MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide 204
UG984 (v2018.2) June 21, 2018 www.xilinx.com
Chapter 5: MicroBlaze Instruction Set Architecture
beqi
Branch Immediate if Equal
beqi
rA, IMM
Branch Immediate if Equal
beqid
rA, IMM
Branch Immediate if Equal with Delay
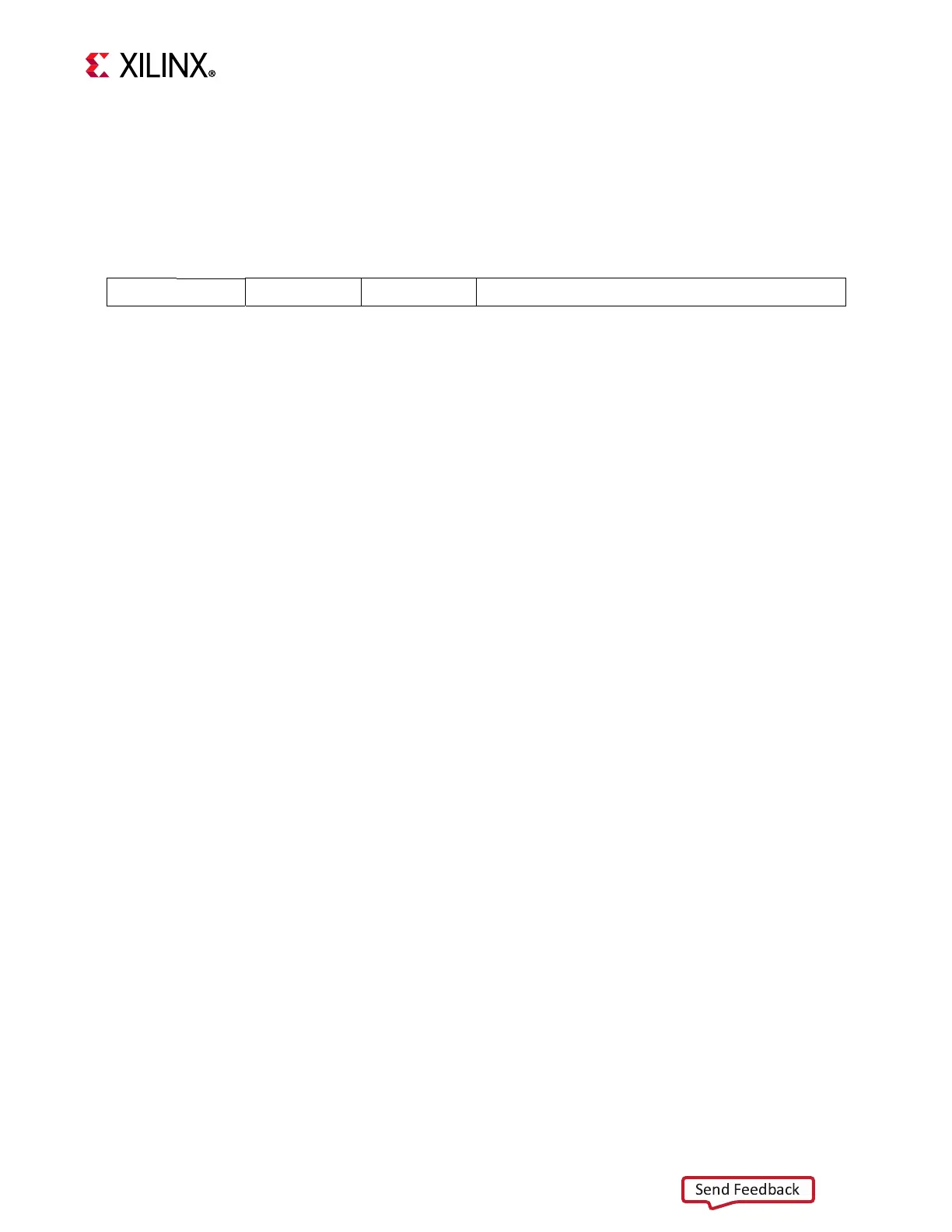
1 0 1 1 1 1 D 0 0 0 0 rA IMM
0 6 11 16
31
Description
Branch if rA is equal to 0, to the instruction located in the offset value of IMM. The target of the branch
will be the instruction at address PC + IMM.
The mnemonic beqid will set the D bit. The D bit determines whether there is a branch delay slot or
not. If the D bit is set, it means that there is a delay slot and the instruction following the branch (that
is, in the branch delay slot) is allowed to complete execution before executing the target instruction.
If the D bit is not set, it means that there is no delay slot, so the instruction to be executed after the
branch is the target instruction.
Pseudocode
If rA = 0 then
PC ← PC + sext(IMM)
else
PC
← PC + 4
if D = 1 then
allow following instruction to complete execution
Registers Altered
•PC
Latency
• 1 cycle (if branch is not taken, or successful branch prediction occurs)
• 2 cycles (if branch is taken and the D bit is set)
• 3 cycles (if branch is taken and the D bit is not set, or a branch prediction mispredict
occurs with
C_AREA_OPTIMIZED=0)
• 7-9 cycles (if a branch prediction mispredict occurs with
C_AREA_OPTIMIZED=2)
Notes
By default, Type B Instructions will take the 16-bit IMM field value and sign extend it to 32 bits to use
as the immediate operand. This behavior can be overridden by preceding the Type B instruction with
an imm instruction. See the instruction
“imm” for details on using 32-bit immediate values.
A delay slot must not be used by the following: imm, branch, or break instructions. Interrupts and
external hardware breaks are deferred until after the delay slot branch has been completed.
 Loading...
Loading...









