multi N/C 2100S Function and setup
31
3.2 Principle of operation
The analyzer multi N/C 2100S is a compact and powerful device to determine the total
carbon content and/or total nitrogen content in aqueous samples.
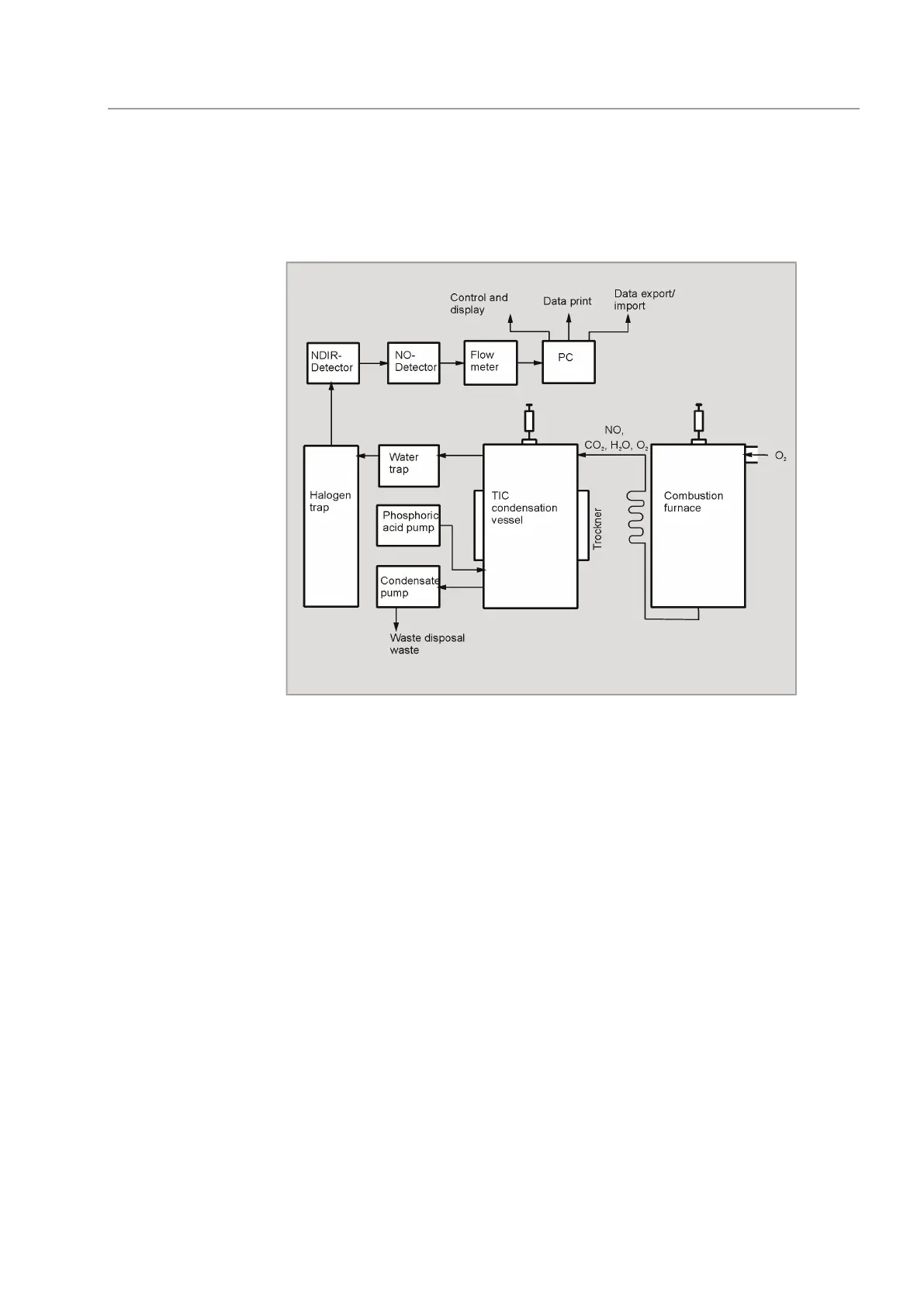
Fig. 18 Principle of operation
The digestion is performed in the multi N/C 2100S by thermocatalytic high-temperature
oxidation in the presence of special catalysts. This enables a quantitative digestion even
for very stable, complex carbon and nitrogen compounds.
The sample aliquot is directly dosed into the hot zone of the filled reactor (combustion
tube). Here the pyrolysis and oxidation of the sample in the carrier gas flow is performed
with the aid of the catalyst (e. g. equations (1) - (3)). The carrier gas is also used as an
oxidation agent.
R + O
2
→
CO
2
+ H
2
O (1)
R - N+ O
2
→
NO + CO
2
+ H
2
O (2)
R - Cl+ O
2
→
HCl + CO
2
+ H
2
O (3)
R … carbonic substance
The pyrolysis gas is cooled in the condensation coil and condensed water is separated
from the measuring gas in the subsequent TIC condensate container. After further
drying and removal of corrosive acting gases, the measuring gas CO
2
is added to the
NDIR detector or NO detector (CLD or ChD).
Inorganic carbon is detected by injecting a sample aliquot into the acidic TIC reactor and
driving out the formed CO
2
via the NDIR detector.

 Loading...
Loading...