ESP32 Starter Kit
(continued from previous page)
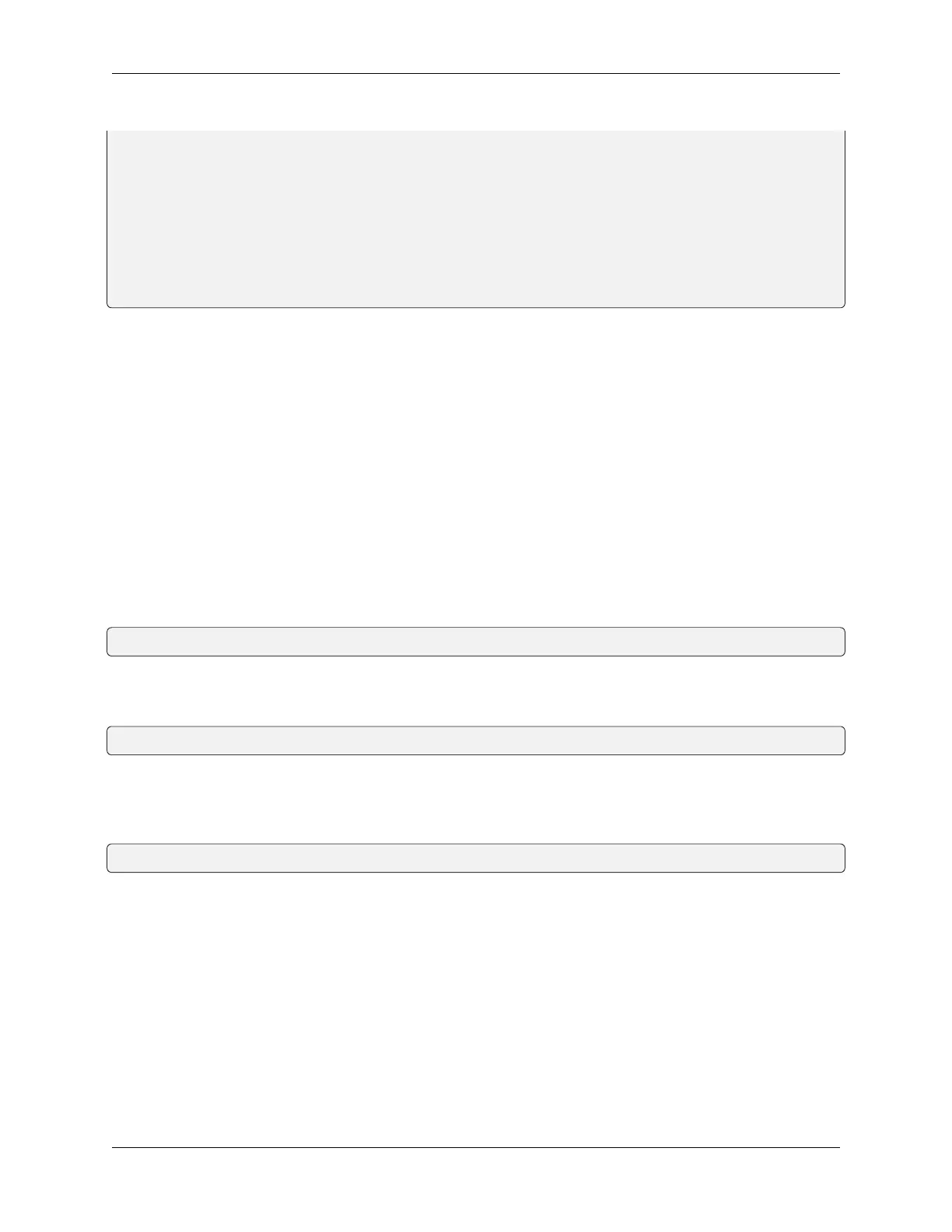
for (int i = 0; i < 255; i++) { //make light fade in
ledcWrite(CHN, i);
delay(10);
}
for (int i = 255; i > -1; i--) { //make light fade out
ledcWrite(CHN, i);
delay(10);
}
}
5. Test Result
After uploading the code, we can see that the LED dims gradually rather than all of a sudden. It “breathes” evenly.
6. Code Explanation
#define: It is used to define constants ( unchanged)
ledcSetup(): It is used to set the frequency and count bits corresponding to the LEDC channel (duty ratio resolution)
The first parameter chan represents the channel number, which ranges from 0 to 15, and can set 16 channels. The high-
speed channel (0 ~ 7) is driven by 80MHz clock, and the low-speed channel (8~ 15) is driven by 1MHz clock. The
second parameter freq is the desired frequency. The third parameter is the count number of duty ratio resolution, which
ranges from 0 to 20. (This value determines the writable value of duty ratio in the ledcWrite method. For example, if
the value is 10, the maximum value of duty ratio is 1023, that is, (1<<bit_num)-1.
double ledcSetup(uint8_t chan, double freq, uint8_t bit_num)
ledcAttachPin(): Its function is to bind the specified LEDC channel to the specified IO port to achieve PWM output.
The pin represents the IO port we want to output, and the channel is the LEDC channel we specify.
void ledcAttachPin(uint8_t pin, uint8_t channel);
ledcWrite(): Its function is the output duty cycle of the specified LEDC channel.
The chan is the LEDC channel we specify. The duty means duty cycle, whose range depends on the bit_num of the
ledcSetup() function.
void ledcWrite(uint8_t chan, uint32_t duty)
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i ++){ . . . }: It indicates that variable i ranges from 0 to 255, i++ means i increments by 1 each
time until the judgment expression i <= 255 is not satisfied. Otherwise, the code in braces is executed for 256 times in
total.
for (int i = 255; i >= 0; i –){ . . . }, i– indicates that i is reduced by 1 each time. If i>= 0 is not satisfied, the for() loop
is jumped out, and 256 times are executed in total.
i++ : The variable will add 1 per loop
For more details, please refer to the link:https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/
50 Chapter 8. Arduino Tutorial
 Loading...
Loading...