Configuration
5.3 Examples
1FN3 linear motors
Configuration Manual, 10/2018, 6SN1197-0AB86-0BP2
125
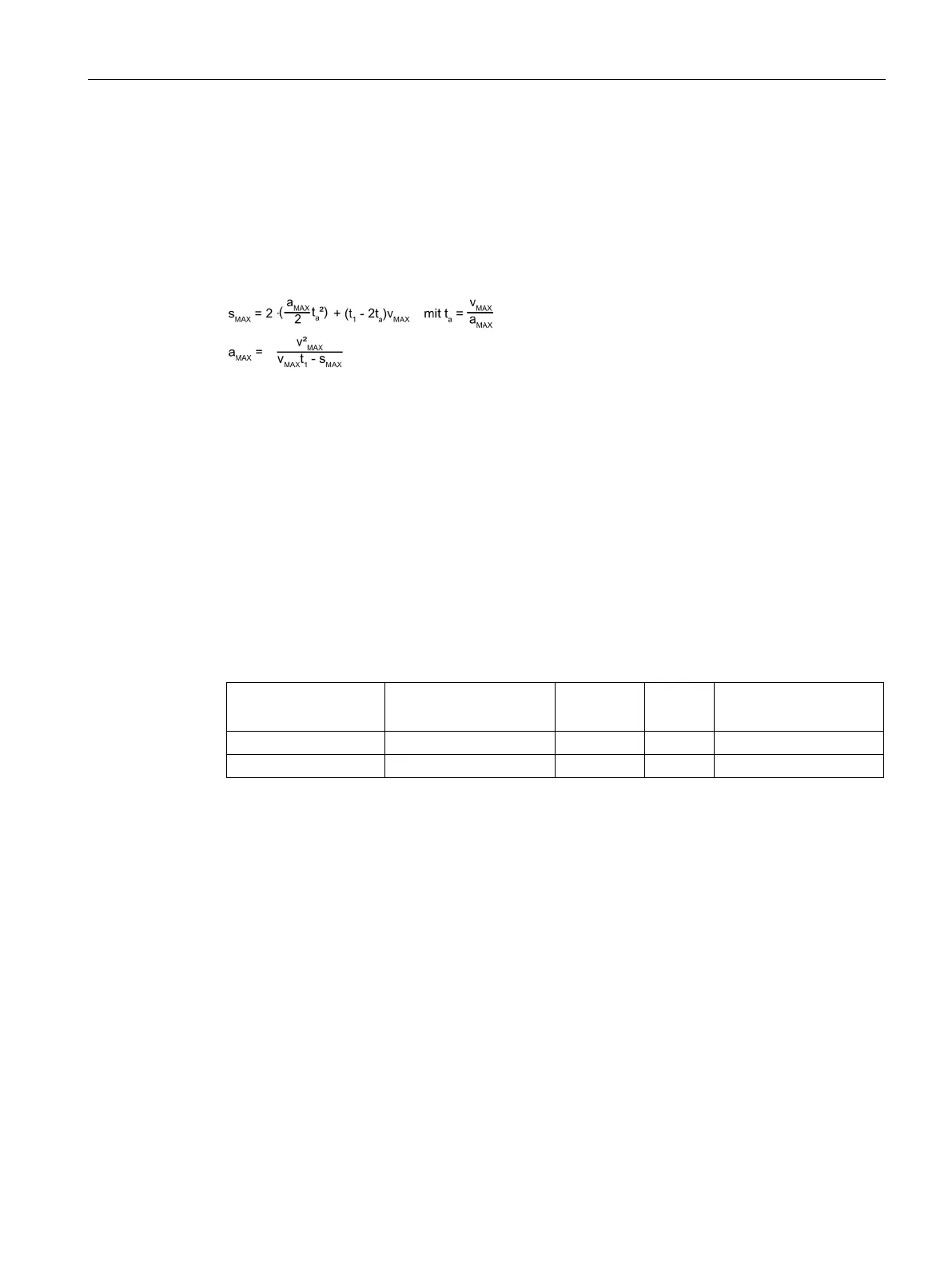
Otherwise, the duration of time t
1
will not be long enough to position the motor at s
MAX
. In the
current example, the following must apply for the maximum velocity of the motor:
v
MAX
≥ 1.24 m/s = 74.3 m/min
A higher acceleration a
MAX
must be used than with the previous profile so that the motor can
be positioned in the same time t
1
. At the defined maximum velocity, this acceleration can be
calculated:
A primary section can be selected using this data.
Preselection of the primary sections
To avoid restricting the configuration too much, a maximum velocity of
MAX
vMAX = 1.5 m/s = 90 m/min
is assumed. With this condition for the maximum velocity,
only a few primary sections are eliminated from the selection.
This results in
MAX
2
for the acceleration. The maximum force F
L,MAX
that the motor
must produce during the duty cycle is calculated as follows:
F
L,MAX
= m ‧ a + F
r
= 50 kg ‧ 41 m/s
2
+ 100 N
L,MAX
For this example, the following motors are suitable (see motor data sheets):
m
Motor
(with precision cooler)
Checking the mechanical constraints
You must now check two points:
● Is the reserve force of the selected primary section also sufficient for the mass of the
primary section (which has not yet been taken into account)?
● Is the effective force of the duty cycle F
eff
below the permissible rated force of the motor
F
N
?

 Loading...
Loading...