Page 6-20
In the next example we will use the DARCY function for finding friction factors in
pipelines. Thus, we define the function in the following frame.
Special function for pipe flow: DARCY (ε/D,Re)
The Darcy-Weisbach equation is used to calculate the energy loss (per unit
weight), h
f
, in a pipe flow through a pipe of diameter D, absolute roughness ε,
and length L, when the flow velocity in the pipe is V. The equation is written as
. The quantity f is known as the friction factor of the flow and
it has been found to be a function of the relative roughness of the pipe, ε/D,
and a (dimensionless) Reynolds number, Re. The Reynolds number is defined as
Re = ρVD/μ = VD/ν, where ρ and μ are the density and dynamic viscosity of
the fluid, respectively, and ν = μ/ρ is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid.
The calculator provides a function called DARCY that uses as input the relative
roughness ε/D and the Reynolds number, in that order, to calculate the friction
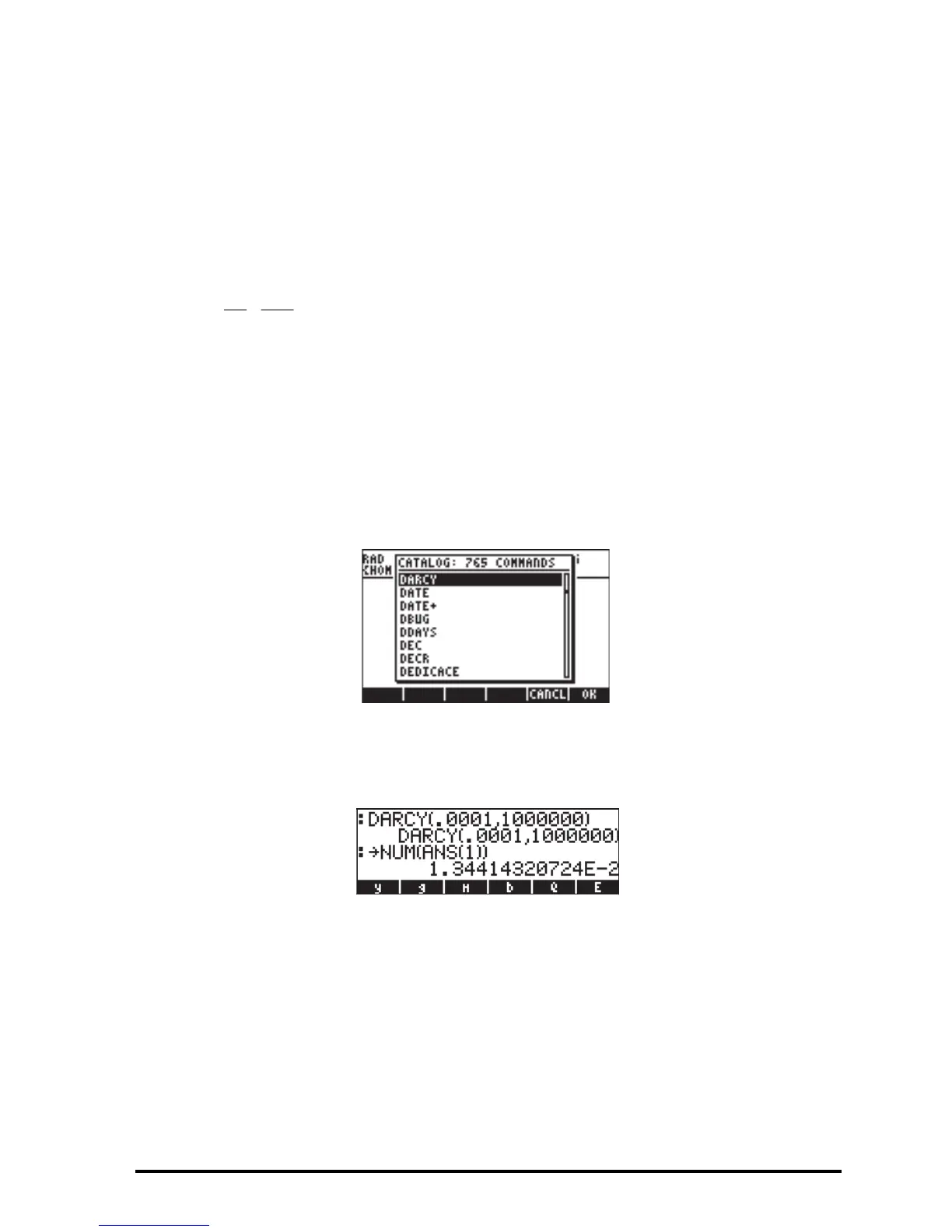
factor f. The function DARCY can be found through the command catalog:
For example, for ε/D = 0.0001, Re = 1000000, you can find the friction factor
by using: DARCY(0.0001,1000000). In the following screen, the function
NUM () was used to obtain a numerical value of the function:
The result is f = DARCY(0.0001,1000000) = 0.01341…
The function FANNING(ε/D,Re)
In aerodynamics applications a different friction factor, the Fanning friction
factor, is used. The Fanning friction factor, f
F
, is defined as 4 times the Darcy-
Weisbach friction factor, f. The calculator also provides a function called
FANNING that uses the same input as DARCY, i.e., ε/D and Re, and provides
the FANNING friction factor. Check that FANNING(0.0001,1000000) =
0.0033603589181s.
g
V
D
L
fh
f
2
2
⋅⋅=

 Loading...
Loading...




