Page 6-17
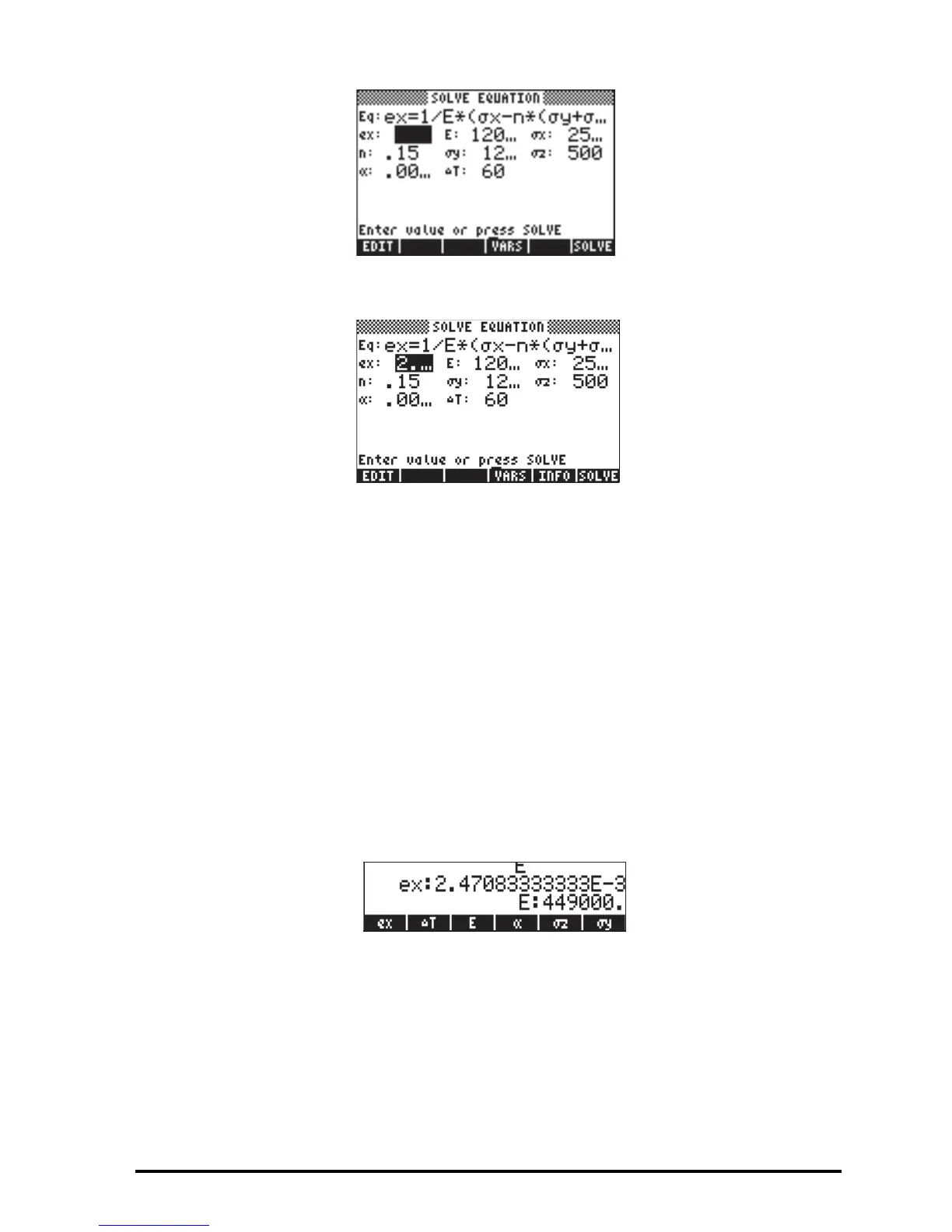
With the ex: field highlighted, press @SOLVE@ to solve for ex:
The solution can be seen from within the SOLVE EQUATION input form by
pressing @EDIT while the ex: field is highlighted. The resulting value is
2.470833333333E-3. Press @@@OK@@ to exit the EDIT feature.
Suppose that you now, want to determine the Young’s modulus that will produce
a strain of e
xx
= 0.005 under the same state of stress, neglecting thermal
expansion. In this case, you should enter a value of 0.005 in the ex: field, and
a zero in the
Δ
T: field (with ΔT = 0, no thermal effects are included). To solve
for E, highlight the E: field and press @SOLVE@. The result, seeing with the @EDIT
feature is, E = 449000 psi. Press @SOLVE@ ` to return to normal display.
Notice that the results of the calculations performed within the numerical solver
environment have been copied to the stack:
Also, you will see in your soft-menu key labels variables corresponding to those
variables in the equation stored in EQ (press L to see all variables in your
directory), i.e., variables ex,
Δ
T,
α
,
σ
z,
σ
y, n,
σ
x, and E.
Example 2 – Specific energy in open channel flow

 Loading...
Loading...




