Chapter 4 Microscopy Techniques
100
4.6 Details of NAMC Microscopy
4.6.1 Principles of NAMC Microscopy
NAMC microscopy (Nikon Advanced Modulation
Contrast) is a method of observing colorless,
transparent specimens such as living cells in an
unstained way using dia-illumination.
Objects that change the amplitude of light are called
amplitude objects (such as transparent objects, or
stained objects) and objects that change the phase
of light are called phase objects (such as colorless,
transparent specimens, or living cells). NAMC
microscopy visualizes phase objects, which are
unrecognizable to the human eye.
Visualizing phase objects
The illumination that has reached the specimen
changes the refractive direction according to the
refractive index and the shape of the phase object.
Use of a slit aperture diaphragm and modulator
enables optical elements of different transmittance to
pass according to the slope of the position in the
specimen where the illumination passes. For
example, when a trapezoidal phase object is
observed, the left side is bright, the top is gray, and
the right side is dark and modulated in the obtained
image.
Refraction of beams in a phase object
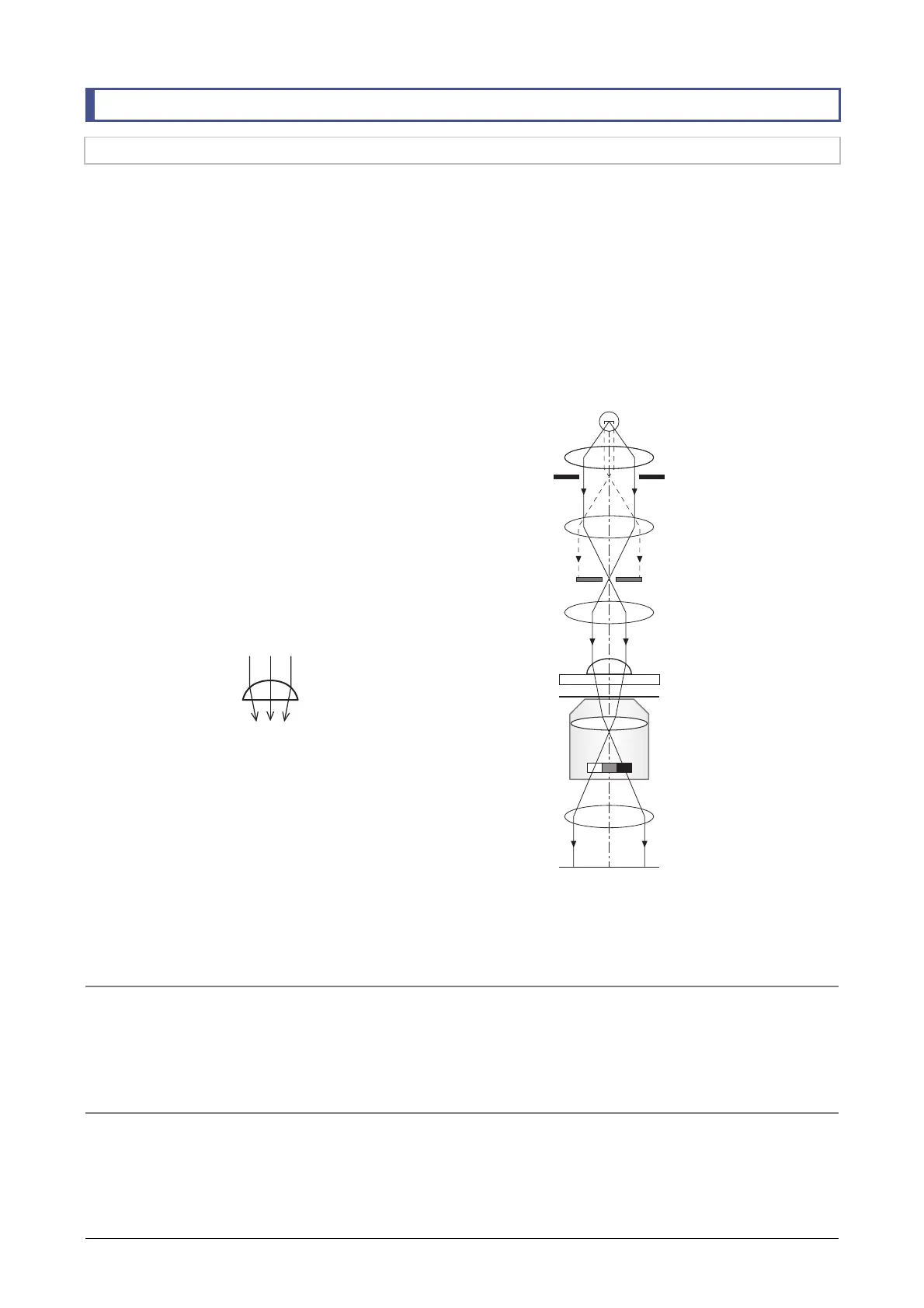
NAMC microscopy optical system
The NAMC microscopy optical system is shown in
the following figure.
The light emitted from the light source is narrowed in
a rectangular shape by the slit diaphragm. It passes
the condenser lens, and then obliquely illuminates
the specimen. The illumination changes the direction
of movement according to the shape of the specimen.
After passing through the objective for modulation
microscopy, the illumination passes through different
portions of the modulator in the objective. The
modulator is an optical element having three-level
transmittance. Depending on the slope of the shape
of the specimen through which the beams pass, the
modulator provides three levels of brightness. As a
result, 3D modulation contrast images similar to
those obtained in DIC microscopy are formed.
Optical path diagram of NAMC microscopy
Advantages of NAMC microscopy
• NAMC microscopy enables observation of thick specimens, such as egg cells, usually not suited to Ph
microscopy.
• NAMC microscopy does not use polarized beams, unlike DIC microscopy, so even if specimens have
polarization properties (such as plastic dishes), contrast is maintained.
Disadvantages of NAMC microscopy
• This microscopy is limited to specimens that have images with orientation (adjustment is possible) and
have a slope of shape in the direction of illumination.
• Resolution of this microscopy is poor as compared with Ph microscopy and DIC microscopy.
Bright Dark
Phase objects
Light source
Collector lens
Field diaphragm
Field lens
Slit aperture diaphragm
Condenser lens
Specimen
Objective
Modulator
2nd tube lens
Image plane
 Loading...
Loading...