Fluidics system
Introduction
The fluidics system carries the sample out of the sample tube and into the sensing region of the flow cell. Cells
are carried in the sample core stream in single file and measured individually.
System indicators
There are two system indicators (System status and Activity) on the control panel.
l
System status. Shows the status of the sheath and waste tank levels. The following table describes the LED
indicators, conditions that trigger them, and any action that must be taken.
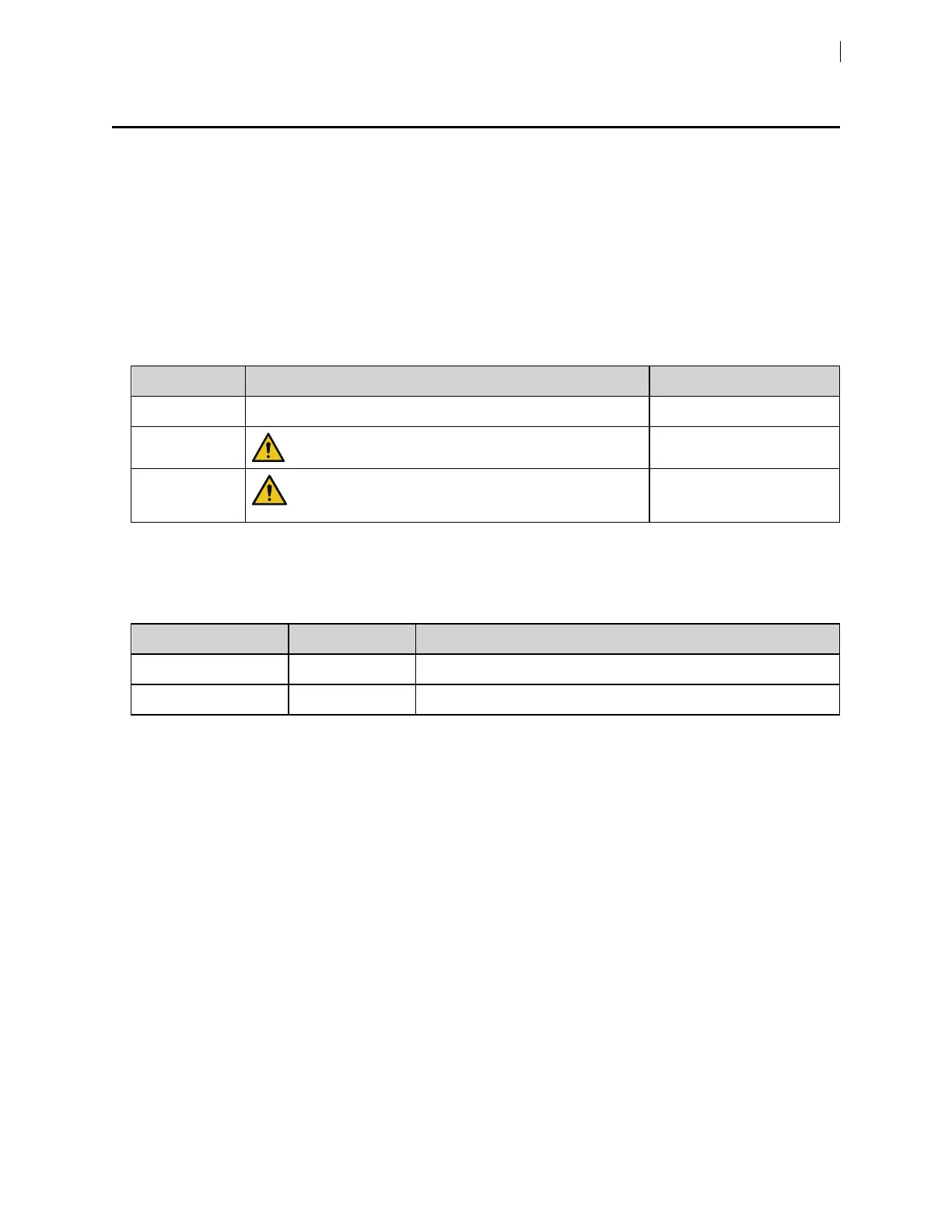
LED color Status Action
Green Good None
Yellow
Sheath and waste tanks need attention.
Check tank levels
Red
Take immediate action.
l
Empty waste tank
l
Fill sheath tank
System status is also displayed on the Status screen. See Status screen (page 16) for a description of the
Status screen.
l
Activity. Shows whether the cytometer power is on and the status of acquisition. The following table
describes the indicator LEDs, and the status that triggers them.
Indicator LED color Status
Steady pulse Blue Cytometer is powered on.
Fluctuates Blue Cells are passing through the flow cell.
Fluid control
The three fluid control buttons (Run, Standby, and Prime) set the cytometer operation.
l
Run Pressurizes the sample tube to transport the sample through the sample injection tube and into the flow
cell.
The Run button is green when the sample tube is on and the support arm is centered. When the tube support
arm is moved left or right to remove a sample tube, the cytometer switches to an automatic standby status
to conserve sheath fluid, and the Run button changes to orange.
l
Standby Stops fluid flow to conserve sheath fluid.
When you leave the cytometer for more than a few minutes, place a tube containing 1mL of deionized (DI)
water on the sample injection port (SIP) and press Standby.
l
Prime Prepares the fluidics system by draining and filling the flow cell with sheath fluid.
The fluid flow initially stops, and pressure is reversed to force fluid out of the flow cell and into the waste
container. After a preset time, the flow cell fills with sheath fluid at a controlled rate to prevent bubble
formation or entrapment. At completion, the cytometer switches to standby mode.
Chapter 2 Introduction 15
 Loading...
Loading...