Scalar Analysis Measurement with User Flatness Corrections,
Example 4
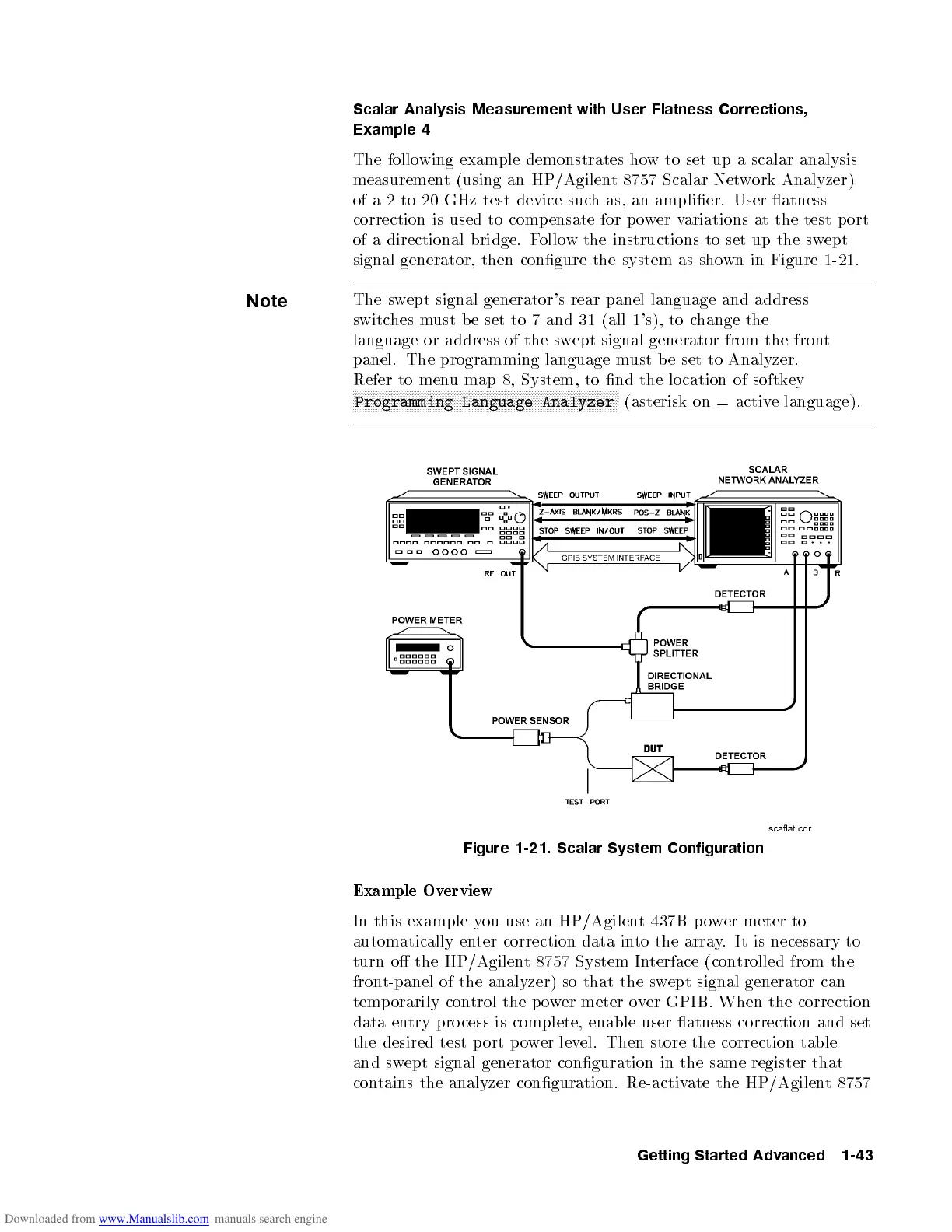
The following example demonstrates how to set up a scalar analysis
measurement (using an HP/Agilent 8757 Scalar Network Analyzer)
of a 2 to 20 GHz test device such as, an amplier. User atness
correction is used to comp ensate for p ower variations at the test port
of a directional bridge. Follo w the instructions to set up the swept
signal generator, then congure the system as shown in Figure 1-21.
Note
The swept signal generator's rear panel language and address
switches must be set to 7 and 31 (all 1's), to change the
language or address of the swept signal generator from the front
panel. The programming language must be set to Analyzer.
Refer to menu map 8, System, to nd the lo cation of softkey
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Programming Language Analyzer
(asterisk on = active language).
Figure 1-21. Scalar System Configuration
Example Overview
In this example you use an HP/Agilent 437B power meter to
automatically enter correction data into the array. It is necessary to
turn o the HP/Agilent 8757 System Interface (controlled from the
front-panel of the analyzer) so that the swept signal generator can
temporarily control the p ower meter over GPIB. When the correction
data entry pro cess is complete, enable user atness correction and set
the desired test port power level. Then store the correction table
and swept signal generator conguration in the same register that
contains the analyzer conguration. Re-activate the HP/Agilent 8757
Getting Started Advanced 1-43

 Loading...
Loading...