3 - 10
Transpector MPH Operating Manual
3.5 The Ion Detector
The ion detector region of the sensor consists of the quadrupole exit lens and the
detector itself. Often, the quadrupole exit aperture is biased negatively with respect
to the anode, focusing ions that have been transmitted through the quadrupole into
the detector element. The detector can be a simple Faraday Cup (FC), an Electron
Multiplier (EM), or a combination of both.
3.5.1 The Faraday Cup Detector
The Faraday Cup detector is typically a metal plate or a cup-shaped electrode, on
which the ion beam impinges. Ions strike the detector and are neutralized, thus
drawing a current from the circuitry connected to the electrode. Usually, the current
flow that results is exactly equal to the incident ion current. In Transpector MPH
instruments, the Faraday Cup is at ground potential.
The minimum sensitivity for a 100 amu Transpector MPH instrument equipped
with a simple Faraday Cup detector is typically 6 x 10
-4
amps per Torr. The
detected currents can be as small as 1 x 10
-15
amps for ultra-high vacuum levels.
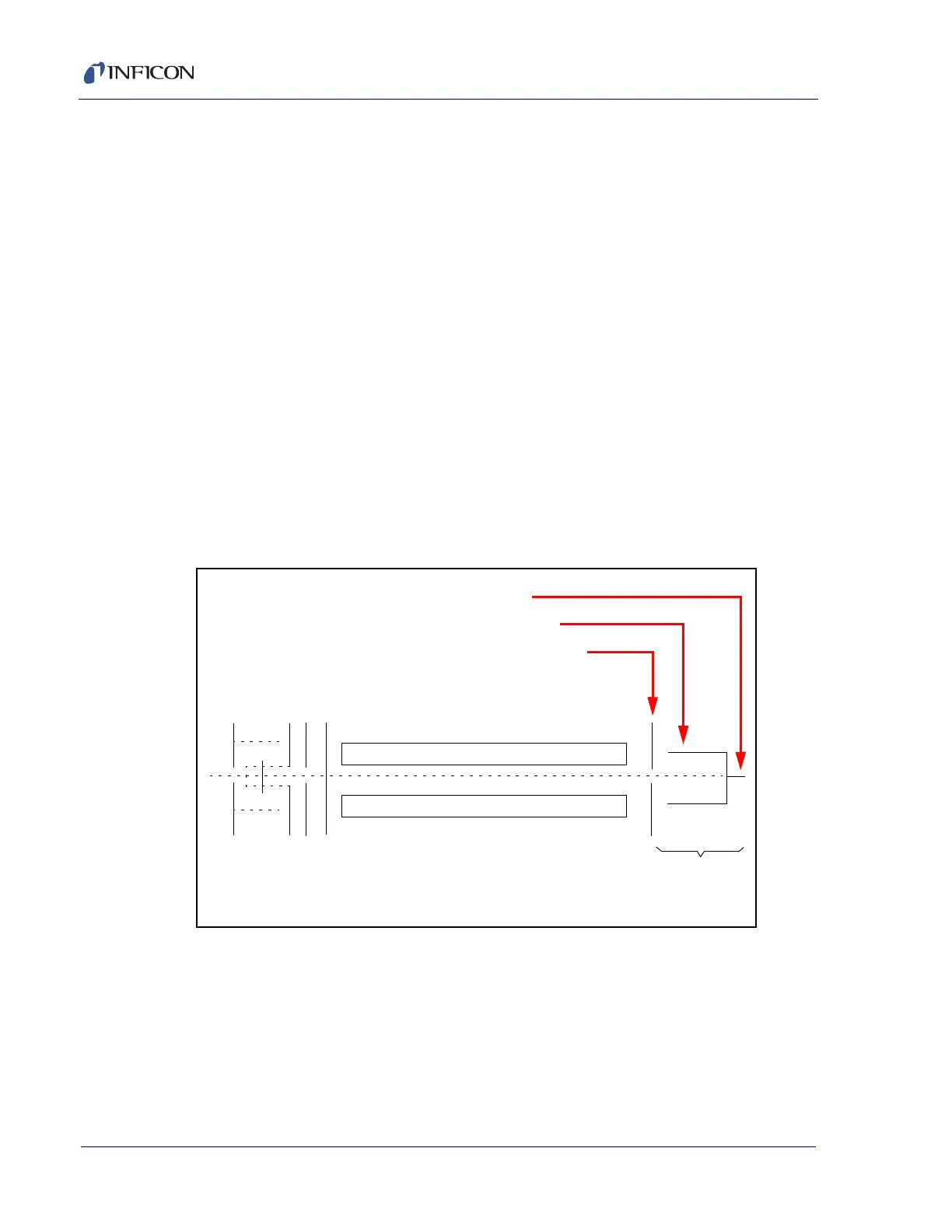
See Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 Faraday Cup Detector
Detector
Quadrupole Exit Lens
Faraday Cup
Signal Output
 Loading...
Loading...