Model 8640B TM 9-4935-601-14-7&P Model 8640B TM 9-4935-601-14-7&P
SERVICE SHEET 9A
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
General
When either the AM or FM modulation select switch is set to INT, the
Modulation Oscillator is enabled. The oscillator feeds a signal with a
frequency selected by the MODULATION FREQUENCY switch into the
AM or FM modulator circuits and to the AM or FM front panel OUTPUT
ports. The variable-frequency modulation oscillator, shown on this Service
Sheet, is supplied with Option 001.
Modulation Oscillator (A11)
The Modulation Oscillator is a Wein-bridge type. Transistors Q7 to Q12
form a differential amplifier. The gate of FET Q11 is a high impedance
non-inverting input of the amplifier. Transistor Q12 is an emitter-follower
buffer amplifier. Trimmer capacitor C9 compensates for the high
frequency phase shift of the amplifier. Transistors Q9 and Q10 provide
voltage gain and drive the complementary symmetry output transistors Q7
and Q8. The inverting input to the amplifier is the emitter of Q9. Diodes
CR2 to CR4 bias and thermally compensate Q7 and Q8. Components
R19, C11, and C12 frequency compensate the amplifier. Resistor R26
provides negative dc feedback.
A frequency-selective Wein ladder forms a positive feedback path. This
network is a band pass filter with zero phase shift at the maximum of the
pass band. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the resistors and
capacitors of the ladder. In the FIXED FREQ range, C6 and C7 are the
ladder capacitors and either R2 and R6 or R3 and R5 in parallel with R6
are the resistors. In the variable frequency ranges, C1A and C1B are the
variable ladder capacitors and R1 and R4 (each in parallel with one or
none of the resistors on the A11A1 Frequency Select Switch) are the
resistors. Capacitors C2, C3, C4, and C5 set the frequency end points and
maximize flatness for a given frequency range. The negative feedback
path is a voltage divider in which the amount of feedback is determined by
the output signal level. The amount of feedback adjusts to maintain
oscillation at a constant amplitude. The voltage divider consists of R28
and RT1, a thermistor assembly. Diodes VR1, VR2, CR5, and CR6 add a
small amount of odd-harmonic distortion to stabilize the amplitude
characteristic of the oscillator.
Buffer Amplifiers (A11)
Transistors Q1 to Q4 form the AM/FM Output Buffer Amplifier which is
similar in operation to the oscillator output amplifier. Gain of the amplifier
is adjusted by R40. The outputs drive the external AM or FM ports.
Resistors R34, R35, and R36 attenuate the oscillator output to a level of
Fixed-Frequency Modulation
Oscillator (A11, A13)
SERVICE SHEET 9
SERVICE SHEET 9A (Cont'd)
0.84 Vrms. Transistor Q5 drives the FM PEAK
DEVIATION potentiometer (Service Sheet 6), and
Q6 drives the AM MODULATION potentiometer
(Service Sheet 14).
TROUBLESHOOTING
It is assumed that a problem has been isolated to
the variable-frequency modulation oscillator as a
result of using the troubleshooting block diagrams.
Troubleshoot by using the test equipment listed
below, performing the initial test conditions and
control settings, and following the procedures
outlined in the table.
Test Equipment
Digital Voltmeter........................ HP 3480B/3484A
Oscilloscope ..................... HP 180A/1801A/1820C
Initial Test Conditions
Top and bottom covers removed (see Service
Sheet F for removal procedure). Extend All
Variable-Frequency Modulation Oscillator
Assembly on extender board (see Service Sheet
C for removal procedure).
Initial Control Settings
AM ................................................................. INT
AUDIO OUTPUT LEVEL...................................cw
MODULATION FREQUENCY........400 Hz (Fixed)
Amplitude Stability and Distortion
The signal level of the oscillator is adjusted (by
selection of R28) for best compromise between
harmonic distortion and amplitude stability
(squegging at turn-on or range change). See
Table 5-1, Factory Selected Components.
