Chapter 3
| Network Settings
DHCP Snooping
– 59 –
Cellular Network Information List (PLMN) — (Optional) Identifies the 3GPP
cellular networks available through the AP. Specifically, this field identifies the
Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) ID, comprised of the Mobile Country Code
(MCC) and Mobile Network Code (MNC) of the mobile operator. Up to 10
PLMN IDs can be configured. Input the pair of MCC, MNC.
For example: 400, 00
MCC: Three decimal digits (000-999)
MNC: Two (00-99) o
r three decimal digits
(000-999)
Operator Friendly Name — The name of the network operator and the
specified language. Up to 10 names can be configured.
Roaming Consortium List — (Optional) A roaming consortium is a group of
service providers (SP) with which a user’s credentials can be used for
authentication. Each roaming consortium is identified by an organization
identifier (OI) that is assigned by the IEEE. An OI is often 24 bits in length, but
can also be 36 bits. Up to 10 identifiers can be configured.
Domain Name List — Lists one or up to 10 domain names for the entity
operating the AP. This is critical for OpenRoaming network
selection policy, as it
identifies the operator of the network. It indicates to the mobile device whether
they are at a home hotspot or a visited hotspot.
NAI Realm List — (Optional) The network access identifier (NAI) realm list
identifies those service provider or other networks that are accessible through
the AP. By discovering which authentication realms are supported by a network,
a mobile device can selectively authent
icate to its preferred network.
Up to 10
identifiers can be configured.
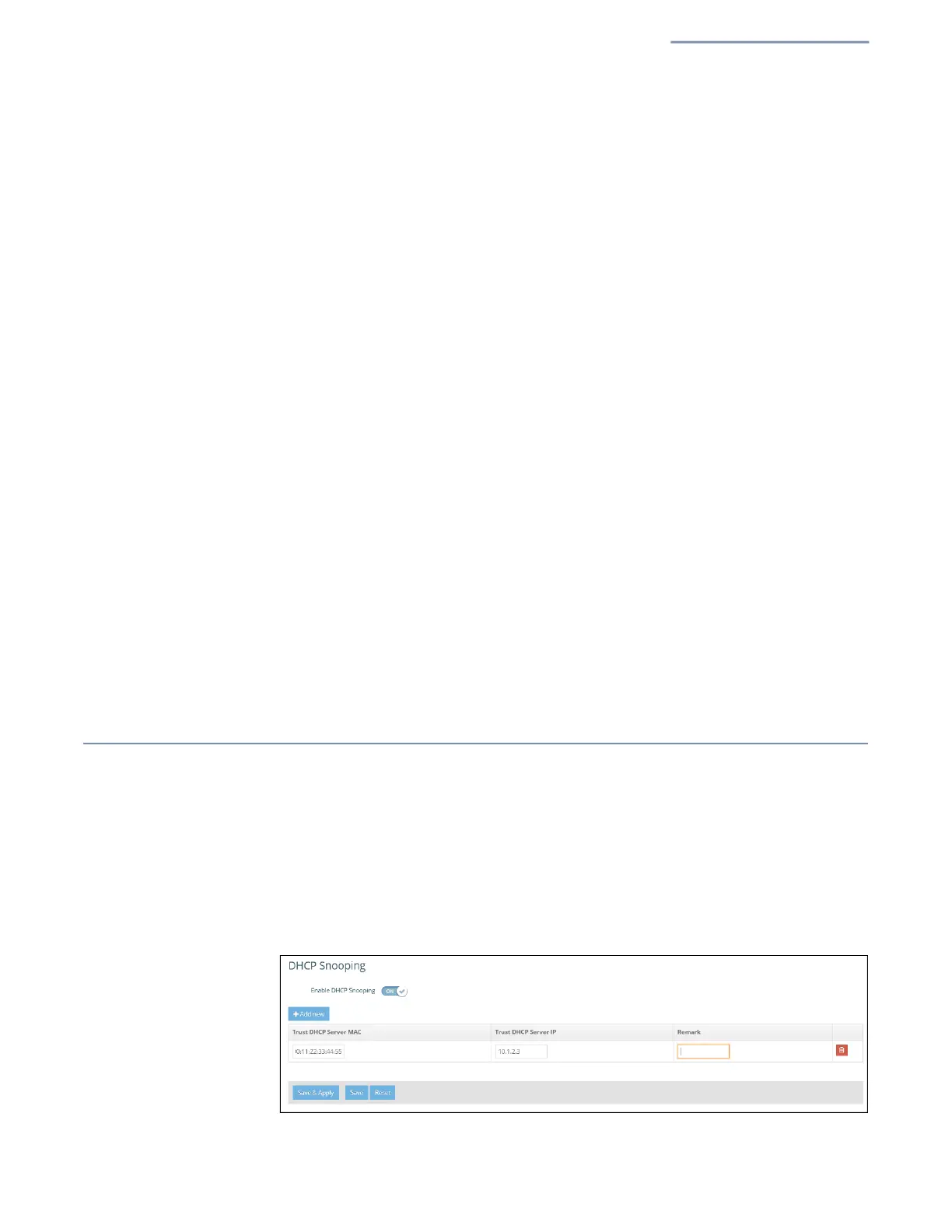
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping is used to validate and filter DHCP messages received by the AP.
When DHCP snooping is enabled, DHCP messages received from a device not
listed in the DHCP snooping table are dropped.
You can add known and trusted DHCP servers to the table by specifying their MAC
and IP addresses.
Figure 38: DHCP Snooping
 Loading...
Loading...