163
2467S–AVR–07/09
ATmega128
Serial
Peripheral
Interface – SPI
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) allows high-speed synchronous data transfer between the
ATmega128 and peripheral devices or between several AVR devices. The ATmega128 SPI
includes the following features:
•
Full-duplex, Three-wire Synchronous Data Transfer
• Master or Slave Operation
• LSB First or MSB First Data Transfer
• Seven Programmable Bit Rates
• End of Transmission Interrupt Flag
• Write Collision Flag Protection
• Wake-up from Idle Mode
• Double Speed (CK/2) Master SPI Mode
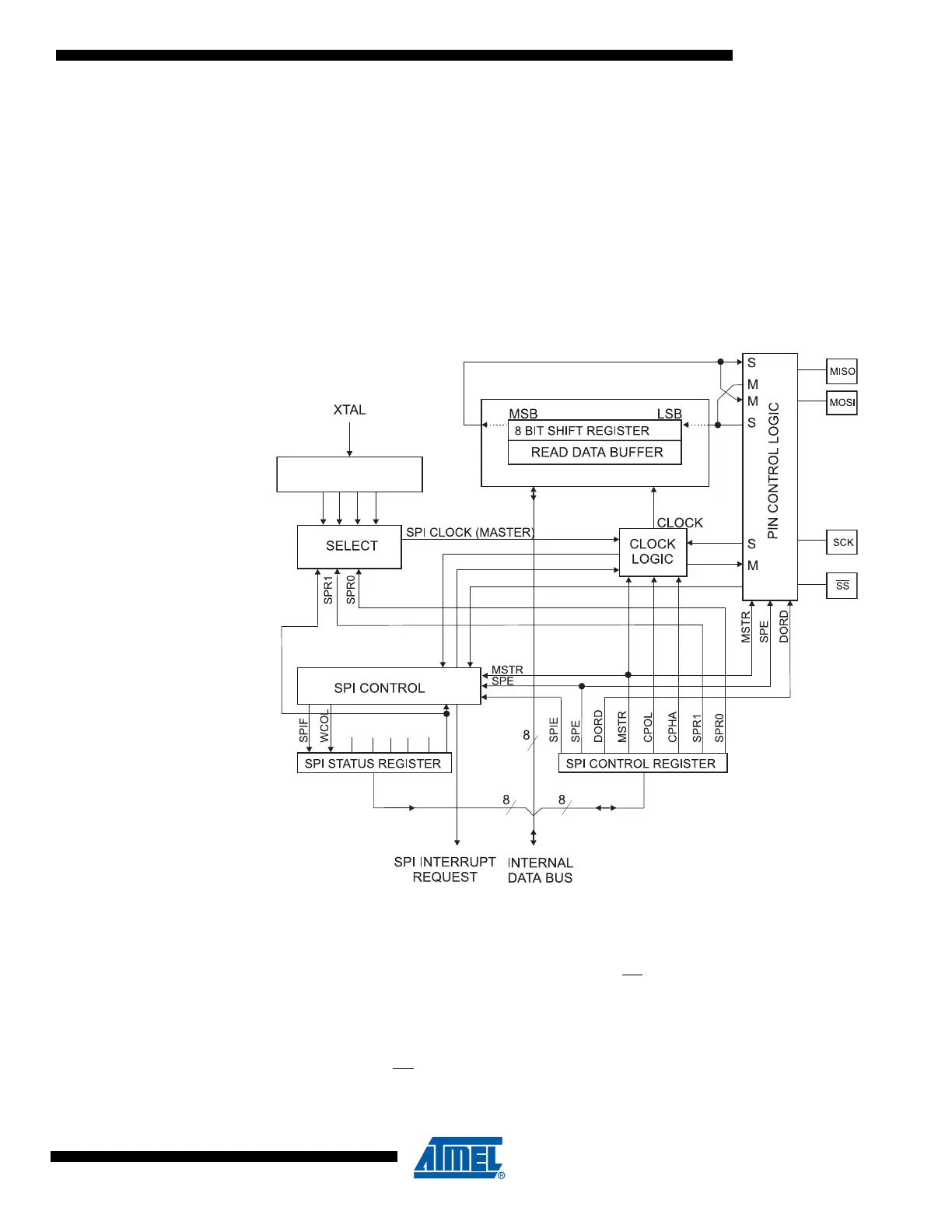
Figure 75. SPI Block Diagram
Note: Refer to Figure 1 on page 2 and Table 30 on page 74 for SPI pin placement.
The interconnection between Master and Slave CPUs with SPI is shown in Figure 76. The sys-
tem consists of two Shift Registers, and a Master clock generator. The SPI Master initiates the
communication cycle when pulling low the Slave Select SS
pin of the desired Slave. Master and
Slave prepare the data to be sent in their respective Shift Registers, and the Master generates
the required clock pulses on the SCK line to interchange data. Data is always shifted from Mas-
ter to Slave on the Master Out – Slave In, MOSI, line, and from Slave to Master on the Master In
– Slave Out, MISO, line. After each data packet, the Master will synchronize the Slave by pulling
high the Slave Select, SS
, line.
SPI2X
SPI2X
DIVIDER
/2/4/8/16/32/64/128
 Loading...
Loading...