Appendix B Japanese Guideline for Suppressing Harmonics by Customers Receiving High
Voltage or Special High Voltage (General-purpose Inverters)
Appendix-18
[ 3 ] Examples of calculation
(1) Equivalent capacity
Input capacity and
No. of inverters
[Example (1)] 400 V, 3.7 kW, 10 units
with AC/DC reactor
4.61 x 10 x 1.4 = 64.54 kVA
[Example (2)] 400 V, 1.5 kW, 15 units
with AC reactor
2.93 x 15 x 1.8 = 79.11 kVA
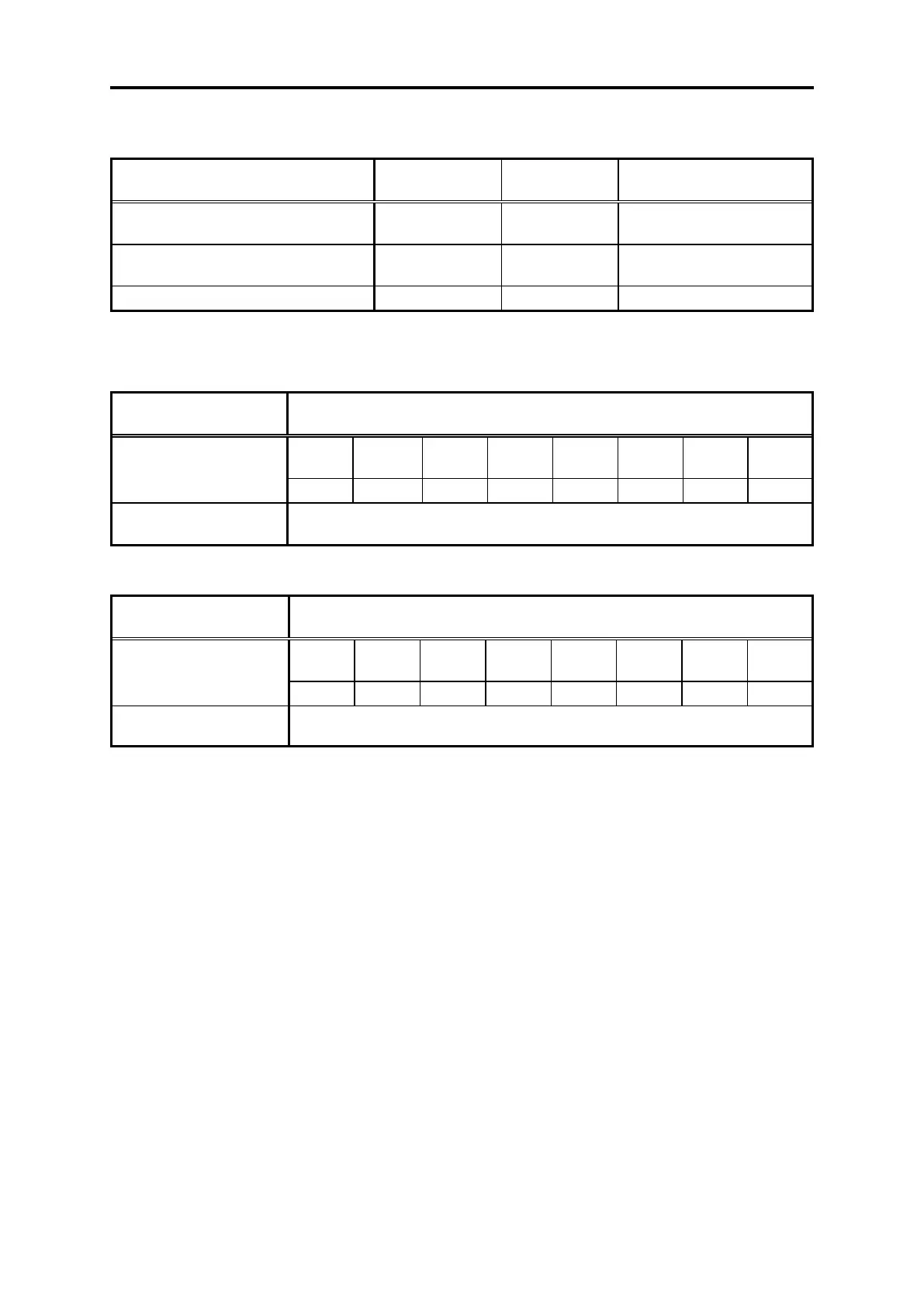
(2) Harmonic current for every harmonic order
Example 1: 400 V, 3.7 kW, 10 units (with AC reactor), maximum availability factor: 0.55
6.6 kV side
fundamental current (mA)
Harmonic current onto 6.6 kV lines (mA)
394 x 10 = 3940
3940 x 0.55 = 2167
See Table B.2-3 and
Table B.2-5
Example 2: 400 V, 3.7 kW, 15 units (with AC/DC reactor), maximum availability factor: 0.55
6.6 kV side
fundamental current (mA)
Harmonic current onto 6.6 kV lines (mA)
394 x 15 = 5910
5910 x 0.55 = 3250.5
See Table B.2-3 and Table
B.2-5

 Loading...
Loading...











