Page 3-15
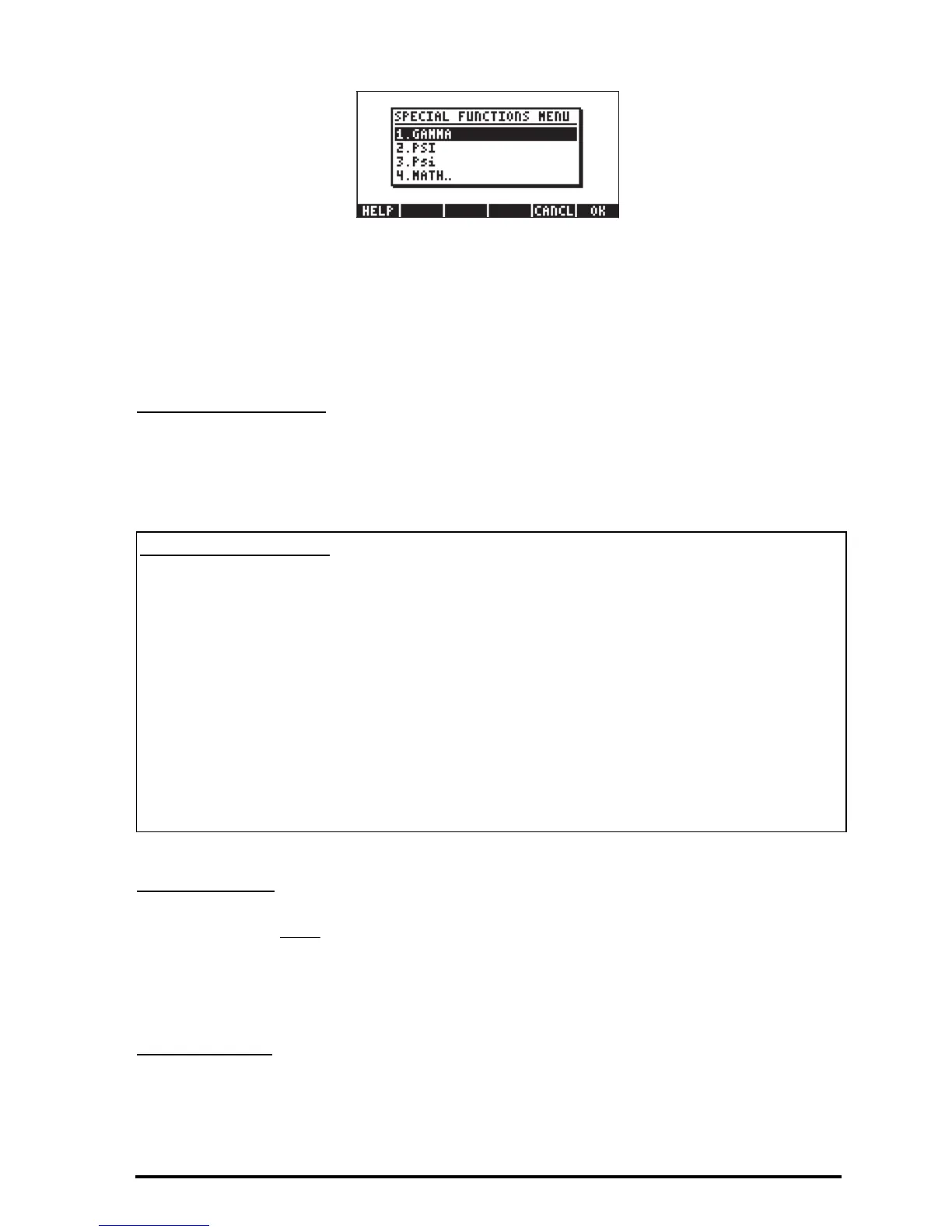
GAMMA: The Gamma function Γ(α)
PSI: N-th derivative of the digamma function
Psi: Digamma function, derivative of the ln(Gamma)
The Gamma function
is defined by . This function has
applications in applied mathematics for science and engineering, as well as in
probability and statistics.
The PSI function
, Ψ(x,y), represents the y-th derivative of the digamma function,
i.e., , where
Ψ
(x) is known as the digamma function, or
Psi function. For this function, y must be a positive integer.
The Psi function
,
Ψ
(x), or digamma function, is defined as .
Factorial of a number
The factorial of a positive integer number n is defined as n!=n
⋅
(n-1)×(n-2)
…3×2×1, with 0! = 1. The factorial function is available in the calculator by
using ~‚2. In both ALG and RPN modes, enter the number first,
followed by the sequence ~‚2. Example: 5~‚2`.
The Gamma function, defined above, has the property that
Γ(α) = (α−1) Γ(α−1)
, for α > 1.
Therefore, it can be related to the factorial of a number, i.e.,
Γ(α) = (α−1)
!,
when α is a positive integer. We can also use the factorial function to calculate
the Gamma function, and vice versa. For example,
Γ
(5) = 4! or,
4~‚2`. The factorial function is available in the MTH menu,
through the 7. P R O B A B I L I T Y. . menu.
∫
∞
−−
=Γ
0
1
)( dxex
x
α
α
)(),( x
dx
d
xn
n
n
ψ
=Ψ
)](ln[)( xx Γ=

 Loading...
Loading...




