Status Structure 14-17
Event registers
As Figure 14-1 shows, each status register set has an event register. When an event occurs,
the appropriate event register bit sets to 1. The bit remains latched to 1 until the register is reset.
Reading an event register clears the bits of that register. *CLS resets all four event registers.
The commands to read the event registers are listed in Table 14-6. For details on reading reg-
isters, see Reading registers.
Event enable registers
As Figure 14-1 shows, each status register set has an enable register. Each event register bit
is logically ANDed (&) to a corresponding enable bit of an enable register. Therefore, when an
event bit is set and the corresponding enable bit is set (as programmed by the user), the output
(summary) of the register will set to 1, which in turn sets the summary bit of the Status Byte
Register.
The commands to program and read the event enable registers are listed in Table 14-7. For
details on programming and reading registers, see Programming enable registers and Reading
registers.
NOTE The bits of any enable register can be reset to 0 by sending the 0 parameter value
with the appropriate enable command (i.e. STATus:OPERation:ENABle 0).
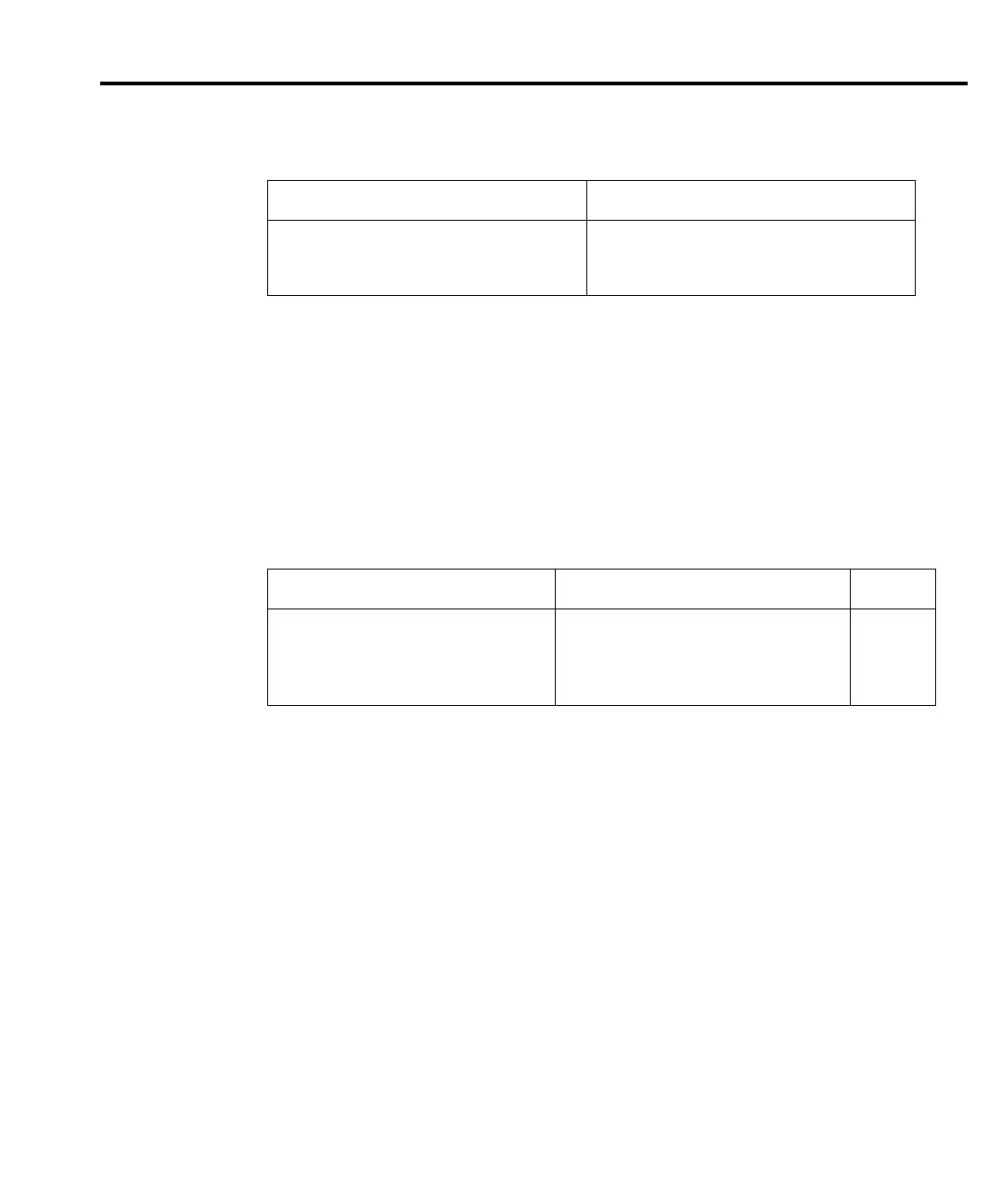
Table 14-5
Condition register commands
Command Description
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
:STATus:MEASurement:CONDition?
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Read Operation Condition Register.
Read Measurement Condition Register.
Read Questionable Condition Register.
Table 14-6
Event register commands
Command Description Default
*ESR?
:STATus:OPERation:[:EVENt]?
:STATus:MEASurement:[:EVENt]?
:STATus:QUEStionable:[:EVENt]?
Read Standard Event Status Register.
Read Operation Event Register.
Read Measurement Event Register.
Read Questionable Event Register.
Note
Note: Power-up and *CLS resets all bits of all event registers to 0. STATus:PRESet has no effect.
 Loading...
Loading...