Page 11-34
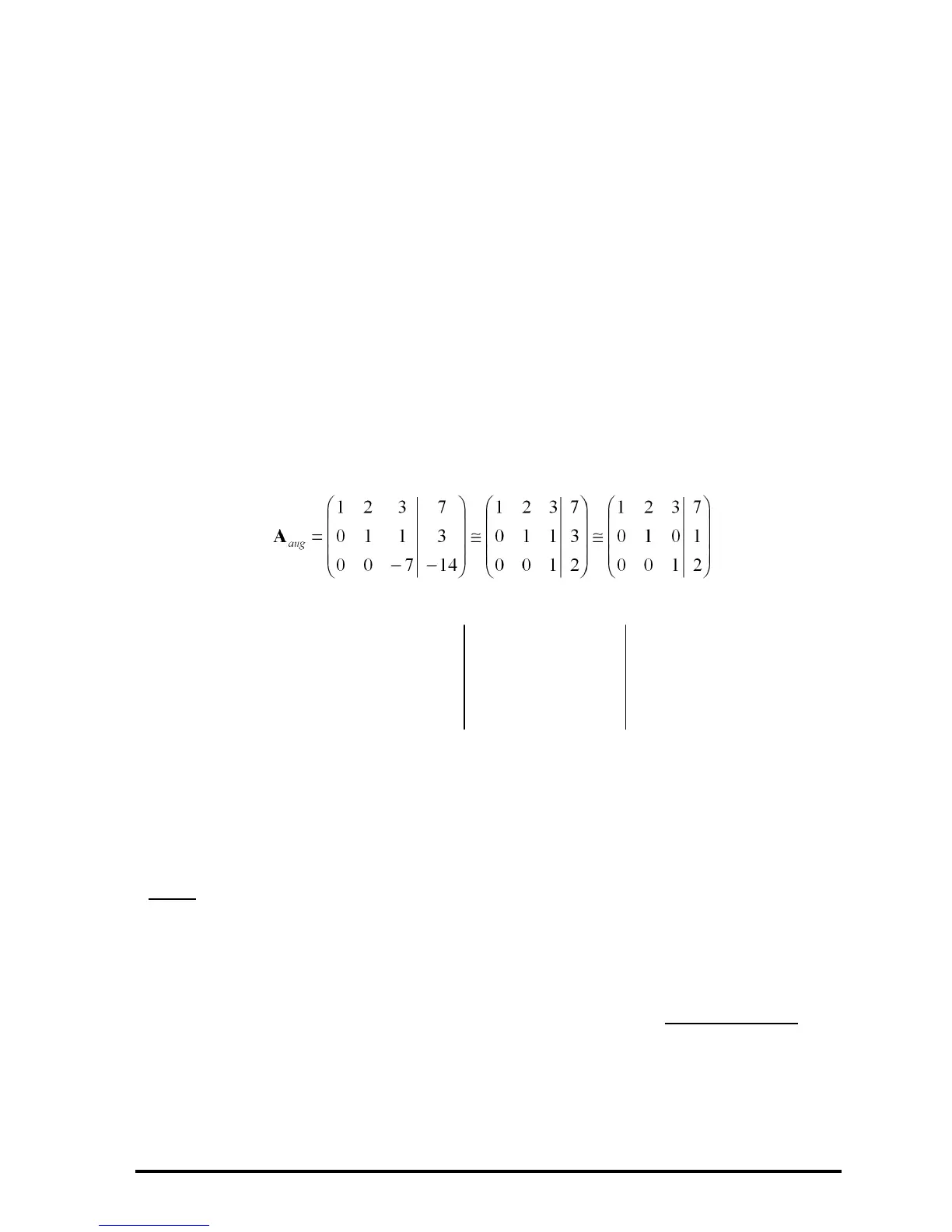
Multiply row 3 by –1/7: 7\Y 3 @RCI!
Multiply row 3 by –1, add it to row 2, replacing it: 1\ # 3
#2 @RCIJ!
Multiply row 3 by –3, add it to row 1, replacing it:
3\#3#1@RCIJ!
Multiply row 2 by –2, add it to row 1, replacing it: 2\#2#1
@RCIJ!
Writing this process by hand will result in the following steps:
Pivoting
If you look carefully at the row operations in the examples shown above, you
will notice that many of those operations divide a row by its corresponding
element in the main diagonal. This element is called a pivot element, or simply,
a
pivot. In many situations it is possible that the pivot element become zero, in
which case we cannot divide the row by its pivot. Also, to improve the
numerical solution of a system of equations using Gaussian or Gauss-Jordan
elimination, it is recommended that the pivot be the element with the largest
absolute value in a given column. In such cases, we exchange rows before
performing row operations. This exchange of rows is called partial pivoting
. To
follow this recommendation is it often necessary to exchange rows in the
augmented matrix while performing a Gaussian or Gauss-Jordan elimination.
.
2
1
1
100
010
001
2
1
1
100
010
021
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
≅
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
≅
aug
A

 Loading...
Loading...




