GENERAL ENGINEERING DATA
ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
475
VOLTAGE CONVERSION
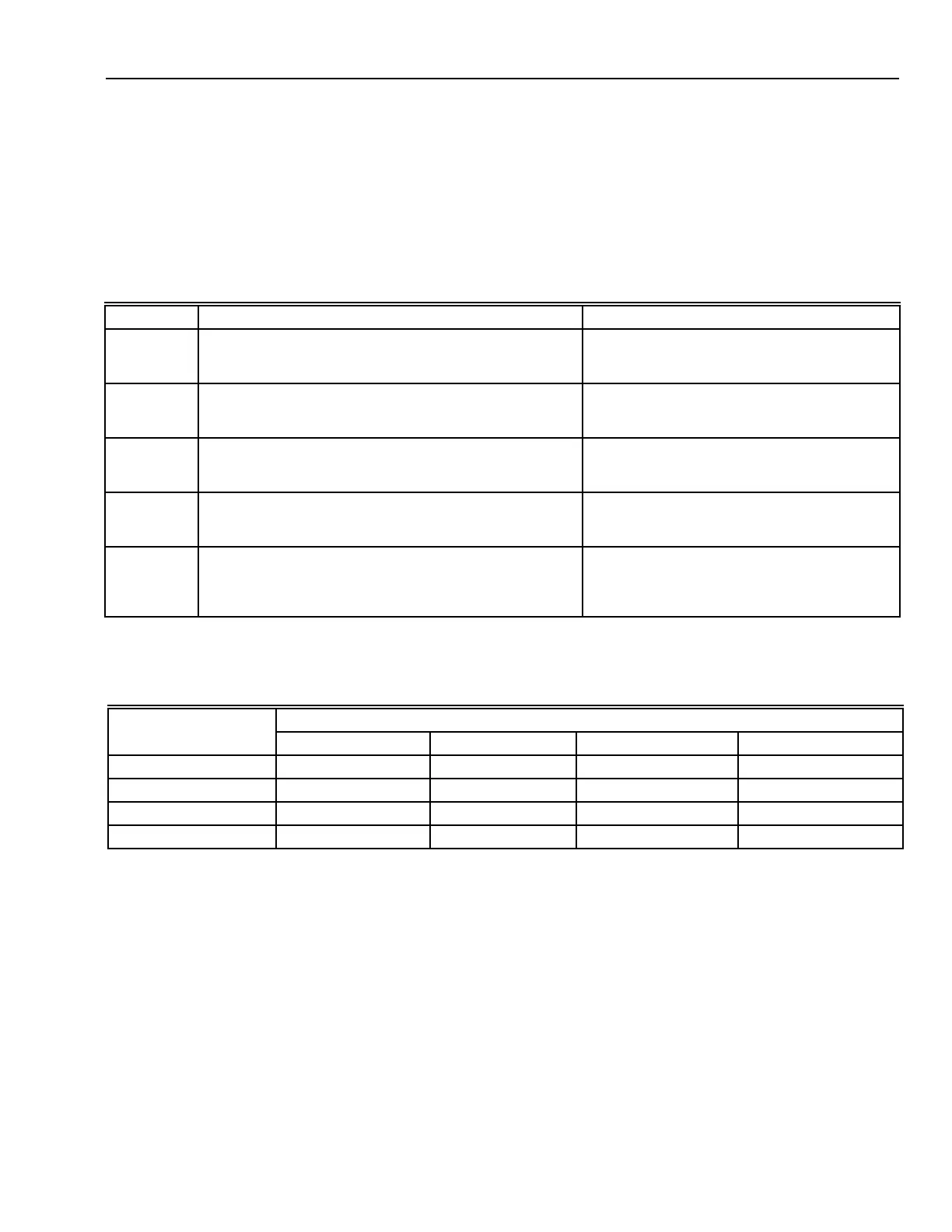
Table 19. Voltage Conversion Multipliers.
Desired Voltage
Existing Voltage EMS Effective Average Peak Peak-to-Peak
EMS Effective — 0.900 1.414 2.828
Average 1.110 — 1.570 3.141
Peak 0.707 0.637 — 2.000
Peak-to-Peak 0.354 0.318 0.500 —
ELECTRIC MOTORS
Single-phase electric motors are classified by the method used
to start the motor. Table 18 describes the characteristics and
typical applications of single-phase motors by classification.
No special means of starting is required for three-phase motors,
since starting (rotational) torque is inherent in three-phase
motors. A three-phase motor can be reversed by switching any
two phases.
Table 18. Single-Phase Motor Characteristics and Applications.
Motors have two current ratings locked rotor (LRA) and full
load (FLA). Locked rotor current is drawn at the instant power
is applied and before the motor starts rotating. It is also drawn
if the motor is stalled. Full load current is drawn when the motor
is running at its full load rating.
Motor Type Characteristics Application
Universal
(Series)
Armature and field connected in series. Operates on dc or
ac with approximately the same speed and torque.
Where either ac or dc may be available. Used for
portable tools, vacuum cleaners, electric
typewriters, etc.
Split-Phase
Starting
Uses a pair of field windings for starting with one winding
slightly lagging. One winding is disconnected by a
centrifugal switch when running speed is reached.
Where starting torque and varying load are not
excessive. Used for oil burners, washing
machines, grinding wheels, etc.
Capacitor
Starting
Same as split-phase with a capacitor connected to the
winding that stays on line. Provides greater starting torque
with high efficiency and power factor.
Where high starting torque and heavy varying
loads exist. Used for air conditioners,
refrigerators, air compressors, etc.
Shaded-Pole
Starting
A short-circuited winding is used on each pole piece along
with a normal winding. Magnetic flux in the shorted turn
produces starting torque. Torque is low.
Where starting torque is low and less than 1/20
horsepower is required. Used for electric clocks.
Repulsion
Starting
Operates as a repulsion motor on starting and a centrifugal
switch converts it to an induction motor when running speed
is reached. Motor has a commutator as in a dc motor.
Provides high starting torque.
Where high starting torque is required. Used in
machine shops.

 Loading...
Loading...











