4.10 Operation Check
4-42
4.10.3 Adjusting the function code for motor control
Adjusting the current function code data sometimes resolve issues such as insufficient torque or overcurrent.
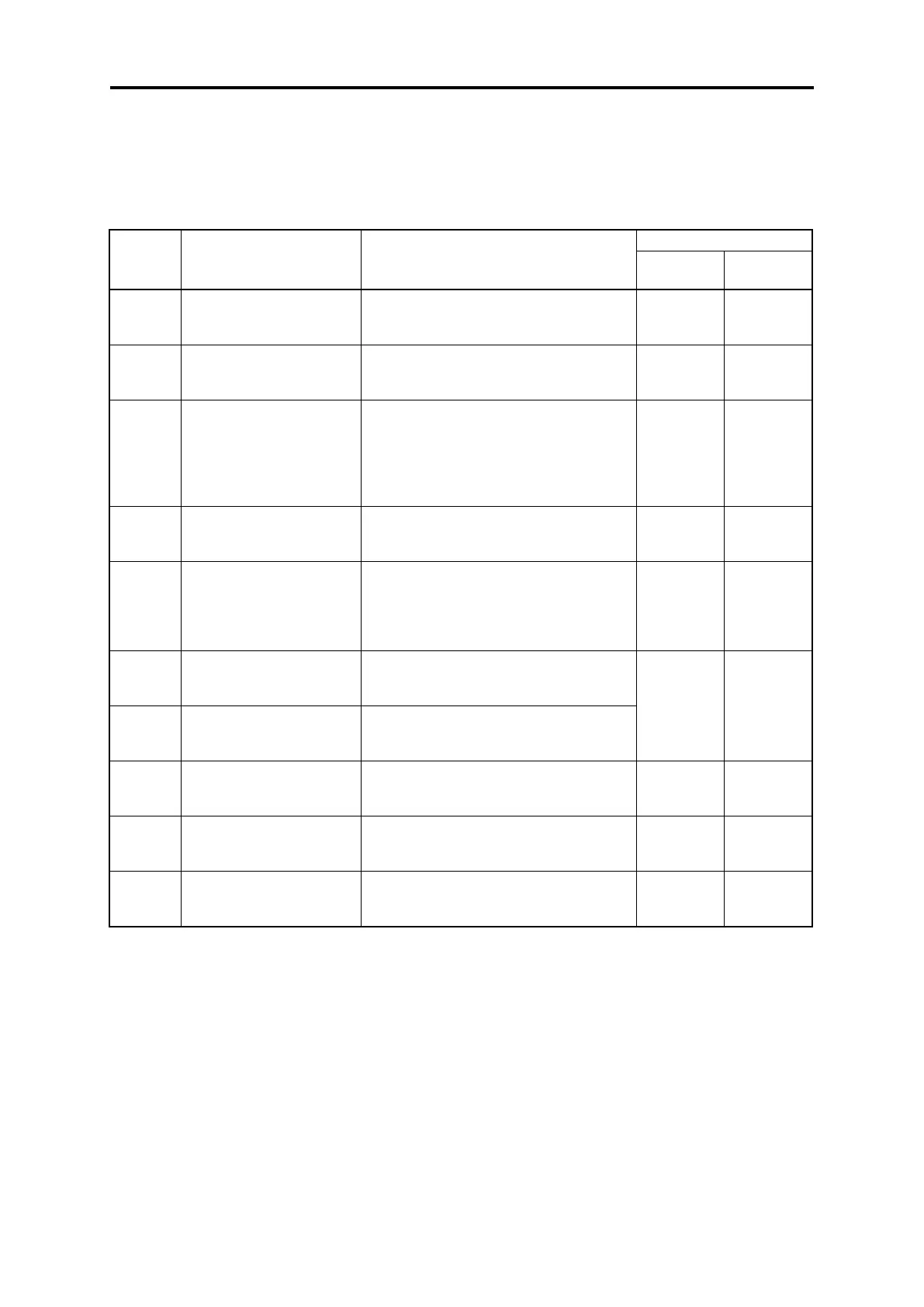
Table 4.9 1 lists the major function codes to be accessed.
Refer to Chapter 5 “FUNCTION CODES” and Chapter 6 “TROUBLESHOOTING” for details.
Table 4.10-1
If the current limiter is activated due to a
short acceleration time and large drive
current, prolong the acceleration time.
If an overvoltage trip occurs due to a short
deceleration time, prolong the deceleration
time.
If the starting motor torque is deficient
under V/f control mode, increase the
torque boost.
If the motor with no load is overexcited
(current increasing), decrease the torque
boost.
If the stall prevention function is activated
by the current limiter during acceleration or
deceleration, increase the operation level.
If the starting motor torque is insufficient
under automatic torque boost and torque
vector control, increase %R1. If the motor
with no load is over-excited (current
increasing), decrease %R1.
Motor 1
(Slip compensation gain for
driving)
For excessive slip compensation during
driving, decrease the gain; for insufficient
one, increase the gain.
V/f
(sensorless)
(sensorless
vector)
Motor 1
(Slip compensation gain for
braking)
For excessive slip compensation during
braking, decrease the gain; for insufficient
one, increase the gain.
Curve
acceleration/deceleration
If overshoot to the change in speed
command is large, make curve
acceleration/deceleration speed effective.
Anti-regenerative control
If an overvoltage alarm occurs without a
braking resistor, enable the
anti-regenerative control function.
Output current fluctuation
damping gain for motor 1
If motor current vibration occurs, adjust in
the direction that increases the damping
gain.
If there is no improvement by adjusting the above function codes when performing V/f control with sensor, with
sensor/sensorless vector control, with sensor/sensorless vector control for synchronous motors, adjust the
following function codes also. In the above control methods, PI regulator is used for speed control. The desired
response can be obtained by adjusting the control constants (PI constants) to match the load inertia. The major
function codes to adjust are shown below.

 Loading...
Loading...











