.bin remote: temp.bin
150 Connecting to port 47457
226 File successfully transferred
23951480 bytes received in 95.399 seconds (251.0 kbyte/s)
# Download the file temp.bin from the PC to the Flash root directory of the subordinate member
(with member ID of 2).
ftp> get temp.bin slot2#flash:/temp.bin
# Use the ASCII mode to upload the configuration file config.cfg from the IRF fabric to the PC for
backup.
ftp> ascii
200 TYPE is now ASCII
ftp> put config.cfg back-config.cfg
local: config.cfg remote: back-config.cfg
150 Connecting to port 47461
226 File successfully transferred
3494 bytes sent in 5.646 seconds (618.00 kbyte/s)
ftp> bye
Internet
IRF (FTP client)
IP:
10.2.1.1/16
Master
(Member_ID=1)
Subordinate
(Member_ID=2)
10.1.1.1/16
FTP server
PC
Note: The orange line represents an IRF connection.

 Loading...
Loading...














