Chapter 4 Microscopy Techniques
84
Advantages of Ph microscopy
• Ph microscopy is highly effective in detecting phase contrast. It is said that an optical path phase contrast
of up to about 1/1000λ can be detected.
• The image view remains the same regardless of the direction of the specimen placed.
• By using an annular diaphragm for bright field on the condenser side, BF microscopy can be performed
without changing the Ph objective.
Disadvantages of Ph microscopy
• If the phase contrast between specimens is too large (as with thick specimens), brightness and darkness
might be reversed or image quality might be deteriorated significantly.
• Because of a halo phenomenon, which looks like a shading, occurring at the boundary in a large structure,
the fine structure at the periphery might disappear.
Objective using an apodization phase plate
To emphasize the fine structure by reducing halo, use of an objective with an apodization phase plate is
recommended.
An apodization phase plate has a special absorption film around the phase film. The feature of the
apodization phase plate is to provide low contrast with diffracted light weakened by a large structure of
diameter 10 μm or more, while the contrast of fine structure of diameter 10 μm or less is left as is.
4.2.2 Optical Elements Required for Ph Microscopy
Ph microscopy requires the following components as well as the status of bright field.
• Ph objective (including the phase ring in the figure “Optical path diagram for Ph microscopy”)
• Ph module (equivalent to the annular diaphragm in the figure “Optical path diagram for Ph microscopy”)
• Condenser lens
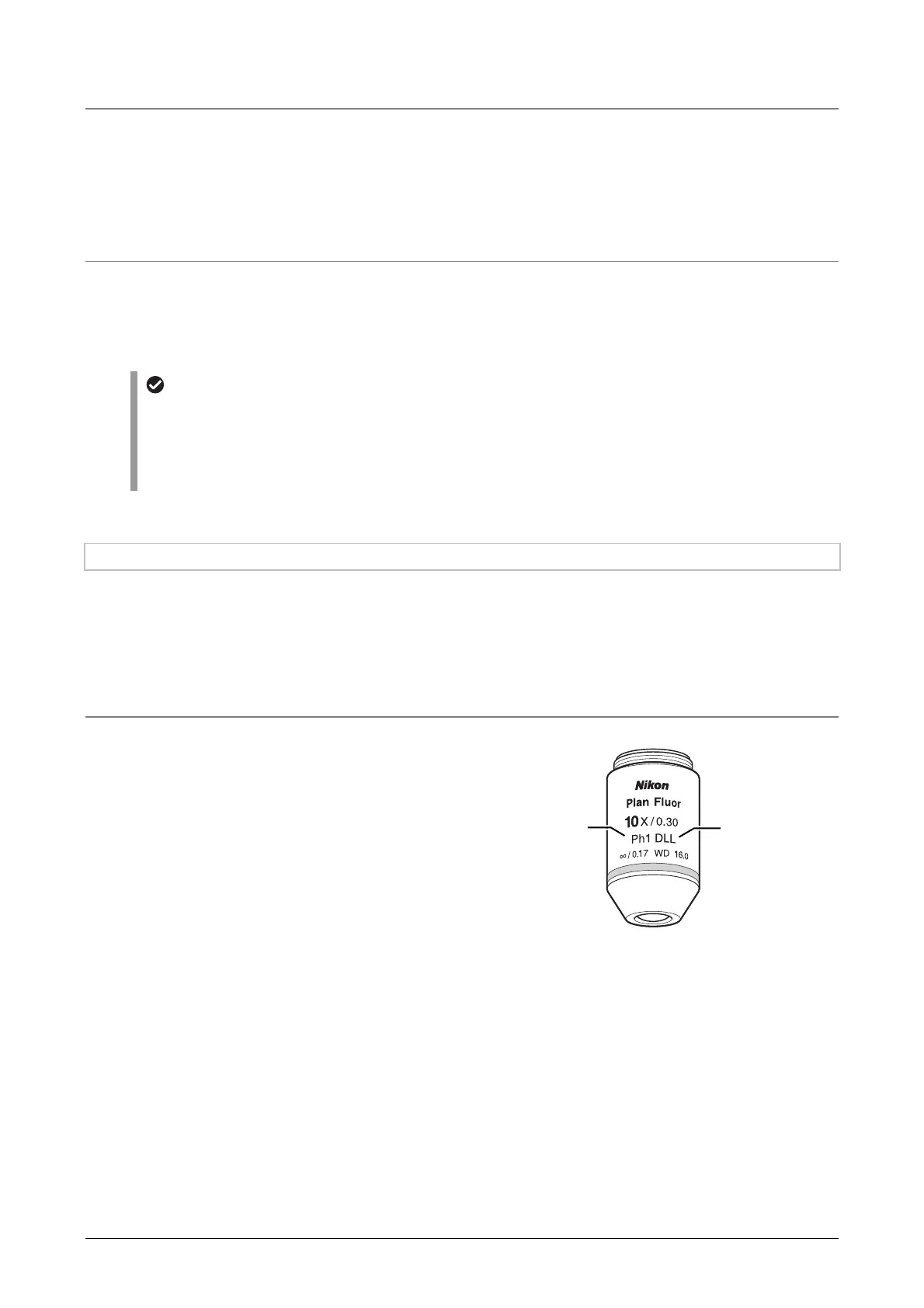
Ph objective (including the phase ring in the figure “Optical path diagram for Ph microscopy”)
Depending on the color aberration and correction
degree of curvature of the image plane, Ph
objectives are classified as Achromat, Plan Achromat,
Plan Fluor, and Plan Apochromat. In addition, these
lenses can also be grouped into several types
according to the characteristics of the internal phase
ring. Satisfactory microscopy cannot be performed
unless the phase contrast of specimens and the
characteristics of the phase ring match.
See the following table for use characteristics of
phase contrast objectives.
Example of a Ph contrast objective
Characteristics of Ph
ring
•
DLL
•
DL
•
DM
•
BM
•
ADL
•
ADH
Ph code
•
PhL
•
Ph1
•
Ph2
•
Ph3
•
Ph4
 Loading...
Loading...