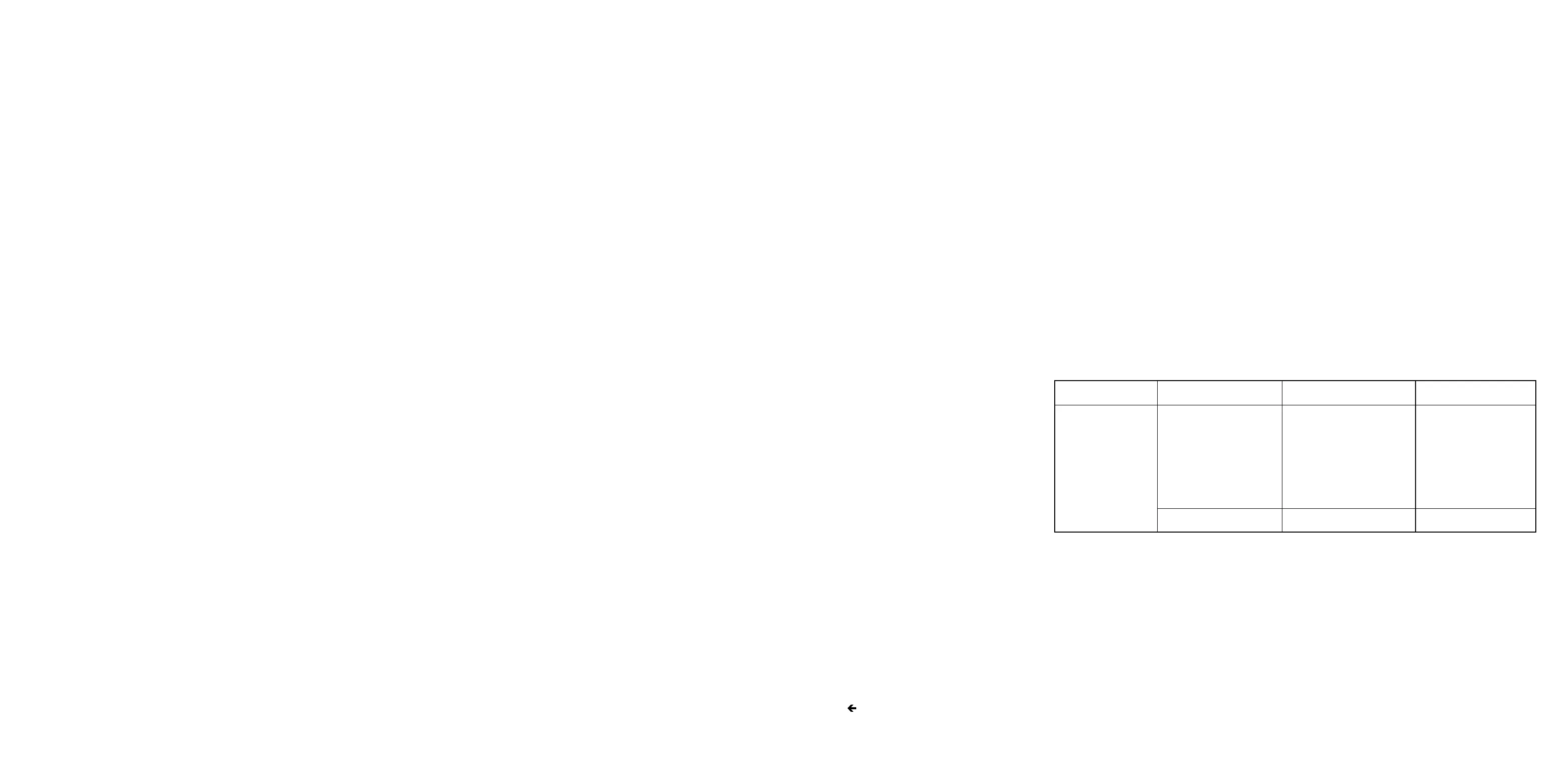
Variable-Frequency Modulation Oscillator Troubleshooting
Component Test Conditions and Normal Indication If Indication
or Circuit Control Settings is Abnormal
MODULATION Initial conditions and Peak-to-peak voltages are Check appropriate
OSCILLATOR settings. Then set as shown on schematic circuit and replace
ASSY (A11) MODULATION FRE- faulty component
QUENCY to 1000 Hz
(fixed) and to each of
the variable ranges
(X1, X10, etc.)
Vary the vernier on
each range.
Set AM to OFF DC voltages are as shown Replace faulty compon-
on schematic ent
8-36
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com
 Loading...
Loading...