ENGINE <NON-TURBO>
-
Control System
I-45
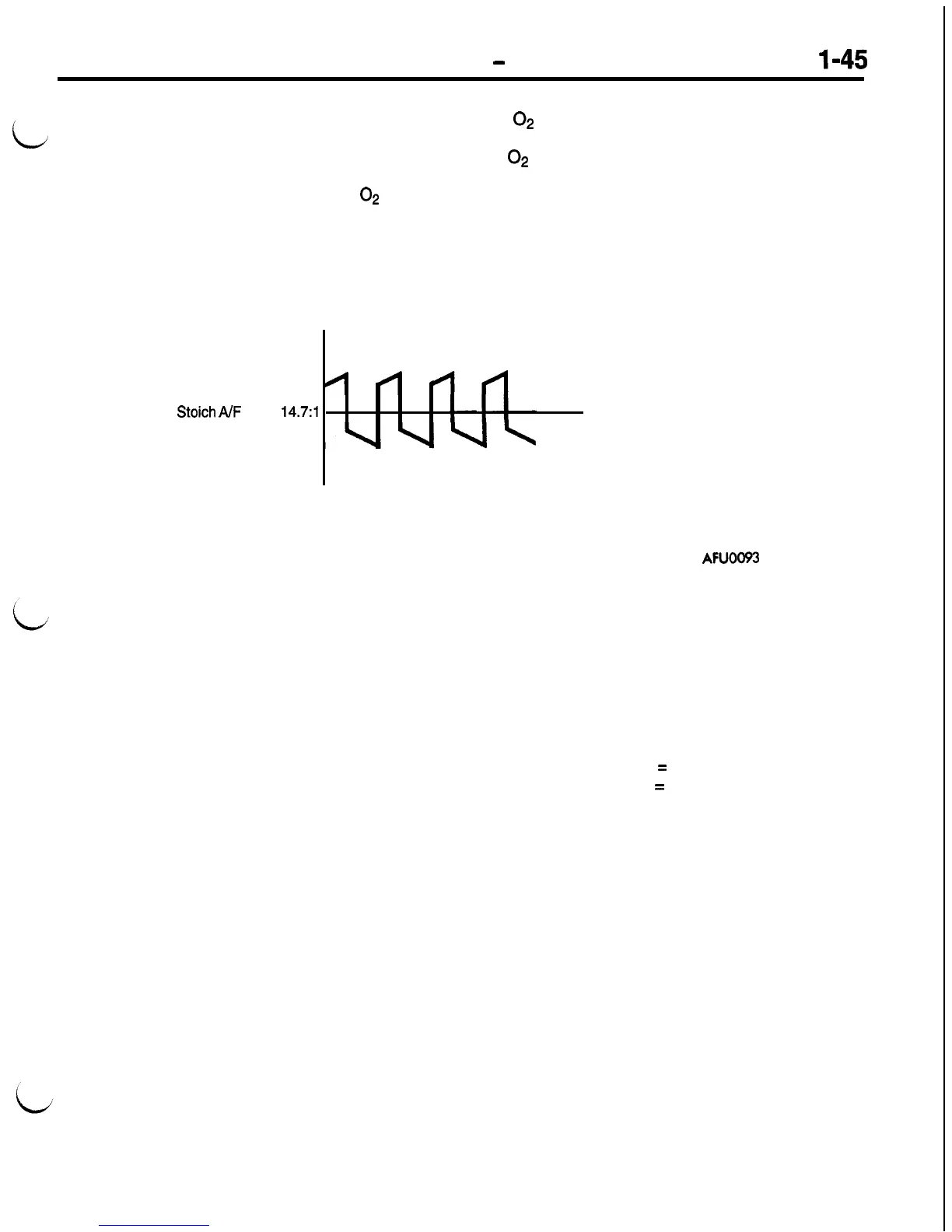
If the oxygen sensor registers a rich or lean condition
L
while driving in this cell, the cell will require updating
to aid in fuel control. The short term correction is
used first. It starts increasing pulse width quickly
(kick), then ramps up slowly. Each control is in in-
verse relation to the signal sent from the
02
sensor.
For example:
The 02 sensor switches lean to rich. Short term
compensation kicks in lean, then ramps lean until
the
02
sensor switches lean. At this point short
term compensation reverses the process.
Stoich
AIF
ratio
14.7:1
.
AFU0093
If the oxygen sensor shows lean, the short term
compensation goes rich and multiplies the pulse
width from long term memory in that cell by an
amount greater than 1. If the sensor shows rich,
the short term compensation drives the pulse width
narrower by multiplying by a number less than 1
(perhaps 0.97). The short term compensation can
multiply pulse width by as much as 1.25 or as little
as 0.75 to compensate for lean or rich conditions.
In this way, the short term compensation can in-
crease pulse width by up to 25% (by multiplying
by 1.25) or decrease pulse width by up to 25%
(by multiplying by 0.75).
Example:
Pulse width 0.05 x 1.25
=
0.0625 (increase of 25%)
Pulse width 0.05 x 0.75
=
0.0375 (decrease of 25%)

 Loading...
Loading...











