EPSON Stylus CX4900/CX4905/CX5000/DX5000/DX5050/CX5900/CX6000/DX6000/DX6050 Revision A
OPERATING PRINCIPLES Scanner Mechanism 80
2.3 Scanner Mechanism
The Scanner Mechanism of Stylus CX4900/CX4905/CX5000/DX5000/DX5050/
CX5900/CX6000/DX6000/DX6050 is constructed of a Scanner Carriage Unit,
Scanner Motor, Scanner HP Sensor, etc., in the same way as previous A4 size scanners.
2.3.1 Scanner Carriage Mechanism
2.3.1.1 Scanner Carriage Unit Overview
The Scanner Carriage Unit is constructed of a CIS Board (including linear CCD), Rod
Lens Array, LED (light source), etc.
CIS Board
CIS Board
contains the sensing elements that are placed across the entire width of
an original. The sensing elements, which does not install a color filter, read an
original through the Rod Lens Array by turning on red, green, and blue light-
emitting diodes (LEDs) alternately. It is not the CIS Board but the Main Board that
converts the analog light signal read by the Rod Lens Array into digital signal.
Rod Lens Array
A num
ber of rod-shaped lenses, which are arranged on the sensing elements, are
also placed across the entire width of an original. These lenses read the light
reflected from the original that is produced by the light source (LEDs) and pass the
information to the sensing elements. Compared to conventional CCD method, this
optical system allows the focal length (distance between sensor and image
scanned) to be shallow. Therefore, an original to be scanned should be brought
close to the document glass. The optical system, in addition, is 1:1, (there is no
optical reduction or enlargement) and this results in a scanner offering the solid
performance in terms of accuracy.
LE
D
EPSON Stylus CX4900/CX4905/CX5000/DX5000/DX5050/CX5900/CX6000/
DX6000/DX6050 use three color LEDs (the three colors being red, green, and
blue) to illuminate the line to be scanned in the document. Unlike cold cathode
fluorescent lamp used in CCD method, usage of LEDs requires no warm-up time
and allows the CIS to be highly power efficient.
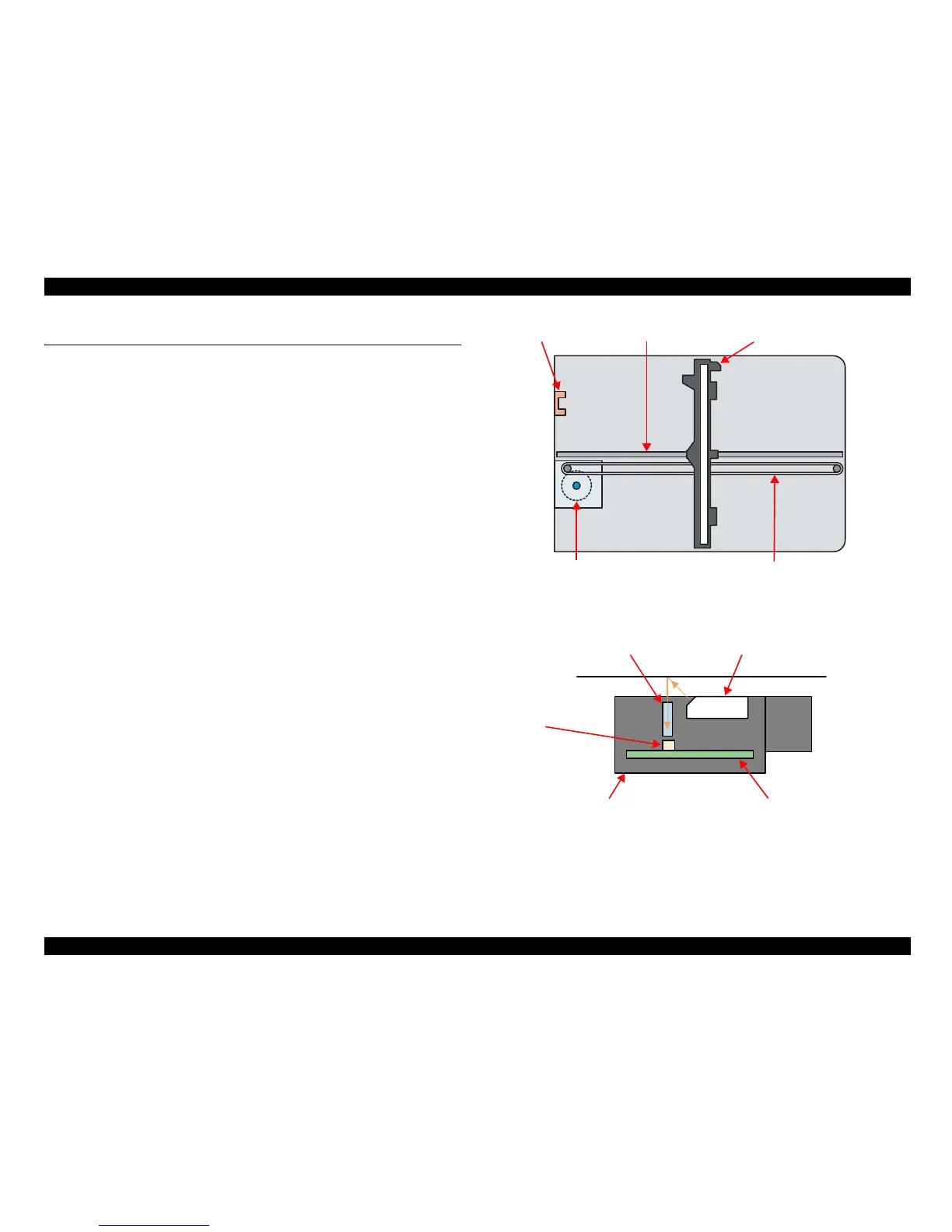
Figure 2-13. Scanner Mechanism
Figure 2-14. Scanning image
Scanner Carriage UnitScanner HP Sensor Scanner Carriage Shaft
Scanner Motor Timing Belt
LEDRod Lens Array
CIS Board
CIS
Scanner Carriage Unit

 Loading...
Loading...