Page 12-31
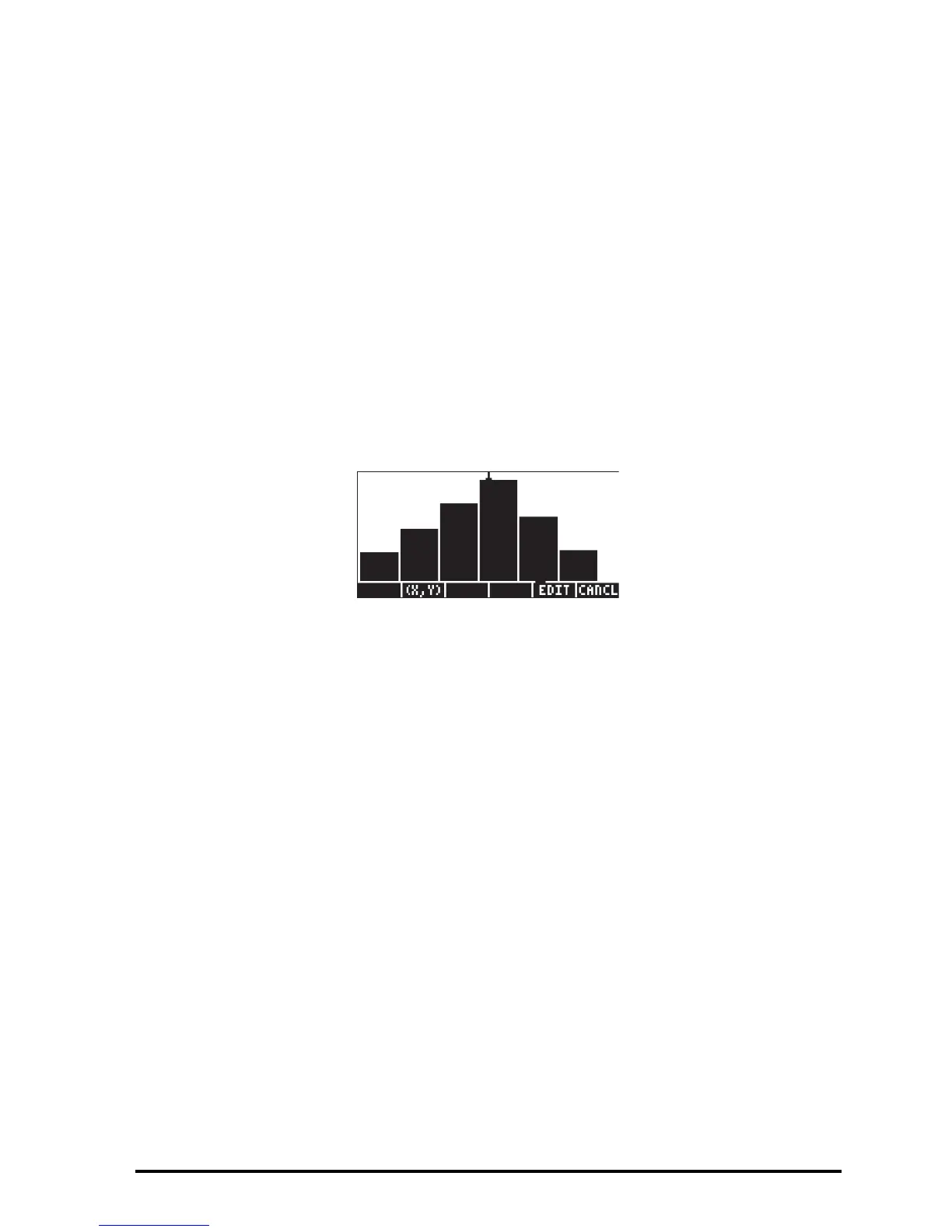
accommodate the maximum value in column 1 of ΣDAT. Bar plots are useful
when plotting categorical (i.e., non-numerical) data.
Suppose that you want to plot the data in column 2 of the ΣDAT matrix:
Θ Press „ô, simultaneously if in RPN mode, to access to the PLOT SETUP
window.
Θ Press ˜˜ to highlight the
Col: field and type 2 @@@OK@@@, followed by
L@@@OK@@@.
Θ Press „ò, simultaneously if in RPN mode, to access to the PLOT SETUP
window.
Θ Change V-View to read
V-View: 0 6
Θ Press @ERASE @DRAW.
Θ Press @CANCL to return to the PLOT WINDOW screen, then $ to return to
normal calculator display.
Scatter plots
We will use the same ΣDAT matrix to produce scatter plots. First, we will plot
the values of y vs. x, then those of y vs. z, as follows:
Θ Press „ô, simultaneously if in RPN mode, to access to the PLOT SETUP
window.
Θ Change
TYPE to Scatter.
Θ Press ˜˜ to highlight the
Cols: field. Enter 1@@@OK@@@ 2@@@OK@@@ to
select column 1 as X and column 2 as Y in the Y-vs.-X scatter plot.
Θ Press L@@@OK@@@ to return to normal calculator display.
Θ Press „ò, simultaneously if in RPN mode, to access the PLOT
WINDOW screen.
Θ Change the plot window ranges to read:
H-View: 0 6, V-View: 0 6.

 Loading...
Loading...




