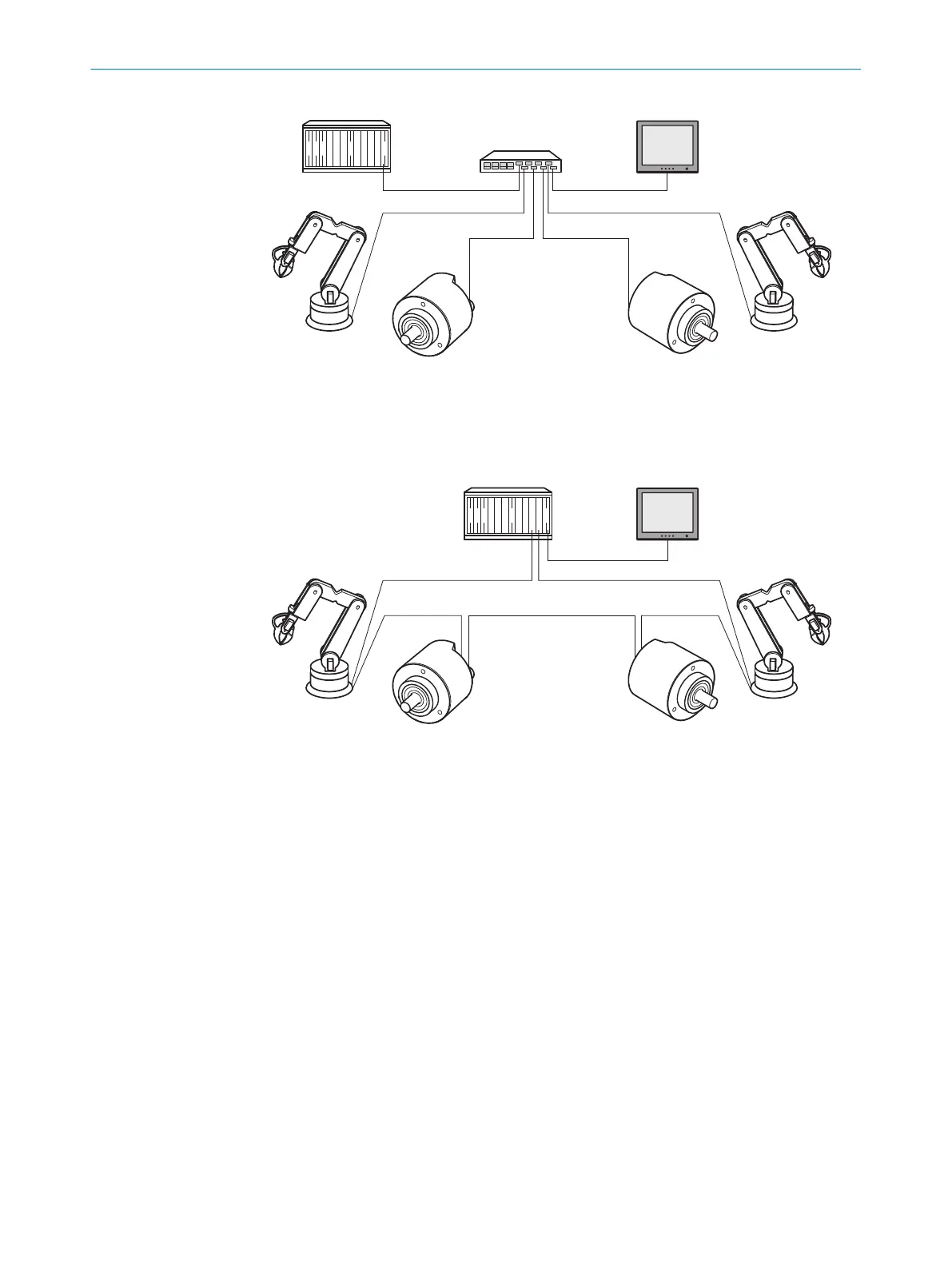
Figure 4: Example of an EtherNet/IP network in a star structure
However, to achieve greater availability and reduce the wiring work required, the system
can also be integrated in a device level ring (DLR).
Figure 5: Example of an EtherNet/IP network in a device level ring
3.4.2 Communication in EtherNet/IP
MAC address
Each encoder is assigned a globally unique MAC address as device identification at
the factory. This serves for the identification of the Ethernet node. This 6-byte device
identification cannot be changed and consists of the following components:
•
3 byte ident number
•
3 byte device identifier
TCP/IP and UDP/IP
EtherNet/IP uses TCP/IP or UDP/IP for communication.
The IP address is necessary for identification. This is permanently entered for the
encoder via address switches or obtained via DHCP server.
If the IP address is fixed, only the least significant byte can be set. 192.168.1.xxx is
fixed.
In addition, the subnet mask (default = 255.255.255.0) and, if necessary, a gateway
must be configured in the network.
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
16
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | AFS/AFM60 EtherNet/IP 8014213/1EF3/2021-12-08 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

 Loading...
Loading...