2-94
POWER TRAIN
-
Automatic Transaxle
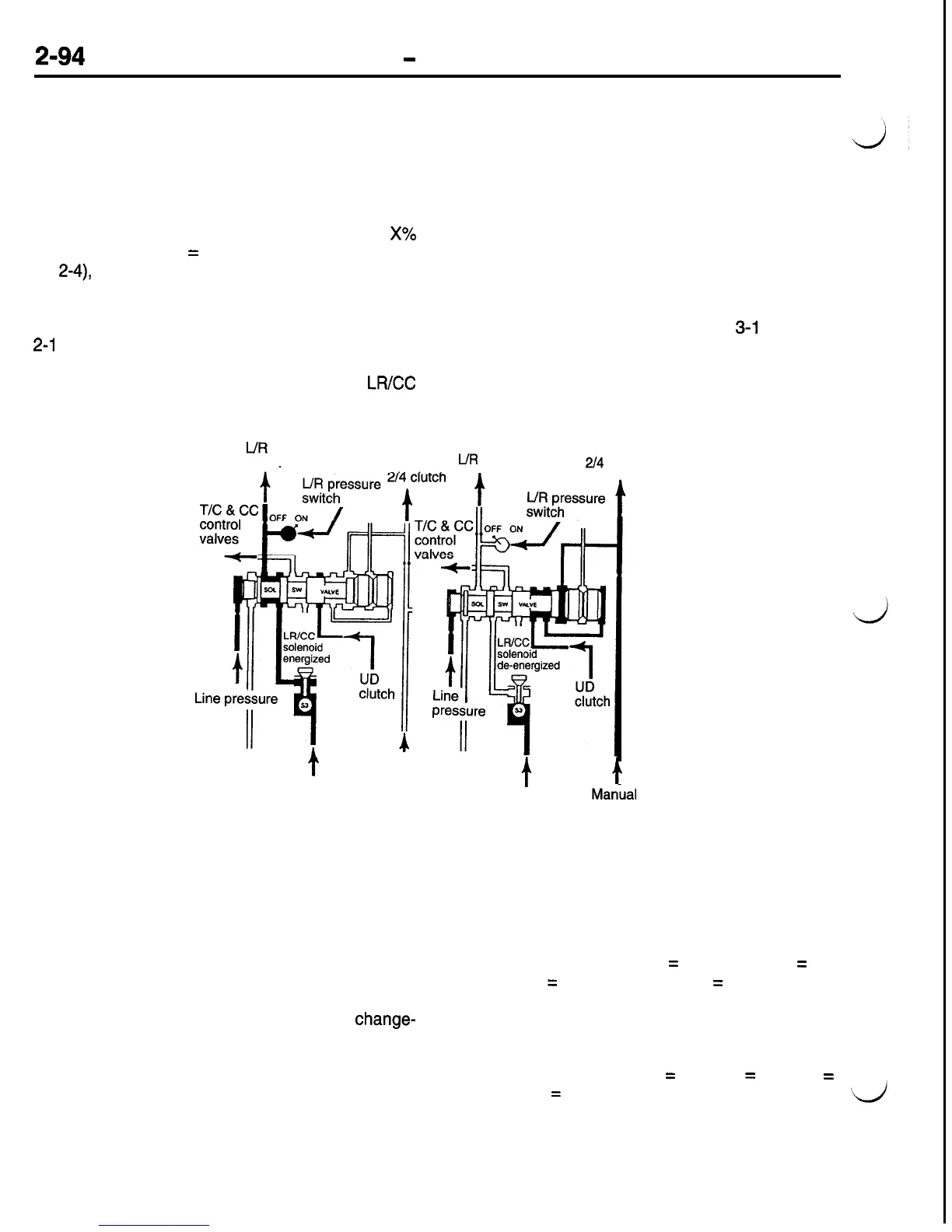
Solenoid Switch Valve Control Logic
This valve protects against the inadvertent applica-
tion of LR clutch in second, third, or fourth gear
ranges. When shifting to first gear, the Solenoid
Switch Valve (SSV) must be in the downshifted posi-
tion or action must be taken to shift the SSV into
the downshifted position. As long as any of three
pressures (2-4, OD, or UD) are greater than
X%
of line pressure (X
=
60% for UD and OD, 70%
for
2-4),
the SSV will remain upshifted. To confirm
that the SSV has downshifted, both the LR solenoid
and LR pressure switch must be high (voltage value
seen by TCM). To downshift the valve for 3-1 or
2-1
shifts, shift logic will briefly vent the UD clutch
(shift logic must vent the other two clutches also)
and test for valve motion by eneraizing the
LR/CC
L/R
clutch
solenoid and verifying that the LR pressure switch
turns on.
A SSV diagnostic trouble code will only be stored
if the transaxle operating temperature range is hot,
and the malfunction occurs at least three times.
The fault counter is reset during the start routine.
Under certain conditions, such as very cold fluid
temperatures, it is possible that the SSV valve may
not move as quickly as it normally would at operating
temperature. This slow response may occasionally
result in a second gear launch or a change mind
shift to second gear from a 2-l or
3-1
shift. No
diagnostic trouble code will be set if the transaxle
operating temperature range is cold.
UR
clutch
2/4
clutch
I
Manual
Manual
valve
valve
Clutch Apply Status
To execute the shift logic, the TCM must maintain
a continuous record of each clutch element apply
status. This is done by tracking the instantaneous
fluid volumes in each clutch circuit. Instantaneous
fluid volumes are tracked using predetermined flow
rates and learned “clutch fill volumes”. This is partic-
ularly useful for closely-spaced shifts or
change-
mind shifts.
Learned clutch fill volumes represent the volume
of fluid that is required to stroke a clutch piston
to the point where zero clutch pack clearance is
obtained. The clutch fill volume learn value is the
fill volume
without stroking the accumulator or pick-
ing up any torque load on the clutch. This learned
fill volume is updated for each clutch element as
it wears and clutch pack clearance increases.
Manual
valve
Manual
valve
The Clutch Volume Index (CVI) display of the scan
tool (MUT-II) can be used to view learned clutch
fill volumes for each clutch. The normal range for
clutch fill volumes are LR
=
35 to 85, OD
=
75
to 150, 2-4
=
20 to 77, and UD
=
24 to 70.
If the battery feed is disconnected from the TCM,
the learned clutch fill volumes will be lost, and initial
values will be substituted until correct values can
be re-learned. Shifting may be somewhat harsh.
The initial values are; LR
=
64, OD
=
89, 2-4
=
48, and UD
=
45.
A transmission which has experienced a sudden
clutch failure may not be capable of learning the
correct values. A road test of a transaxle with this
condition may exhibit an upshift runaway condition,
but have acceptable clutch fill volumes.

 Loading...
Loading...











