ENGINE <NON-TURBO>
-
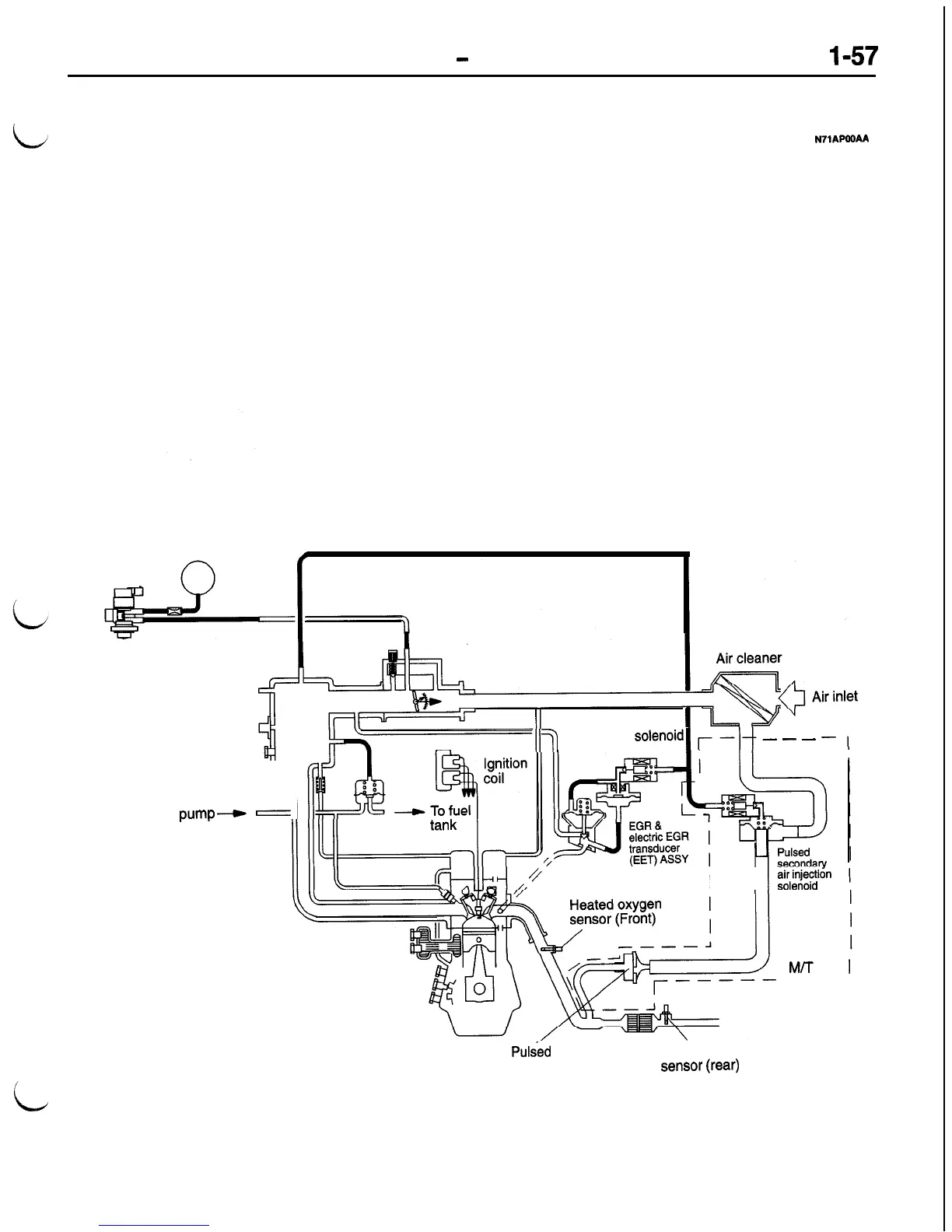
Emission Control System
I-57
L
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
There are three sources of vehicle exhaust emis-
sions generated: the exhaust gases resulting from
combustion, the blow-by gases generated within
the crankcase, and the evaporative emissions gen-
erated from the fuel tank and other components
of the fuel line.
The emissions-control system, which is designed
to control the discharge of these exhaust gases
into the atmosphere, is composed of the following
system components.
(1) Exhaust emission control system
(2) Crankcase emission control system
(3)
Evaporative emission control system
Canister
Evaporative emission
purge solenoid
r
From fuel
pump
Positive
crankcase
ventilation
valve
1
+-
N71APOOAA
The exhaust emissions-control system reduces the
amount of carbon monoxide, hydro carbon and ox-
ides of nitrogen in the exhaust gases by adding
the exhaust gas recirculation device and the catalytic
converter to fundamental improvements such as
an improvement of the combustion chamber and
the camshaft, as well as other improvements to
the engine such as feedback control of the air/fuel
ratio by the electronically controlled fuel injection
system.
The crankcase emissions-control system is a closed
type so that blow-by gases are not discharged out
to the atmosphere. The evaporative emissions-con-
trol system is the canister type; vapors that are
generated within the fuel tank are introduced into
the intake manifold and are cornbusted so that they
are not emitted out to the atmosphere.
/I
Electric EGR
‘3
transducer
solenoid1
_
-
_
_
,
I
i
,
MIT
only
1
----
Pulskd
secondary
air injection valve
Heated oxygen
sensor
(rear)
A F U 0 0 6 3
i

 Loading...
Loading...











