Microtronix Access User Guide
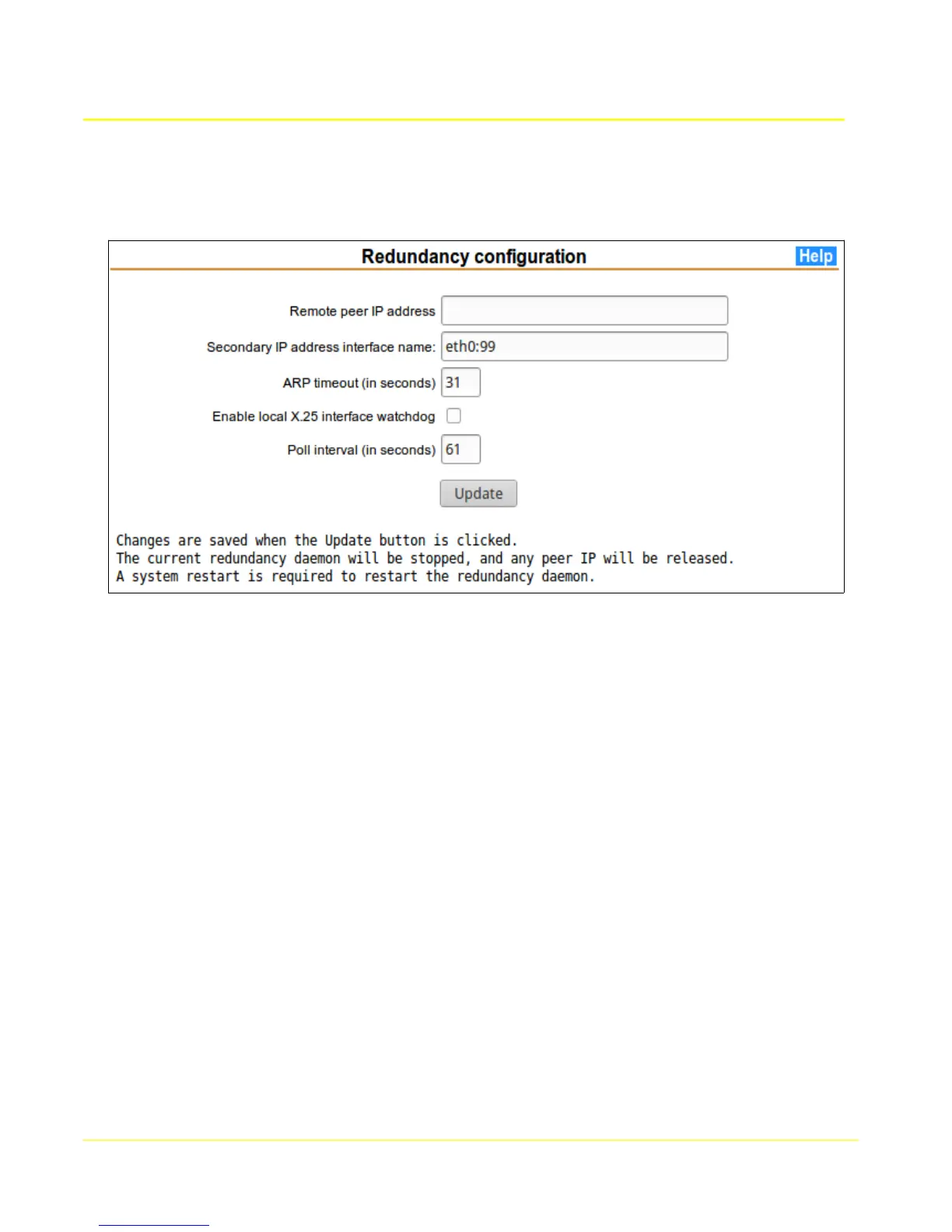
4.8 Redundancy
This page allows configuration of redundancy between a pair of Access units. One may be master, the
other slave, or they can be set up for co-redundancy.
Redundancy is accomplished by monitoring an IP address assigned to the peer unit. If that IP address
does not respond for any reason, the monitoring unit will assume it as its own secondary IP address.
In general, it is best for the monitered IP address to be a secondary IP address definition in the
monitored unit. This secondary IP address will be used for applications like X.25/TCP gateway, and the
primary used for configuration and management. It would be counter-productive for a unit to take over
anothers primary IP and “masquerade” its configuration and management interface.
4.8.1 Remote peer IP address
This is the IP address of the remote peer unit, preferably defined as a secondary IP address in the peer
unit. The secondary IP address in the peer unit is defined in the Ethernet page using Interface name
“eth0:0”.
4.8.2 Secondary IP address interface name
If the Remote peer IP address is taken over, it will be temporarily defined as a secondary IP address
using this interface name. If takeover has occurred, the temporary definition will appear in the table in
the Ethernet page.
4.8.3 ARP timeout
This is the number of seconds to wait for an arping response from the peer. If it expires without
response the peer, the IP takeover will occur.
33
 Loading...
Loading...