Measurement Considerations F-5
Noise and source impedance
Noise can seriously affect sensitive current measurements. This section discusses how DUT
(device under test) resistance and capacitance affect noise performance.
DUT resistance
The resistance of the DUT will affect the noise performance of the ammeter. As the DUT
resistance is reduced, the noise gain of the ammeter will increase. Noise gain can be given by
the following equation:
Output V
NOISE
= Input V
NOISE
(1 + R
F
/R
DUT
)
where;
• Output V
NOISE
is noise seen at the output of the ammeter.
• Input V
NOISE
is the noise seen at the input of the ammeter.
• R
F
is the internal feedback resistance for the ammeter.
• R
DUT
is the resistance of the DUT.
Note that as R
DUT
decreases in value, the output noise increases. For example, when
R
F
= R
DUT
, the input noise is multiplied by a factor of two. Since decreasing the source resis-
tance can have a detrimental effect on noise performance, there are usually minimum recom-
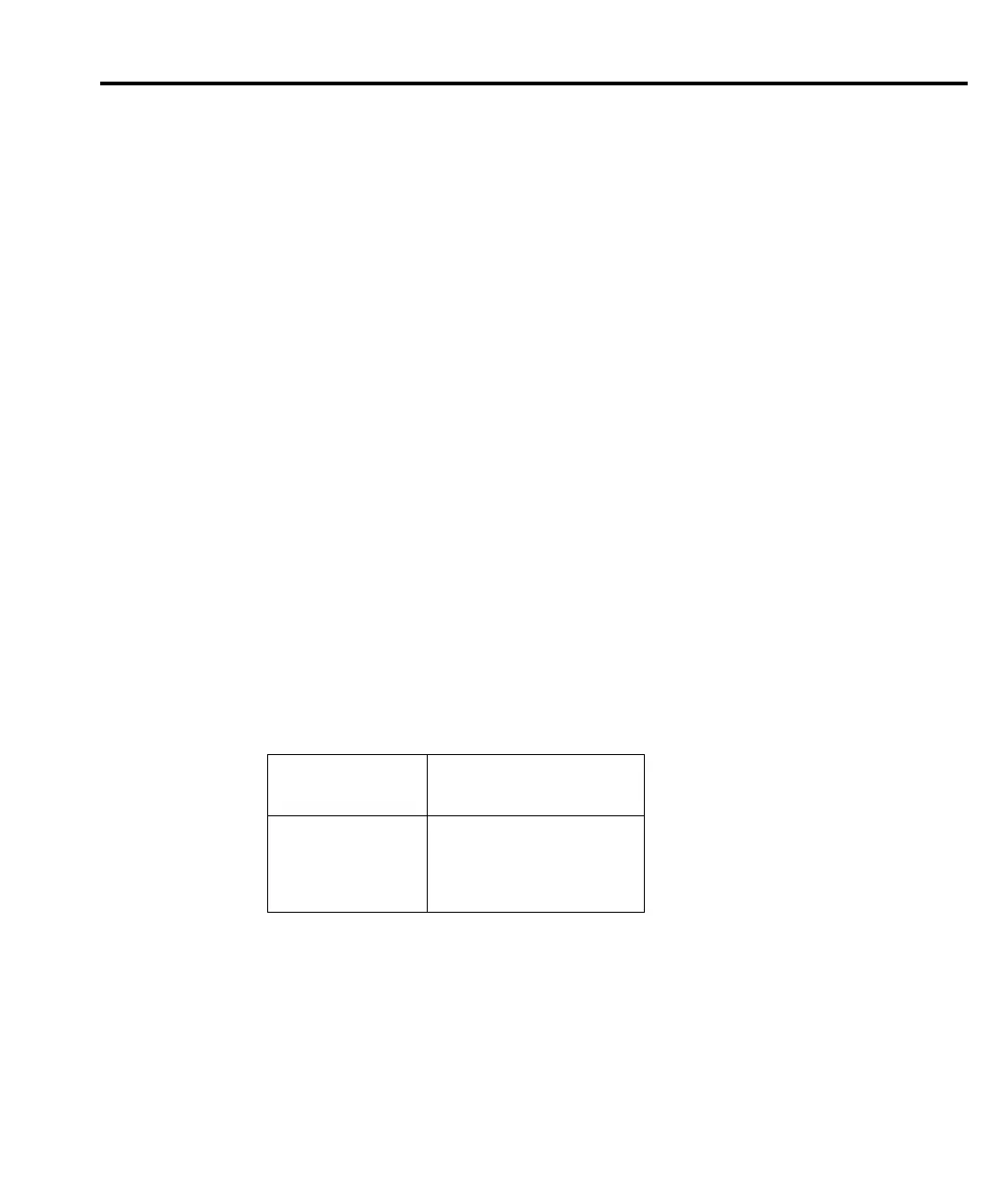
mended source resistance values based on measurement range. Table F-1 summarizes
minimum recommended source resistance values for various measurement ranges for the
ammeter. Note that the recommended source resistance varies by measurement range because
the R
F
value also depends on the measurement range.
Table F-1
Minimum recommended source resistance values
I-measure range
Minimum recommended
source resistance
1pA – 100pA
1nA – 100nA
1µA – 100µA
1mA – 100mA
1GΩ to 100GΩ
1MΩ to 100MΩ
1kΩ to 100kΩ
1Ω to 100Ω
 Loading...
Loading...