169
Appendix 1 Four-Terminal (Voltage-Drop) Method
The Four-Terminal method is essential for measuring very small
resistance values.
With two-terminal measurements (Fig. 1), the resistance of the test
leads is included in the measured resistance, resulting in
measurement errors.
The four-terminal method (Fig. 2) consists of current source terminals
to provide constant current, and voltage detection terminals to detect
voltage drop.
Because of the high input impedance of the voltmeter, measurement
requires practically no current flow through the leads connecting the
voltage detection terminals to the test object, practically eliminating
the effects of lead and contact resistance on the measurement.
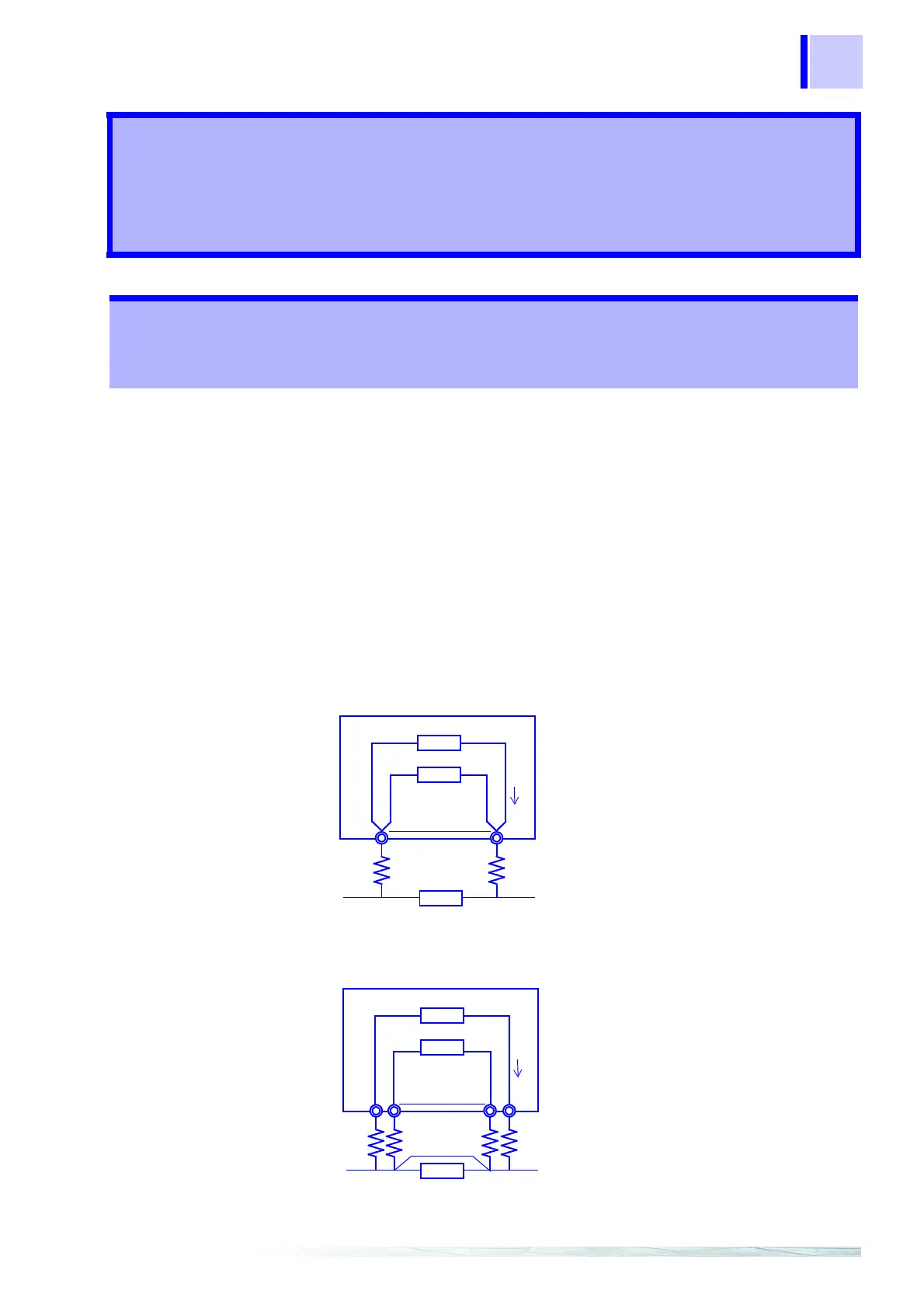
Two-Terminal Measurement Method
Measurement current I flows through
test object resistance R
0
as well as lead
resistances r
1
and r
2
.
The voltage to be measured is obtained
by E = I(r
1
+R
0
+r
2
), which includes lead
resistances r
1
and r
2
.
Four-Terminal Measurement Method
All of measurement current I flows
through test object resistance R
0
. So
the voltage drop across r
3
and r
4
is
practically nil, and voltage E across the
measurement terminals and voltage E
0
across test object resistance R
0
are
essentially equal, allowing test object
resistance to be measured without
being affected by r
1
to r
4
.
Appendix
Appendix 1 Four-Terminal (Voltage-Drop)
Method
Figure 1.
r
1
r
2
E
I
Resistance R
0
Voltmeter
Constant current source
Figure 2.
r
1
r
2
E
I
Resistance R
0
Voltmeter
Constant current source
r
3
r
4
E
0

 Loading...
Loading...